Introduction
In today's competitive business landscape, ensuring the safety and well-being of workers is not just a regulatory requirement but a fundamental aspect of ethical practice. SA8000 Audits play a pivotal role in this process, providing organizations with a framework to evaluate their compliance with health and safety standards. By focusing on the critical components of health and safety risks, companies can foster an environment that prioritizes employee welfare while enhancing operational efficiency.
The Importance of SA8000 Audits
SA8000 Audits are essential for identifying gaps in workplace safety protocols and ensuring adherence to international labor standards. These audits serve as a comprehensive assessment tool that helps organizations recognize potential hazards, thereby mitigating risks before they escalate into serious incidents. The importance of these audits cannot be overstated; they not only protect employees but also enhance the organization's reputation and operational sustainability.
Key Components of Health and Safety Risks
Understanding the key components of health and safety risks is crucial for effective risk management within any organization. Factors such as physical hazards, chemical exposures, ergonomic issues, and psychosocial stressors contribute to an unsafe work environment if left unaddressed. By integrating these elements into the SA8000 framework, businesses can better navigate the complexities associated with maintaining a safe workplace.
Understanding the Role of SA8000 in Compliance
The role of SA8000 in compliance extends beyond mere adherence to regulations; it embodies a commitment to ethical labor practices and worker rights. This standard provides clear guidelines for implementing effective health and safety measures while fostering accountability through rigorous auditing processes. By embracing SA8000 Audits as part of their compliance strategy, organizations position themselves as leaders in workplace safety, paving the way for continuous improvement.
Understanding the SA8000 Health and Safety Requirements

Overview of SA8000 Standards
The SA8000 standards are designed to ensure ethical labor practices across various industries, focusing significantly on health and safety. These standards outline specific criteria that organizations must meet, including safe working conditions, access to clean water, and proper training for employees. By adhering to these standards, companies can improve their reputation while also minimizing risks associated with non-compliance during SA8000 Audits.
Understanding the nuances of these standards is essential for any organization aiming to enhance its operational integrity. It’s not just about ticking boxes; it’s about fostering an environment where worker rights are prioritized alongside safety protocols. Companies that integrate these standards into their operational framework often see a marked improvement in employee morale and productivity.
Significance of Worker Rights and Safety
Worker rights are at the heart of the SA8000 framework, emphasizing that every employee deserves a safe working environment free from hazards. This focus on human dignity is crucial because when workers feel protected, they are more likely to perform at their best—an undeniable win-win for both employers and employees alike. Moreover, addressing health and safety issues proactively reduces the likelihood of incidents during What H&S Risk Detection with SA8000 Looks Like in Practice.
The significance extends beyond mere compliance; it encompasses a broader commitment to ethical business practices that resonate with consumers today. Organizations that prioritize worker rights often attract top talent eager to be part of a responsible company culture. In this way, embracing health and safety as part of worker rights becomes not just an obligation but also a strategic advantage.
Implementing Effective Safety Protocols
Implementing effective safety protocols is paramount in ensuring compliance with the SA8000 standards while protecting workers from potential hazards. This involves establishing clear guidelines for risk assessment processes as well as continuous monitoring mechanisms within workplaces—key components highlighted during Reporting and Corrective Action within the SA8000 Framework discussions. Companies should invest in training sessions that equip employees with knowledge about recognizing hazards before they escalate into serious issues.
Moreover, creating an open channel for communication allows workers to voice concerns without fear of reprisal; this openness is essential for Building a Culture of Continuous Detection and Prevention throughout an organization. Regular drills and refreshers on emergency procedures further reinforce this culture by keeping everyone informed about best practices in health and safety measures relevant to their specific roles or environments.
Ultimately, effective implementation goes hand-in-hand with regular evaluations through audits—ensuring that all protocols remain relevant amidst changing industry dynamics or emerging risks in Critical Risk Areas in High-Risk Industries like construction or manufacturing sectors.
What H&S Risk Detection with SA8000 Looks Like in Practice
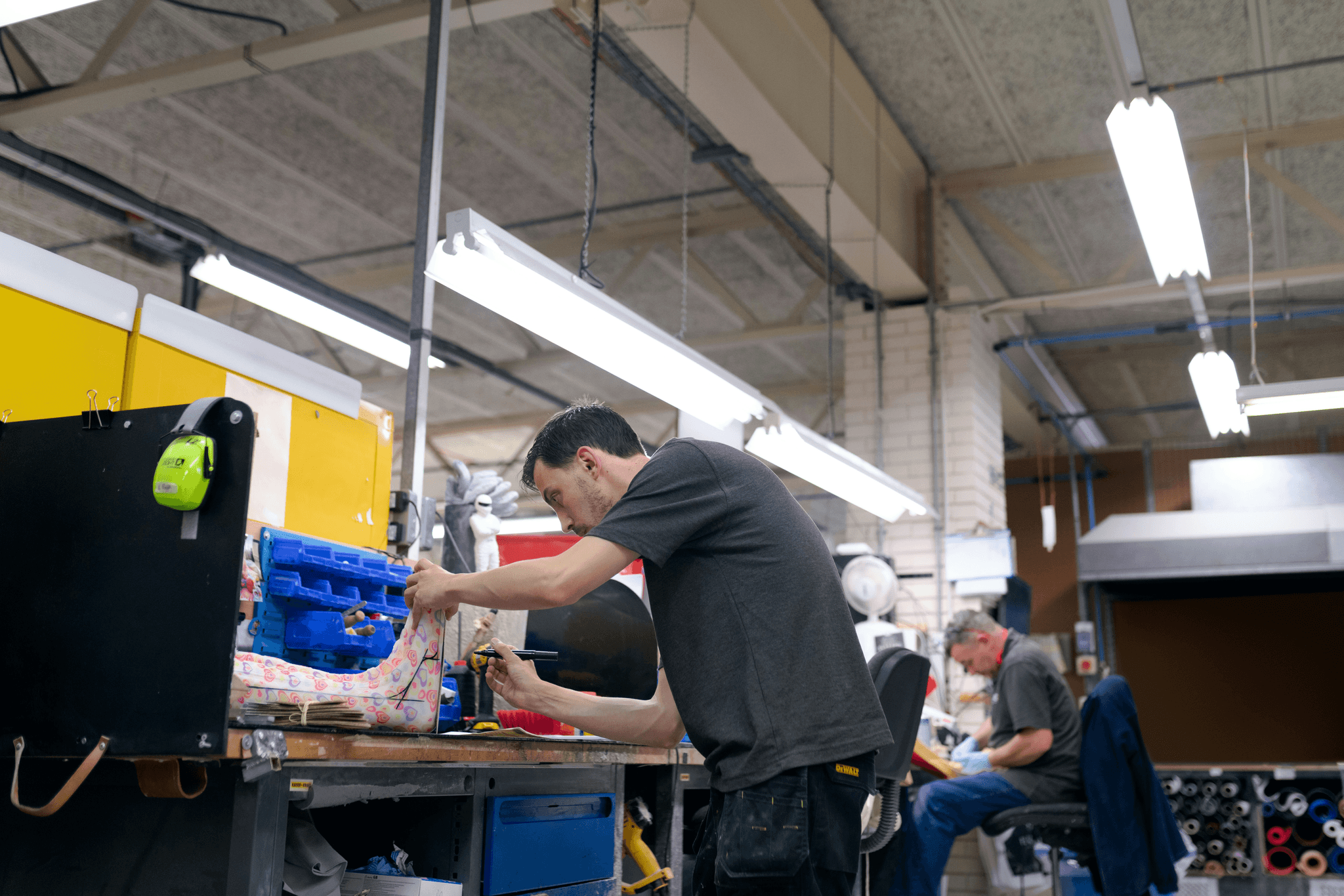

Understanding the practical aspects of health and safety risk detection through SA8000 Audits is crucial for organizations aiming to improve workplace safety. This section delves into effective methods for risk assessment, tools for identifying hazards, and real-world examples that demonstrate the effectiveness of these audits. By grasping these concepts, organizations can ensure compliance with the SA8000 Health and Safety Requirements while fostering a safer work environment.
Practical Methods for Risk Assessment
Risk assessment is the backbone of effective health and safety management under the SA8000 framework. One practical method involves conducting regular workplace inspections to identify potential hazards, followed by engaging employees in discussions about their experiences and concerns related to safety risks. Another method includes implementing a systematic approach known as Job Safety Analysis (JSA), which breaks down tasks to pinpoint specific risks associated with each activity.
Additionally, organizations can use quantitative methods such as incident rate analysis to assess past accidents and near misses, helping them understand trends over time. The combination of qualitative insights from employee feedback and quantitative data creates a comprehensive picture of health and safety risks within an organization. Ultimately, these practical methods not only align with SA8000 requirements but also promote a culture of continuous detection and prevention.
Tools and Techniques for Identifying Hazards
When it comes to identifying hazards in line with SA8000 Audits, various tools and techniques can enhance an organization's ability to detect risks effectively. Checklists are a straightforward yet powerful tool that allows auditors to systematically evaluate compliance with health and safety standards during audits. These checklists can cover everything from equipment maintenance schedules to emergency exit accessibility.
Another valuable technique is the use of hazard mapping—an approach where potential hazards are visually represented on site layouts or blueprints. This method helps teams quickly identify critical risk areas in high-risk industries such as manufacturing or construction by highlighting zones that require immediate attention or further investigation. Furthermore, technology plays an increasingly important role; wearable devices equipped with sensors can monitor environmental conditions in real-time, providing immediate alerts when unsafe levels are detected.
Real-World Examples of Effective Audits
Real-world examples illustrate how effective audits under the SA8000 framework have significantly improved workplace safety across various industries. For instance, a manufacturing company implemented comprehensive SA8000 Audits that revealed inadequate machine guarding practices leading to injuries among workers; corrective actions were promptly taken after documenting these violations within the Reporting and Corrective Action within the SA8000 Framework process.
In another case within the agriculture sector, an audit highlighted insufficient training regarding handling hazardous materials—prompting management to introduce enhanced training programs focused on chemical safety protocols tailored specifically for their employees’ needs. These proactive measures not only addressed existing issues but also fostered a culture where employees felt empowered to communicate about risks openly—a vital component in Building a Culture of Continuous Detection and Prevention.
These examples showcase that when organizations commit wholeheartedly to understanding what H&S Risk Detection with SA8000 Looks Like in Practice through diligent audits, they not only comply with standards but also create safer workplaces where employees thrive.
Critical Risk Areas in High-Risk Industries
When it comes to SA8000 Audits, identifying critical risk areas in high-risk industries is paramount for ensuring worker safety and compliance. Understanding the SA8000 Health and Safety Requirements allows organizations to pinpoint these hazards effectively. By addressing these risks, companies can foster a safer work environment and adhere to international standards.
Common Hazards in Manufacturing
Manufacturing facilities often present a myriad of hazards that can lead to serious injuries if left unaddressed. Common risks include machinery accidents, exposure to toxic substances, and ergonomic issues due to repetitive tasks or poor workstation design. Implementing What H&S Risk Detection with SA8000 Looks Like in Practice is vital; regular audits can uncover these dangers before they escalate into emergencies.
In the context of SA8000 Audits, workers should be trained on the specific hazards they might encounter daily. This training enhances awareness and empowers employees to report unsafe conditions promptly, contributing to a culture of continuous detection and prevention. Furthermore, effective reporting mechanisms must be established within the Reporting and Corrective Action within the SA8000 Framework to ensure swift corrective measures are taken.
Addressing Risks in Construction and Agriculture
Construction sites are notorious for their hazardous environments—think heavy machinery, heights, and moving vehicles all vying for attention! The risks are compounded by weather conditions that can affect visibility or ground stability. By leveraging insights from Understanding the SA8000 Health and Safety Requirements, companies can implement robust safety protocols tailored specifically for construction workers.
Agriculture also poses unique challenges; workers may face exposure to pesticides or dangerous machinery without adequate training or protective gear. Regular SA8000 Audits help identify these critical areas where safety measures may be lacking or non-compliant with regulations. Addressing these risks not only protects workers but also aligns organizations with best practices in occupational health.
Special Considerations for Electronics Manufacturing
Electronics manufacturing has its own set of challenges that require special consideration during risk assessments under the SA8000 framework. Workers often handle small components that necessitate precision but may expose them to harmful chemicals used in soldering processes or cleaning agents. Therefore, understanding what H&S Risk Detection with SA8000 Looks Like in Practice is crucial here; targeted audits can reveal hidden dangers related to chemical exposure.
Moreover, ergonomic considerations play a significant role as employees frequently work at assembly lines requiring repetitive motions over extended periods. Implementing robust reporting mechanisms as part of Reporting and Corrective Action within the SA8000 Framework ensures that any identified issues are documented accurately for follow-up actions. As such, fostering a culture focused on Building a Culture of Continuous Detection and Prevention becomes essential in this high-tech sector.
Reporting and Corrective Action within the SA8000 Framework

Effective reporting and corrective action are vital components of the SA8000 framework, ensuring that health and safety violations are promptly addressed. In this section, we will explore how to document safety violations, navigate the corrective action process, and emphasize the importance of follow-up audits. By integrating these practices, organizations can enhance their commitment to continuous improvement in workplace safety.
How to Document Safety Violations
Documenting safety violations is a critical step in maintaining compliance with SA8000 Audits. Accurate documentation involves recording specific details about the incident, including date, time, location, individuals involved, and a clear description of the violation itself. This information not only serves as a basis for corrective actions but also helps in identifying patterns that may indicate systemic issues within an organization.
Furthermore, it’s essential to utilize standardized forms or digital tools for consistency in reporting across all departments. By ensuring that every safety violation is documented uniformly, organizations can create a comprehensive database that aids in understanding trends related to health and safety risks. This practice aligns with Understanding the SA8000 Health and Safety Requirements by fostering accountability and transparency.
The Corrective Action Process
Once safety violations have been documented under Reporting and Corrective Action within the SA8000 Framework, it's time to initiate the corrective action process. This process typically begins with an investigation into the root cause of each violation to ensure that solutions address underlying issues rather than just symptoms. Engaging employees during this phase can provide valuable insights into practical solutions while promoting a culture of continuous detection and prevention.
After identifying root causes, organizations should develop an action plan detailing specific steps needed to rectify each violation along with assigned responsibilities and timelines for completion. Regularly reviewing progress against this plan ensures accountability while demonstrating commitment to worker rights and safety as outlined in Understanding the SA8000 Health and Safety Requirements.
Importance of Follow-Up Audits
Follow-up audits play a crucial role in reinforcing compliance after initial corrective actions have been taken under What H&S Risk Detection with SA8000 Looks Like in Practice. These audits help verify whether implemented changes effectively mitigate identified risks or if further adjustments are necessary. Moreover, follow-up audits act as a feedback mechanism for employees regarding their concerns about health and safety conditions.
By conducting regular follow-up audits within Critical Risk Areas in High-Risk Industries such as manufacturing or construction, organizations can continuously refine their practices based on real-world outcomes rather than assumptions alone. Ultimately, this commitment not only enhances workplace safety but also fosters trust among employees who see tangible evidence of management's dedication to their well-being through ongoing assessments.
Building a Culture of Continuous Detection and Prevention
Creating a culture of continuous detection and prevention within an organization is essential for effective SA8000 Audits. This proactive approach not only enhances compliance with the SA8000 Health and Safety Requirements but also fosters an environment where safety becomes second nature to all employees. By embedding safety awareness into the company’s ethos, businesses can better identify and mitigate risks before they escalate.
Training Employees for Safety Awareness
Training is the backbone of any successful health and safety program, particularly when it comes to understanding the SA8000 Health and Safety Requirements. Regular training sessions should be designed to equip employees with knowledge about potential hazards in their work environment, especially in Critical Risk Areas in High-Risk Industries like manufacturing or construction. When workers are well-informed about safety protocols, they become active participants in maintaining a safe workplace, significantly reducing the likelihood of incidents that could result in violations during SA8000 Audits.
Promoting Open Communication about Risks
An open line of communication regarding health and safety risks is vital for effective risk management under the SA8000 framework. Encouraging employees to voice concerns or report unsafe conditions without fear of reprisal creates a transparent environment conducive to continuous improvement. This culture not only aids in immediate hazard identification—an essential aspect of What H&S Risk Detection with SA8000 Looks Like in Practice—but also strengthens trust between management and staff, leading to more robust reporting channels for future issues.
Leveraging Feedback for Ongoing Improvements
Feedback loops are crucial in building a sustainable culture of continuous detection and prevention within organizations adhering to the SA8000 framework. By regularly soliciting input from employees on safety measures and risk management practices, companies can pinpoint areas needing enhancement or adjustment—especially relevant when addressing Reporting and Corrective Action within the SA8000 Framework. This iterative process ensures that safety protocols evolve alongside industry standards, ultimately leading to improved compliance during audits while fostering an engaged workforce committed to maintaining high safety standards.
Conclusion
The journey through the intricacies of SA8000 Audits highlights a crucial aspect of workplace safety that cannot be overlooked. By adhering to the SA8000 standards, organizations not only ensure compliance but also foster a culture that prioritizes health and safety. This commitment ultimately leads to enhanced employee morale and productivity, creating a win-win situation for both workers and employers.
Enhancing Workplace Safety through SA8000
Enhancing workplace safety through SA8000 is more than just ticking boxes on an audit checklist; it’s about creating an environment where employees feel secure and valued. Understanding the SA8000 Health and Safety Requirements equips organizations with the necessary tools to identify potential risks before they escalate into serious issues. By implementing robust safety protocols, companies can effectively mitigate hazards, leading to a safer work environment for everyone involved.
Moreover, What H&S Risk Detection with SA8000 Looks Like in Practice illustrates how proactive measures can transform workplaces into safer havens. Regular audits not only highlight existing issues but also pave the way for continuous improvement in health and safety practices. As organizations embrace these standards, they cultivate a culture of accountability that resonates throughout all levels of the workforce.
Evolving Standards and Their Impact on Compliance
The landscape of compliance is constantly evolving, driven by new regulations and heightened awareness around worker rights. Evolving standards significantly impact how organizations approach their health and safety protocols under SA8000 Audits, pushing them to stay ahead of emerging risks in various industries. This dynamic nature ensures that companies remain vigilant in their efforts to protect employees while fostering an atmosphere where compliance becomes second nature.
As industries face unique challenges—especially in Critical Risk Areas in High-Risk Industries like manufacturing or construction—the need for adaptable frameworks becomes evident. Organizations must continuously reassess their strategies to align with these evolving standards while ensuring they meet or exceed compliance requirements outlined by SA8000. The result is a more resilient workforce equipped to handle unforeseen challenges without compromising on safety.
The Future of Health and Safety Audits
Looking ahead, the future of health and safety audits will likely see an increased integration of technology alongside traditional methods within the SA8000 framework. Innovative tools can enhance Reporting and Corrective Action within the SA8000 Framework by automating hazard detection processes or streamlining documentation practices for violations reported during audits. This technological evolution promises greater accuracy while minimizing human error—a vital aspect when addressing critical risk areas.
Furthermore, Building a Culture of Continuous Detection and Prevention will become essential as businesses strive for excellence in health and safety management systems under evolving regulations. Training programs will emphasize not just compliance but also employee engagement in identifying risks—transforming everyone into active participants rather than passive observers in workplace safety initiatives. As we embrace these changes together, we can look forward to safer working environments that prioritize well-being as much as productivity.
