Introduction
Welding inspection is a crucial process that ensures the integrity and quality of welded structures. In an industry where safety and durability are paramount, understanding the nuances of welding inspections can make all the difference. This introduction sets the stage for exploring various aspects of welding inspections, from visual techniques to nondestructive testing (NDT) methods.
Understanding Welding Inspections
Welding inspections encompass a variety of techniques aimed at assessing weld quality and compliance with established standards. Inspectors utilize visual inspection methods to identify surface defects, while dimensional inspection techniques measure weldments against specified tolerances. Additionally, nondestructive testing (NDT) plays a vital role in evaluating internal weld integrity without compromising the material.
Importance of Compliance
Compliance with industry regulations is essential for ensuring safety and performance in welded structures. Adhering to established standards not only protects personnel but also minimizes costly rework or failures down the line. By prioritizing compliance during welding inspections, organizations can foster a culture of quality that resonates throughout their operations.
Common Challenges in Inspections
Despite its importance, welding inspection faces several challenges that can hinder effective evaluation processes. Inspectors often grapple with identifying subtle defects during visual inspections or ensuring accurate measurements during dimensional inspections. Furthermore, maintaining proper procedure and personnel qualifications is critical; inadequate training can lead to oversight in both materials verification and traceability practices.
The Fundamentals of Welding Inspection
Welding inspection is a critical process that ensures the integrity and quality of welded structures. This section delves into the various types of inspections, the pivotal role inspectors play in maintaining quality control, and the essential regulations that govern these practices. Understanding these fundamentals is crucial for anyone involved in welding to ensure compliance and safety.
Overview of Inspection Types
Welding inspection encompasses several types, each serving a unique purpose in evaluating weld quality. Visual inspection is often the first line of defense; it allows inspectors to identify surface defects such as cracks or inadequate penetration without any specialized equipment. Following this, dimensional inspection comes into play, where precise measurements are taken to ensure that welds meet specified standards and tolerances.
Nondestructive testing (NDT) methods add another layer of assurance by examining weld integrity without causing damage to the material. Techniques like ultrasonic testing or radiographic examination can reveal internal flaws that visual inspections might miss. Each type of inspection plays a vital role in a comprehensive welding inspection program, ensuring that every aspect of the weld is scrutinized for optimal performance.
Role of Inspectors in Quality Control
Inspectors are the guardians of quality control in welding operations; they ensure that all procedures align with industry standards and project specifications. Their keen eye during visual inspections can catch issues early on, preventing costly rework or potential failures down the line. By conducting dimensional inspections, they verify that welded components adhere to precise measurements critical for structural integrity.
Moreover, inspectors often oversee nondestructive testing (NDT) activities to confirm that materials meet required specifications without compromising their functionality. Their expertise extends beyond mere observation; they interpret results from various tests and provide actionable feedback to improve welding processes continually. In essence, inspectors serve as both watchdogs and advisors within quality control frameworks, fostering an environment where excellence is paramount.
Key Regulations to Follow
Navigating through the world of welding inspections requires adherence to key regulations designed to safeguard both workers and structures alike. Organizations such as the American Welding Society (AWS) and other regulatory bodies outline standards for welding practices, including specific guidelines for visual inspection techniques and dimensional tolerances. Compliance with these regulations not only assures quality but also protects against legal repercussions stemming from non-compliance.
In addition to AWS standards, it's crucial for companies engaged in welding activities to stay updated on local codes and international standards relevant to their industry sector—especially when conducting nondestructive testing (NDT). Regulations surrounding procedure and personnel qualifications must also be strictly followed; qualified personnel are essential for executing effective inspections across all methods utilized in welding operations. Ultimately, understanding these key regulations fosters a culture of safety while enhancing overall product reliability.
Visual Inspection Techniques

Visual inspection is the backbone of welding inspection, serving as the first line of defense against defects and ensuring that welds meet specified standards. Inspectors employ keen observation skills to assess both the appearance and integrity of welds, which can reveal a wealth of information about the quality of the work performed. This technique is not only cost-effective but also critical in identifying issues before they escalate into more significant problems.
What Inspectors Look For
During visual inspection, inspectors look for various indicators that may signal potential flaws in welding. They examine weld profiles, bead size, and overall consistency to ensure compliance with established standards. Additionally, inspectors pay close attention to surface conditions—such as discoloration or contamination—that could compromise weld integrity.
Inspectors also assess joint fit-up and alignment, verifying that components are correctly positioned before welding begins. This proactive approach helps prevent dimensional discrepancies that could lead to costly rework later on. By scrutinizing these aspects closely, inspectors play a crucial role in maintaining quality throughout the welding process.
Identifying Common Defects
Common defects identified during visual inspections can range from minor cosmetic issues to major structural concerns that jeopardize safety and performance. Among these defects are cracks, porosity, undercutting, and incomplete fusion—all of which can significantly weaken a weld's structural integrity if left unaddressed. Recognizing these common pitfalls enables inspectors to take corrective action swiftly.
Furthermore, inspectors must be well-versed in distinguishing between acceptable imperfections and critical failures according to industry standards. Training in defect identification is essential for effective visual inspection; it allows inspectors to make informed decisions about whether a weld meets specifications or requires further evaluation through methods like nondestructive testing (NDT). Ultimately, early detection of defects leads to better outcomes for projects and ensures compliance with regulatory requirements.
Tools and Equipment Used
To facilitate effective visual inspection in welding processes, various tools and equipment come into play—each designed to enhance accuracy and efficiency during assessments. Commonly used tools include magnifying glasses or borescopes for examining hard-to-reach areas where defects might lurk undetected by the naked eye. These instruments empower inspectors by providing them with greater detail when evaluating weld quality.
In addition to magnification tools, lighting plays a pivotal role in visual inspections; proper illumination allows inspectors to catch subtle flaws that could otherwise go unnoticed in shadowy corners or poorly lit environments. Other equipment such as calipers or gauges aids in dimensional inspection by providing precise measurements essential for verifying compliance with tolerance standards set forth during procedure and personnel qualifications training.
Lastly, documentation tools—like checklists or digital recording devices—help maintain traceability throughout the inspection process by logging findings systematically for future reference or audits related to materials used during welding projects.
Dimensional Inspection Essentials

Dimensional inspection is a critical aspect of welding inspection that ensures weldments meet specified design criteria and function properly. This type of inspection focuses on measuring various parameters, including length, width, and thickness of the welded components. By thoroughly evaluating these dimensions, inspectors can identify potential issues before they escalate into costly repairs or safety hazards.
Measuring and Evaluating Weldments
When it comes to measuring weldments, precision is key in welding inspection. Inspectors utilize a variety of tools such as calipers, micrometers, and gauges to obtain accurate measurements of welded joints and overall assemblies. Evaluating these measurements against project specifications helps ensure that the final product adheres to required standards for performance and safety.
In addition to using proper measuring techniques, inspectors must also understand how to interpret their findings effectively. This means being familiar with the specific tolerances outlined in engineering drawings or industry standards. Ultimately, accurate measuring and evaluating contribute significantly to the overall quality assurance process within welding inspections.
Tolerance Standards Explained
Tolerance standards are essential in dimensional inspection as they define acceptable limits for variations in measurements during welding inspections. These standards help ensure that components fit together correctly and function as intended without compromising structural integrity. Familiarity with various tolerance classifications—such as tight tolerances for critical applications or looser tolerances for less demanding situations—is crucial for inspectors.
In many cases, tolerance standards are established by organizations like the American Welding Society (AWS) or other relevant regulatory bodies. These guidelines provide a framework that helps inspectors determine whether a weldment meets necessary specifications during visual inspections or when employing nondestructive testing (NDT) methods. Understanding these standards not only aids in compliance but also enhances the reliability of welded structures.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
While conducting dimensional inspections, several common pitfalls can undermine the effectiveness of welding inspections if left unchecked. One frequent mistake is relying solely on visual inspection without incorporating precise measurement techniques; this can lead to oversight of critical defects that may compromise safety or functionality. Additionally, failing to account for thermal expansion during fabrication can result in significant discrepancies between measured dimensions and actual requirements.
Another pitfall involves neglecting proper documentation throughout the inspection process; maintaining thorough records related to materials used and traceability requirements is vital for ensuring compliance with industry regulations. Moreover, inexperienced personnel may misinterpret tolerance specifications or overlook necessary adjustments during evaluations—this emphasizes the importance of procedure and personnel qualifications in achieving consistent results across all inspections.
By being aware of these pitfalls and addressing them proactively through training and adherence to best practices, organizations can enhance their overall welding inspection processes while minimizing risks associated with dimensional inaccuracies.
Nondestructive Testing (NDT) Methods
When it comes to ensuring the integrity of welds, nondestructive testing (NDT) methods are invaluable tools in the welding inspection toolkit. These techniques allow inspectors to evaluate the quality and reliability of welds without causing damage to the components being tested. By employing various NDT methods, inspectors can detect defects that might not be visible through visual inspection or dimensional inspection, ensuring compliance with safety and quality standards.
Overview of NDT Techniques
Nondestructive testing encompasses a variety of techniques designed to identify flaws in materials while preserving their usability. Common methods include ultrasonic testing (UT), radiographic testing (RT), magnetic particle testing (MT), and dye penetrant testing (PT). Each technique has its own strengths; for instance, ultrasonic testing is excellent for detecting internal defects, while visual inspection is often used as a preliminary step before more advanced NDT methods are applied.
Benefits of Using NDT
The benefits of incorporating nondestructive testing into welding inspections are manifold. First and foremost, NDT allows for early detection of potential issues that could lead to catastrophic failures later on, enhancing overall safety. Additionally, using these techniques can save time and money by preventing costly repairs or rework due to undetected defects, thus making them an essential part of any robust procedure and personnel qualifications framework.
When to Implement NDT
Knowing when to implement nondestructive testing is crucial in maintaining high standards in welding inspection processes. Generally, NDT should be employed during critical stages such as before final assembly or after significant repairs have been made. It's also wise to consider using these methods whenever there’s a change in material specifications or when working with high-stakes applications where failure could result in severe consequences.
Procedure and Personnel Qualifications
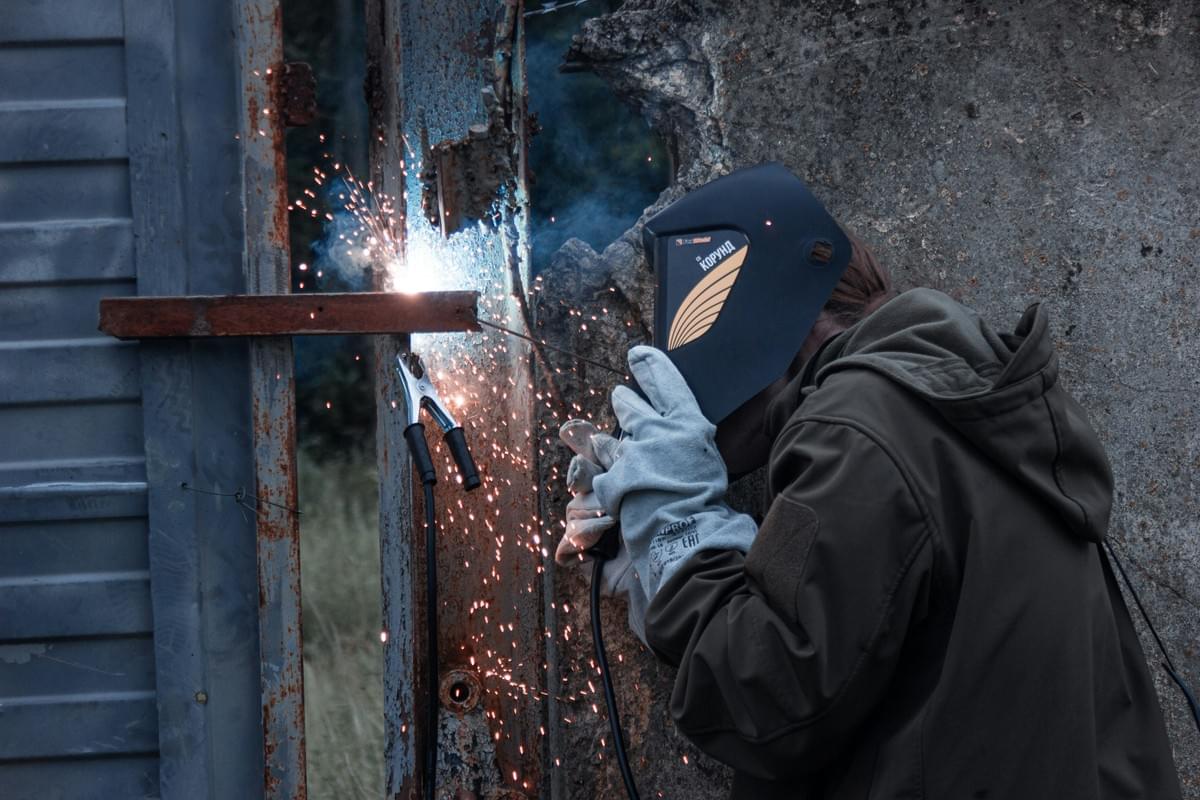

In the realm of welding inspection, the qualifications of personnel play a pivotal role in ensuring quality and compliance. Without qualified inspectors, even the best procedures can fall short, leading to safety hazards and costly rework. Thus, investing in skilled professionals is not just a recommendation; it’s a necessity for successful welding inspections.
Importance of Qualified Personnel
Qualified personnel are essential in every aspect of welding inspection, from visual inspection to nondestructive testing (NDT). Their expertise allows them to identify defects that may not be visible to the untrained eye, ensuring that welds meet rigorous standards. Moreover, their understanding of dimensional inspection techniques helps maintain tolerances critical for structural integrity.
When inspectors are well-trained and certified, they bring a level of confidence to the process that can significantly reduce risks associated with poor workmanship. The impact of their qualifications extends beyond mere compliance; it fosters a culture of quality within the organization. Ultimately, having qualified personnel leads to better outcomes in both safety and efficiency during inspections.
Certification Standards to Consider
Certification standards are crucial benchmarks that guide welding inspection practices across various industries. Organizations like the American Welding Society (AWS) and the International Institute of Welding (IIW) set forth guidelines that ensure inspectors possess necessary skills for visual inspection and NDT methods. Familiarity with these standards helps organizations select qualified personnel who can uphold high-quality welding inspections.
Inspectors should also be familiar with specific regulations relevant to their field, as these will dictate what certifications are necessary for compliance. For instance, certain sectors may require additional training in specialized NDT techniques or dimensional inspection processes that align with industry-specific requirements. Keeping abreast of evolving certification standards ensures inspectors remain effective and relevant in their roles.
Developing Effective Welding Procedures
Developing effective welding procedures is integral to maintaining quality control throughout the welding process. A well-documented procedure outlines all aspects from preparation through final inspection, including visual inspection criteria and NDT methods employed during evaluations. This clear guidance enables qualified personnel to perform consistent inspections while adhering to established tolerances.
Moreover, effective procedures must incorporate traceability requirements for materials used in welding projects—ensuring every component meets specified standards before it reaches the inspector's hands. This connection between procedure development and material verification reinforces accountability throughout each project phase while enhancing overall safety during inspections. By prioritizing thorough procedures alongside skilled personnel qualifications, organizations can achieve superior outcomes in their welding inspections.
Materials and Traceability Requirements
In the realm of welding inspection, understanding materials and traceability is paramount. The integrity of welded structures hinges not only on the quality of the welds themselves but also on the materials used in their construction. Proper material verification ensures that all components meet specified standards, which is essential for compliance during visual inspection, dimensional inspection, and nondestructive testing (NDT).
Importance of Material Verification
Material verification plays a crucial role in welding inspection as it confirms that the materials used are suitable for their intended application. This process helps prevent potential failures due to incompatible or substandard materials, which could lead to catastrophic outcomes in critical structures. By ensuring that only verified materials are utilized, inspectors can significantly reduce risks associated with structural integrity.
Tracking and Documenting Materials
Tracking and documenting materials is essential to maintain a clear chain of custody throughout the welding process. This documentation includes records from procurement to final installation, ensuring that every piece can be traced back to its origin. Effective tracking not only aids in compliance during inspections but also provides valuable data for future reference during visual inspections and dimensional inspections.
Best Practices for Traceability
Implementing best practices for traceability involves establishing robust systems that document every step of material handling and usage in welding projects. Utilizing digital tracking systems can streamline this process, making it easier to access information quickly when needed during inspections or audits. Additionally, maintaining thorough records enhances accountability among personnel involved in procedure and personnel qualifications, reinforcing a culture of quality within organizations.
Conclusion

In the world of welding, inspections are critical to ensuring safety and quality. By understanding the various aspects of Welding Inspection—from visual techniques to Nondestructive Testing (NDT)—you can significantly reduce risks associated with faulty welds. Ultimately, effective inspections not only comply with regulations but also enhance the overall integrity of your projects.
Key Takeaways for Inspecting Welds
When it comes to inspecting welds, several key points stand out. First, Visual Inspection is often the first line of defense against defects; inspectors must be trained to identify issues such as cracks or improper bead formation. Additionally, Dimensional Inspection ensures that weldments meet specified tolerances, while Nondestructive Testing (NDT) methods provide further assurance without compromising the integrity of materials.
Understanding Procedure and Personnel Qualifications is equally vital; having qualified personnel who adhere to certification standards can make a significant difference in inspection outcomes. Lastly, Materials and Traceability requirements cannot be overlooked—proper documentation plays a crucial role in maintaining quality throughout the welding process.
Strategies for Successful Inspections
To elevate your Welding Inspection practices, consider implementing structured strategies that focus on thoroughness and consistency. Start by developing a comprehensive checklist that incorporates all aspects of visual inspection and dimensional inspection criteria; this will help streamline your evaluation process. Moreover, integrating Nondestructive Testing (NDT) at appropriate stages will enhance your ability to detect hidden flaws early on.
Training personnel in Procedure and Personnel Qualifications should be an ongoing effort; regular workshops or refresher courses can keep skills sharp and knowledge up-to-date. Furthermore, establishing robust Materials and Traceability protocols will ensure you have complete visibility into material origins and usage throughout projects—this is key for compliance and quality assurance.
Enhance Your Skills with Expert Guidance
Continuous improvement is essential in the field of welding inspection; seeking expert guidance can significantly bolster your capabilities. Look for mentorship opportunities or professional development programs focused on advanced techniques in Visual Inspection, Dimensional Inspection, or Nondestructive Testing (NDT). Engaging with industry experts can also provide insights into best practices related to Procedure and Personnel Qualifications as well as effective Materials and Traceability systems.
Don’t underestimate the value of networking within professional communities; sharing experiences with peers can lead to innovative solutions for common challenges faced during inspections. In conclusion, honing your skills through education and collaboration will not only enhance your confidence but also elevate the standards within your organization’s welding practices.
