Introduction
In the fast-paced world of electronics, ensuring the reliability and functionality of devices is paramount. The testing of electronic components serves as a critical checkpoint in this journey, safeguarding against failures that could lead to significant setbacks or safety hazards. Without robust testing protocols, manufacturers risk delivering subpar products that could tarnish their reputation and compromise user safety.
Importance of Testing in Electronics
The importance of testing in electronics cannot be overstated; it acts as a gatekeeper for quality assurance. By rigorously test electronic components before they reach consumers, companies can identify potential flaws early on, saving time and resources in the long run. Ultimately, effective testing not only enhances product performance but also builds consumer trust in brand reliability.
The Role of Electronic Quality Control
Electronic quality control plays a vital role in maintaining high standards throughout the production process. It encompasses various strategies and methodologies aimed at ensuring that every component meets stringent specifications before it is integrated into larger systems. By implementing comprehensive quality control measures, manufacturers can significantly reduce defects and enhance the overall integrity of their electronic products.
Overview of Testing Methods
These methods range from functional tests that assess operational capabilities to environmental tests designed to evaluate performance under extreme conditions. Understanding these various testing approaches is essential for manufacturers aiming to optimize their processes and deliver top-notch products consistently.
Types of Testing for Electronic Components
In the realm of electronic quality control, understanding the various types of testing for electronic components is essential. Each method serves a unique purpose, ensuring that components not only function correctly but also withstand environmental stresses and maintain reliability over time. This section delves into three primary testing methods: functional testing, environmental testing, and reliability testing techniques.
Functional Testing Explained
Functional testing is the bread and butter of the testing of electronic components; it assesses whether a component performs its intended functions under specified conditions. This type of testing typically involves applying power to the component and checking its output against expected results, ensuring that everything works as designed. By rigorously test electronic components in this way, manufacturers can identify defects early in the production process and mitigate costly recalls later on.
Functional tests can vary widely depending on the type of component being assessed. For instance, semiconductors might be subjected to signal integrity tests, while power supplies could undergo load tests to verify their output under different conditions. Ultimately, successful functional testing not only enhances product quality but also builds consumer trust in electronic products.
Environmental Testing Methods
Environmental testing methods are crucial for evaluating how well electronic components endure various external factors such as temperature fluctuations, humidity levels, and mechanical stressors. These tests simulate real-world conditions that a device might encounter throughout its lifecycle; they ensure that products can withstand harsh environments without failure. By conducting thorough environmental tests during production, manufacturers can significantly improve their electronic quality control processes.
Common environmental tests include thermal cycling, where components are subjected to extreme temperature changes to assess performance stability; humidity exposure tests that evaluate moisture resistance; and vibration tests designed to simulate transport conditions. The insights gained from these methods help manufacturers understand potential weaknesses in their designs before they hit the market—saving time and resources down the line.
Reliability Testing Techniques
Reliability testing techniques aim to predict how long an electronic component will last under normal usage conditions by simulating aging processes through accelerated life tests (ALT). These techniques provide valuable data about a product's longevity by pushing it beyond typical operational limits for shorter periods—essentially fast-forwarding time to see when failures might occur. Such proactive measures are indispensable in ensuring high standards during the testing of electronic components.
Another popular reliability test is Highly Accelerated Life Testing (HALT), which subjects devices to extreme environmental conditions until failure occurs; this helps identify weaknesses in design or materials used in manufacturing. Additionally, Failure Mode Effects Analysis (FMEA) is often employed alongside these techniques to pinpoint potential failure modes before they materialize into real-world issues. By incorporating robust reliability assessments into their protocols for test electronic components, companies can enhance overall product durability and customer satisfaction.
Key Tools and Equipment

Oscilloscopes for Precision Testing
Oscilloscopes are among the most vital instruments used in the testing of electronic components, providing a visual representation of electrical signals over time. They allow engineers to observe waveforms, measure signal amplitude, frequency, and other characteristics essential for diagnosing issues in circuits. With their ability to capture transient events and anomalies, oscilloscopes enhance the effectiveness of quality control processes by enabling precise analysis during component testing.
Using an oscilloscope can be a game-changer when you need to test electronic components under various conditions. The detailed insights they provide help identify problems that may not be apparent through other testing methods. In essence, oscilloscopes elevate the standard of electronic quality control by ensuring thorough examination and validation of component performance.
Multimeters and Their Uses
Multimeters are versatile tools that serve multiple purposes in the realm of electronics testing, making them indispensable for anyone looking to test electronic components efficiently. These devices can measure voltage, current, resistance, and even continuity within circuits—essential functions that aid in diagnosing faults quickly. Their portability means technicians can perform routine checks directly on-site or within production environments without hassle.
In addition to basic measurements, modern multimeters often come equipped with advanced features like data logging and Bluetooth connectivity for remote monitoring—enhancing their utility in electronic quality control practices. By integrating multimeters into your testing protocols, you can ensure a comprehensive evaluation of component functionality while streamlining your workflow. Ultimately, they play a significant role in maintaining high standards during the testing process.
Automated Test Equipment Overview
Automated Test Equipment (ATE) represents a leap forward in efficiency when it comes to the testing of electronic components at scale. These systems automate various tests across multiple parameters simultaneously—significantly reducing human error while increasing throughput during quality assessments. ATE is particularly beneficial for manufacturers who need reliable results without sacrificing speed or accuracy.
Common Failures in Electronic Components
In the realm of electronics, failures can be both a nuisance and a significant barrier to quality. Identifying these failures promptly is crucial for maintaining the integrity of electronic quality control processes. By understanding how to test electronic components effectively, manufacturers can enhance reliability and minimize costly downtimes.
Identifying Component Failures
Identifying component failures requires keen observation and systematic testing of electronic components. Common indicators include intermittent functionality, unusual heat generation, or visible physical damage such as cracks or burns. Utilizing methods like functional testing can help pinpoint these issues early on, ensuring that defective components are caught before they cause larger system malfunctions.
Causes of Component Malfunctions
Component malfunctions often stem from various sources, including manufacturing defects, environmental factors, and improper handling during assembly or operation. For instance, soldering errors can lead to poor connections that compromise performance over time. Additionally, exposure to extreme temperatures or humidity during use can accelerate wear and tear on sensitive electronic parts—highlighting the importance of rigorous testing of electronic components throughout their lifecycle.
Mitigation Strategies
To mitigate the risks associated with common component failures, implementing robust testing protocols is essential in electronic quality control practices. Regular inspections and environmental testing methods can help detect potential issues before they escalate into major problems. Training personnel in best practices for handling and assembling components ensures that human error is minimized—ultimately leading to a more reliable product that stands up against the rigors of real-world applications.
The Testing Process Step-by-Step
The testing process for electronic components is a structured journey that ensures each component meets quality standards. It involves several stages, from initial inspections to detailed analysis and reporting of results. By following this step-by-step approach, organizations can effectively test electronic components while enhancing electronic quality control.
Initial Inspection Procedures
The first step in the testing of electronic components is the initial inspection, which serves as a critical gatekeeper in the quality assurance process. Here, technicians visually examine components for any obvious defects such as physical damage or incorrect labeling, ensuring that only suitable candidates move forward for rigorous testing. This preliminary check not only saves time but also prevents potential failures down the line, reinforcing the importance of thorough electronic quality control.
Testing Protocols for Various Components
Once initial inspections are complete, specific testing protocols tailored to different types of components come into play. For instance, resistors may undergo resistance measurements using multimeters, while capacitors might be tested for capacitance and leakage current with specialized equipment. Following these defined protocols ensures consistent results and allows teams to efficiently test electronic components across various applications without missing critical performance benchmarks.
Analysis and Reporting of Results
After conducting tests according to established protocols, it's time to analyze and report the results obtained from testing electronic components. This phase involves comparing actual performance data against expected specifications and identifying any discrepancies that could indicate malfunctions or failures. A well-structured analysis not only highlights areas needing improvement but also contributes valuable insights into long-term trends within production processes—essential for ongoing improvements in electronic quality control.
Best Practices for Effective Testing
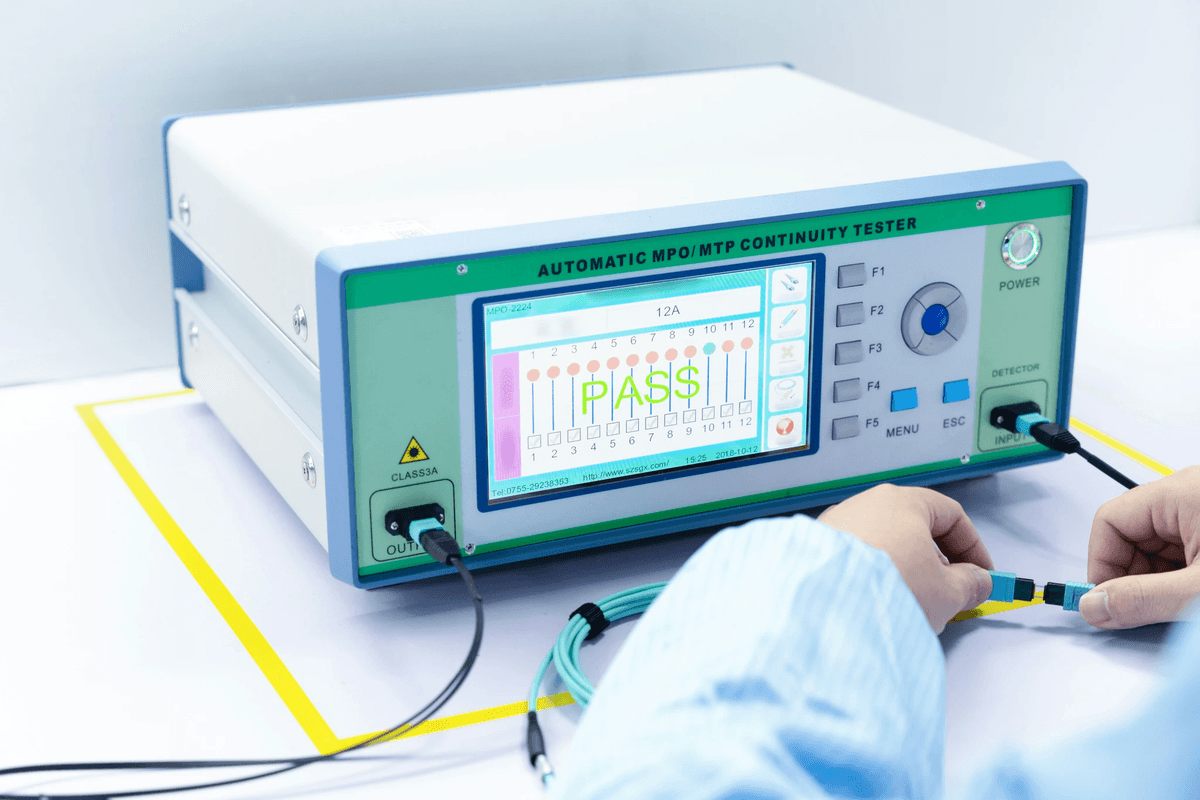
When it comes to the testing of electronic components, adopting best practices is crucial for ensuring accuracy and reliability. These practices not only enhance the quality of the testing process but also contribute significantly to overall electronic quality control. By implementing effective strategies, organizations can optimize their ability to test electronic components efficiently.
Regular Maintenance of Testing Equipment
Regular maintenance of testing equipment is vital for achieving consistent results in the testing of electronic components. Just like a well-oiled machine, test equipment needs periodic checks and calibration to ensure it operates within specified parameters. Neglecting this aspect can lead to inaccurate readings and unreliable outcomes, ultimately compromising electronic quality control.
Routine inspections should include cleaning, recalibrating instruments, and replacing worn-out parts as needed. This proactive approach minimizes downtime and extends the lifespan of testing devices, allowing teams to focus on what matters most—accurately testing electronic components. Remember, a reliable tool is essential for reliable results!
Training Personnel in Testing Standards
Equipping personnel with comprehensive training in testing standards is another cornerstone of effective testing practices. Knowledgeable staff not only understand how to test electronic components but also recognize the importance of adhering to established protocols that govern these procedures. This expertise ensures that everyone involved maintains consistency in their work while upholding rigorous electronic quality control measures.
Training programs should cover both theoretical concepts and practical applications, allowing team members to gain hands-on experience with various testing methods and tools. Additionally, fostering a culture of continuous learning helps keep personnel updated on industry advancements and emerging technologies related to the testing of electronic components. A well-trained team is an invaluable asset in maintaining high-quality standards.
Utilizing Experts Like China Inspection Pro
While internal training is essential, sometimes it's wise to call in reinforcements—experts like China Inspection Pro can make a significant difference in your approach to electronic quality control. These professionals bring specialized knowledge and experience that can enhance your team's capabilities when it comes time to test electronic components thoroughly and accurately. Their insights into industry best practices can help streamline processes while ensuring compliance with regulations.
Engaging experts allows your organization not only access to cutting-edge techniques but also provides opportunities for mentorship within your team as they learn from seasoned professionals on-site or through workshops. Ultimately, leveraging outside expertise ensures that your operations remain competitive while maintaining high standards for the testing process itself—because who wouldn’t want an ace up their sleeve?
Conclusion
In the ever-evolving landscape of electronics, the testing of electronic components is paramount to ensuring reliability and functionality. As technology advances, so does the complexity of electronic systems, making robust testing protocols essential for quality control. By prioritizing effective testing methods, manufacturers can enhance product performance and consumer trust.
Enhancing Reliability Through Testing
The cornerstone of electronic quality control lies in rigorous testing practices that ensure components function as intended. By regularly implementing comprehensive tests on electronic components, manufacturers can identify weaknesses before they lead to failures in the field. This proactive approach not only enhances reliability but also contributes significantly to customer satisfaction and brand loyalty.
Meeting Regulatory Requirements
Regulatory bodies mandate stringent standards for the testing of electronic components to safeguard consumer safety and environmental integrity. Compliance with these regulations is non-negotiable; it ensures that products meet minimum safety thresholds while also fostering innovation within legal frameworks. Companies that invest in thorough testing processes are better positioned to navigate regulatory landscapes and avoid costly penalties.
Future Trends in Electronic Testing
The future of electronic quality control is leaning towards automation and artificial intelligence, revolutionizing how we test electronic components. Emerging technologies promise faster results with increased accuracy, allowing engineers to focus on design rather than troubleshooting issues post-production. As we look ahead, embracing these advancements will be crucial for maintaining competitive advantages in a rapidly changing market.
