Introduction
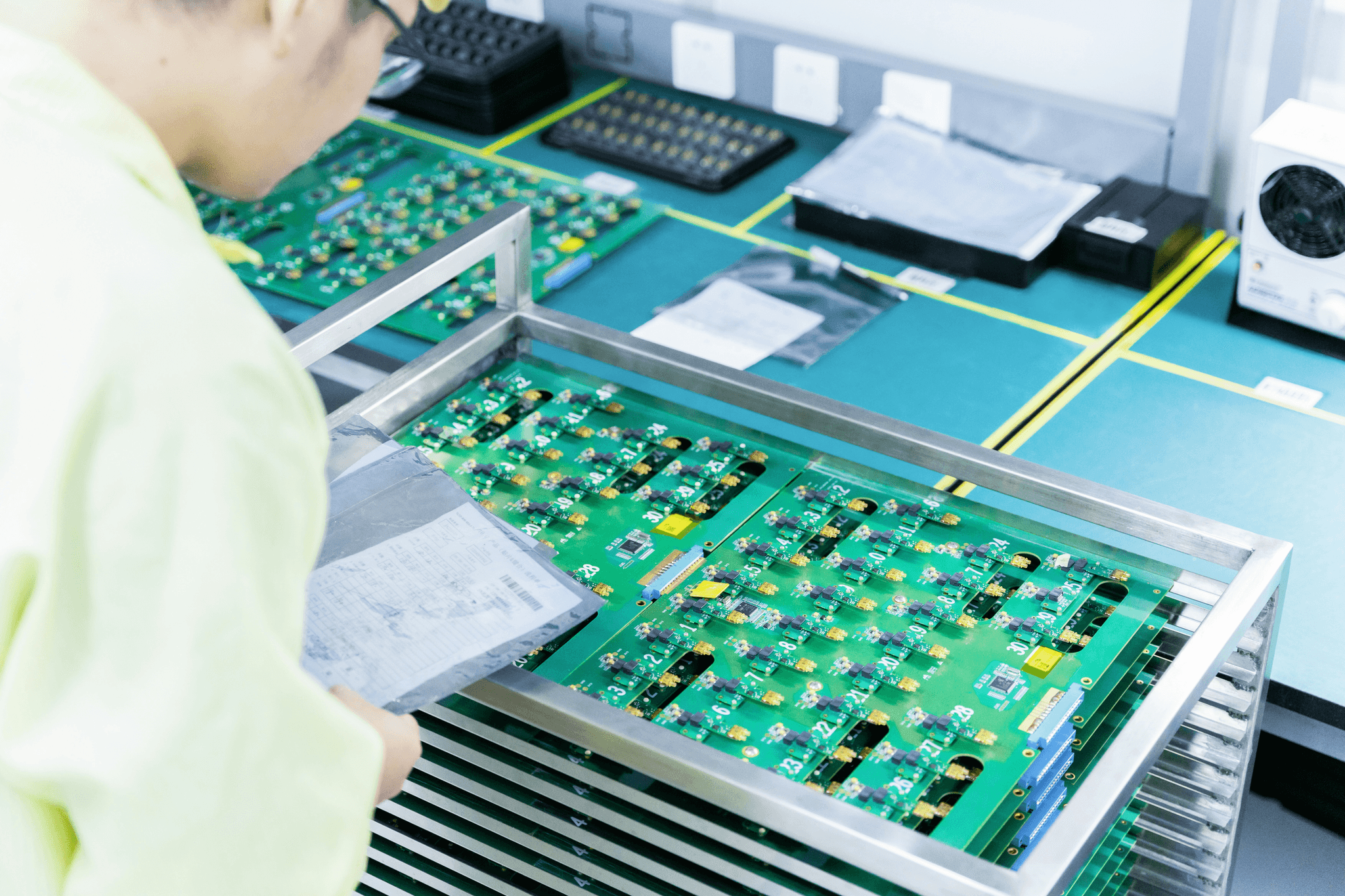
In today's fast-paced market landscape, ensuring product quality is not just a luxury—it's a necessity. The process of checking and testing products to ensure that they meet specifications is called quality assurance (QA) and quality control (QC). These two concepts are critical in maintaining standards and delivering excellence across various industries.
Understanding Quality Assurance and Quality Control
Quality assurance focuses on the processes that lead to the final product, while quality control centers on the product itself. This distinction is crucial for businesses aiming to enhance their offerings systematically. By implementing effective quality control procedures, organizations can identify defects early in the production cycle, thus saving time and resources.
Importance of Quality in Various Industries
Quality plays an indispensable role across diverse sectors, from manufacturing to healthcare. In industries where safety is paramount, such as pharmaceuticals or automotive, rigorous quality control tests list becomes essential to prevent catastrophic failures. Ultimately, prioritizing quality ensures customer satisfaction and fosters brand loyalty.
The Role of Quality Control in Product Excellence
Quality control acts as a guardian of product excellence by systematically evaluating finished goods against predetermined standards. Employing the 4 types of quality control allows companies to address potential issues proactively rather than reactively. By leveraging real-world quality control examples from leading companies like Toyota and Apple, businesses can adopt best practices that elevate their own product offerings.
Defining Quality Assurance and Quality Control

Understanding the intricacies of quality assurance (QA) and quality control (QC) is essential for businesses aiming to deliver top-notch products. While both concepts work hand in hand, they serve distinct purposes in the quest for excellence. This section will clarify what QA entails, delve into quality control procedures, and outline the process of checking and testing products to ensure that they meet specifications.
What is Quality Assurance?
Quality assurance is a systematic approach designed to ensure that products or services consistently meet specified requirements. It focuses on improving and stabilizing production processes to prevent defects before they occur. By implementing QA practices, organizations can foster a culture of continuous improvement, ultimately leading to enhanced customer satisfaction.
In essence, QA is about setting up frameworks and guidelines that help teams adhere to best practices throughout the production cycle. These frameworks often include regular audits, training programs, and process evaluations aimed at minimizing variability in production outputs. Thus, the role of quality assurance becomes pivotal in establishing a reliable foundation for delivering high-quality products.
Understanding Quality Control Procedures
Quality control procedures are specific methods employed during or after production to verify that products align with predefined standards and specifications. These procedures often include inspections, testing protocols, and statistical analysis aimed at identifying defects or inconsistencies within products before they reach consumers. Essentially, these methods act as checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process.
By utilizing various quality control tests lists—such as visual inspections or mechanical tests—businesses can pinpoint areas needing improvement while ensuring compliance with industry standards. The integration of these procedures not only enhances product reliability but also helps companies maintain their reputations by reducing returns or recalls due to faulty items. As such, understanding these quality control procedures is crucial for any organization committed to excellence.
The Process of Checking and Testing Products
The process of checking and testing products to ensure that they meet specifications is called quality control testing—a critical phase in any manufacturing operation. This involves a series of assessments aimed at verifying whether each product meets established criteria before it reaches consumers’ hands. From initial inspections during production runs to final evaluations prior to shipping, every step plays a vital role in maintaining overall product integrity.
Typically divided into several stages, this process may encompass visual checks for defects followed by more detailed assessments using specialized equipment or methodologies tailored for specific industries—like electronics or automotive manufacturing—where precision is paramount. Furthermore, employing one of the 4 types of quality control can significantly enhance this process by introducing statistical tools that aid in monitoring consistency over time.
By embracing effective techniques within this framework—whether through acceptance sampling or continuous improvement processes—companies can optimize their operations while ensuring high-quality outcomes across all product lines. Thus, mastering the art of checking and testing products becomes indispensable for achieving long-term success in today’s competitive marketplace.
Key Differences Between QA and QC
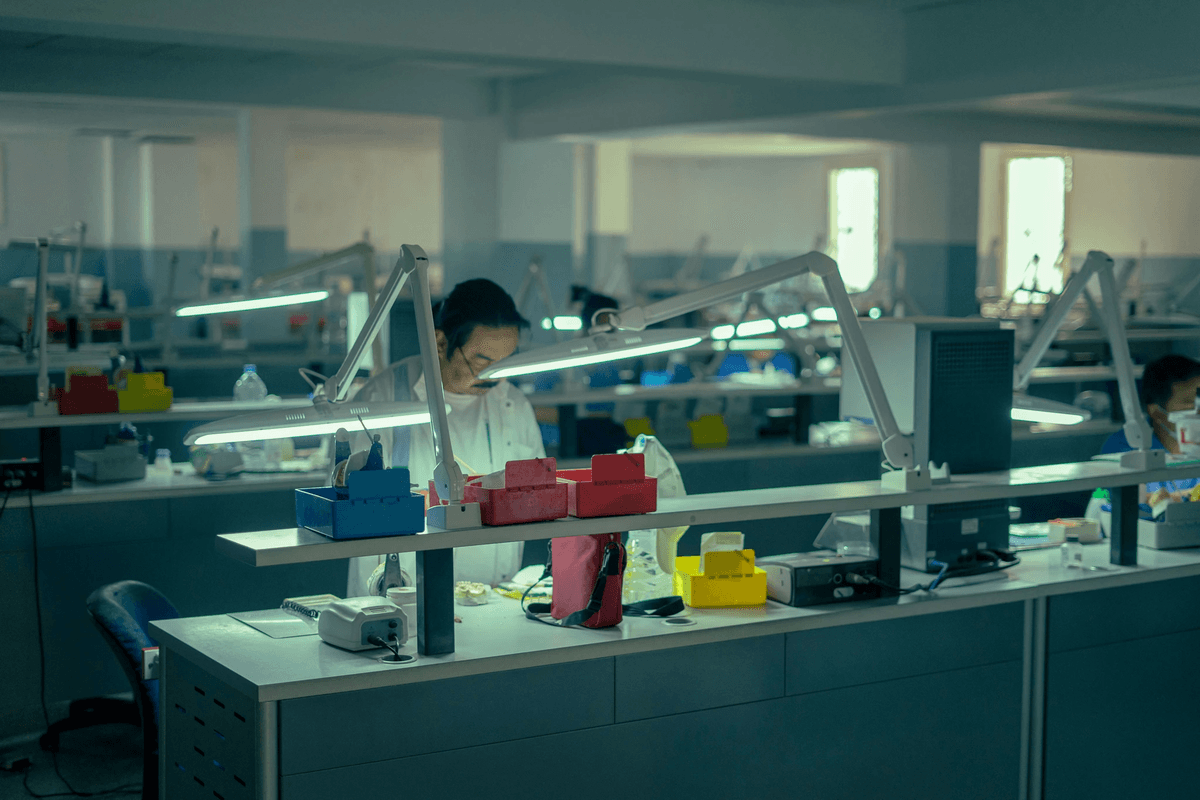

Quality Assurance (QA) and Quality Control (QC) are often used interchangeably, but they serve distinct purposes in the pursuit of excellence. Understanding these differences is crucial for any organization aiming to deliver high-quality products and services. By exploring the proactive versus reactive approaches, the focus on process versus product, and real-world examples, we can appreciate how each contributes uniquely to quality management.
Proactive vs Reactive Approaches
Quality Assurance is inherently proactive; it involves planning and process design to prevent defects before they occur. This means that QA teams work tirelessly behind the scenes to create robust systems that minimize risks associated with product failure. In contrast, Quality Control is more reactive; it focuses on identifying defects after products have been developed through various quality control procedures, ensuring that any issues are caught before reaching consumers.
When discussing the process of checking and testing products to ensure that they meet specifications, it's essential to note that QC steps in after production has begun or completed. By implementing a systematic approach, organizations can utilize various quality control tests lists to identify problems early in their lifecycle. Ultimately, while QA aims for prevention and continuous improvement, QC seeks to catch errors through inspection and testing.
Focus on Process vs Focus on Product
The distinction between QA and QC also lies in their focus areas—process versus product. Quality Assurance emphasizes creating a solid foundation by refining processes that lead to successful outcomes; it's about building a culture of quality within an organization. This proactive approach ensures that all team members understand their roles in maintaining standards throughout every stage of development.
Conversely, Quality Control zeroes in on the final product delivered to customers. It examines whether finished goods meet predetermined specifications through rigorous quality control tests list designed for specific industries or products. While both approaches are vital for achieving excellence, their differing focuses highlight how organizations can tailor their strategies based on specific needs.
Examples Highlighting QA and QC Distinctions
To illustrate these differences further, consider some practical quality control examples from well-known companies across various sectors. For instance, Toyota's Lean Manufacturing practices exemplify an effective Quality Assurance strategy where continuous improvement processes are embedded into daily operations—reducing waste while enhancing efficiency before any product reaches consumers.
On the other hand, Apple's stringent testing protocols serve as an excellent example of Quality Control at work; they meticulously check each device against a comprehensive quality control tests list before market release to ensure customer satisfaction aligns with brand reputation. By examining such examples from leading companies, one can better appreciate how both QA and QC play essential roles in delivering high-quality outcomes while addressing unique challenges faced by different industries.
Real-World Quality Control Examples
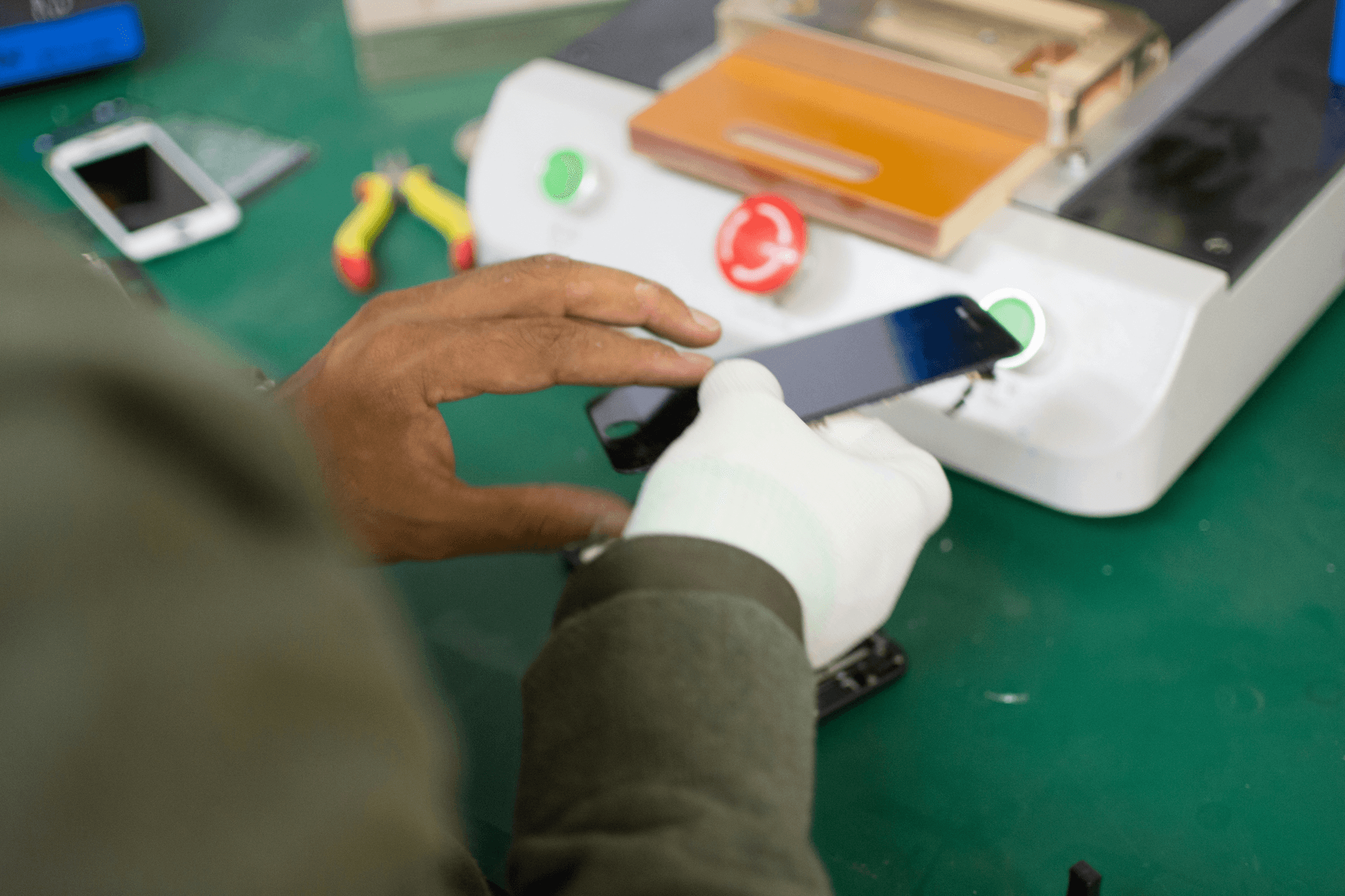

Quality control is not just a buzzword; it’s a critical component that can make or break a company’s reputation and success. By examining real-world examples, we can glean valuable insights into effective quality control procedures that ensure products meet specifications and customer expectations. From automotive giants to tech innovators, the application of quality control tests can lead to exceptional outcomes.
Case Study: Toyota’s Lean Manufacturing
Toyota's lean manufacturing system is often hailed as a benchmark in the realm of quality control examples. The process of checking and testing products to ensure that they meet specifications is called quality assurance within their framework, where every employee is empowered to halt production if they detect an issue. This proactive approach not only minimizes waste but also enhances product quality by focusing on continuous improvement—a hallmark of the 4 types of quality control.
The company's emphasis on Kaizen, or continuous improvement, illustrates their commitment to refining processes and eliminating inefficiencies. By integrating feedback loops into their production lines, Toyota ensures that any defects are addressed immediately, reinforcing their reputation for excellence in quality control procedures. This case study exemplifies how effective quality management can lead to both operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Insights from Apple's Product Testing Practices
Apple Inc., known for its innovative technology, places immense importance on rigorous product testing practices as part of its overall quality strategy. The company employs extensive quality control tests list throughout its development phases, ensuring each device meets high standards before reaching consumers. Their meticulous attention to detail during the process of checking and testing products to ensure that they meet specifications is called “validation,” which involves multiple stages of testing.
From hardware durability assessments to software performance evaluations, Apple leaves no stone unturned in its quest for perfection. This proactive stance allows Apple not only to deliver reliable products but also fosters brand loyalty among consumers who trust the integrity of what they purchase. Ultimately, Apple's example highlights how embracing robust quality control procedures can lead directly to market leadership.
Quality Control Tests List in Electronics
In the fast-paced world of electronics manufacturing, maintaining high-quality standards is paramount for success—enter the essential quality control tests list! These tests encompass various methods designed to evaluate everything from electrical safety and performance reliability to environmental compliance and user experience metrics. The process of checking and testing products to ensure that they meet specifications is called “quality validation,” which includes both automated inspections and manual assessments.
Commonly utilized tests include functional testing (to verify product operation), stress testing (to assess durability under extreme conditions), and compliance testing (ensuring adherence to industry regulations). By implementing these comprehensive quality control procedures, manufacturers can identify potential issues early in production cycles—ultimately saving time and costs while enhancing customer satisfaction with end products. Embracing these 4 types of quality control ensures that electronic devices remain competitive in an ever-evolving market.
The 4 Types of Quality Control
Quality control is a vital aspect of maintaining excellence in products and services, and understanding the various types can enhance effectiveness significantly. The process of checking and testing products to ensure that they meet specifications is called quality control, which encompasses several methodologies. Here, we will delve into the four primary types of quality control that organizations use to uphold their standards.
Statistical Process Control Explained
Statistical Process Control (SPC) is a method that employs statistical techniques to monitor and control processes. By using data from product testing, organizations can identify variations in processes that may lead to defects or non-conformance with specifications. This proactive approach allows companies to make informed decisions based on real-time data, ensuring that quality control procedures are both effective and efficient.
SPC typically involves the use of control charts, which visually represent process performance over time. These charts help teams quickly identify when a process goes out of control or deviates from set specifications. In essence, SPC not only aids in maintaining product quality but also promotes continuous improvement by analyzing trends and patterns in production data.
Acceptance Sampling Overview
Acceptance sampling is another key component within the 4 types of quality control, focusing on evaluating a random sample from a batch rather than inspecting every single item. This method is particularly useful for large production runs where testing every unit would be impractical or costly. By applying acceptance sampling techniques, businesses can determine whether a batch meets predetermined quality standards based on the results from just a subset of items.
The beauty of acceptance sampling lies in its ability to balance efficiency with risk management—organizations can save time and resources while still ensuring compliance with quality standards. However, it’s crucial for companies to establish clear criteria for acceptance tests; otherwise, they risk overlooking defects that could compromise product integrity. Quality control tests lists often incorporate acceptance sampling methods as part of their strategy for maintaining high-quality benchmarks.
Continuous Improvement Process and Tools
Continuous improvement is an ongoing effort aimed at enhancing products, services, or processes over time through incremental improvements rather than major shifts. This type of quality control emphasizes the importance of feedback loops where insights gained from checking and testing products feed back into the production cycle for refinement purposes. Tools such as Six Sigma or Kaizen are commonly employed as part of this continuous improvement process.
By integrating continuous improvement practices into their operations, organizations foster an environment where employees feel empowered to suggest changes that enhance overall product quality. Moreover, this approach aligns seamlessly with other quality control procedures by creating a culture dedicated to excellence and accountability at every level of production. Ultimately, companies utilizing continuous improvement tools consistently see enhanced efficiency along with higher customer satisfaction rates.
Quality Control in Action with China Inspection Pro
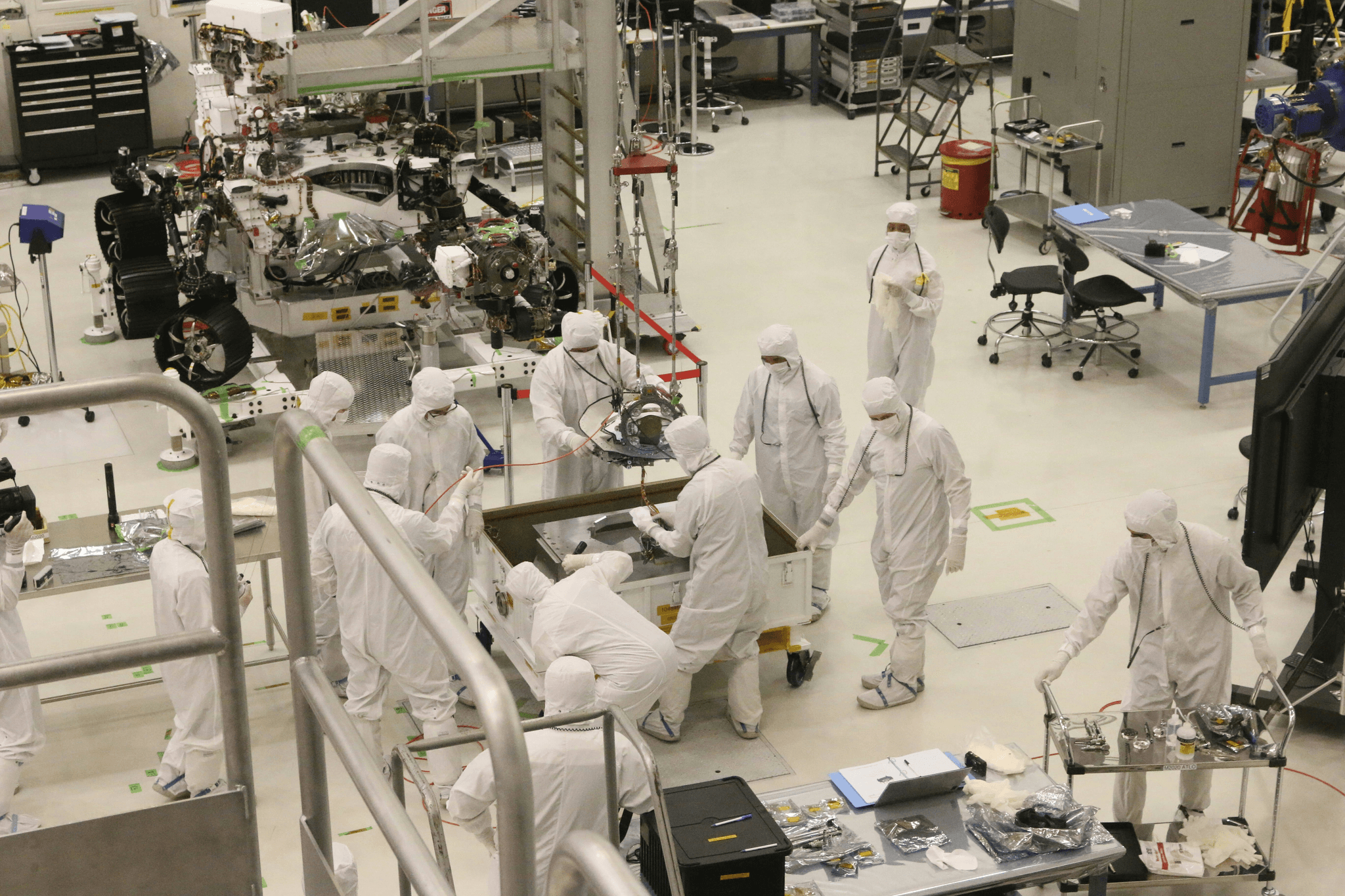
Quality control is an essential aspect of any manufacturing process, and China Inspection Pro stands out with its comprehensive quality inspection services. These services are designed to cater to various industries, ensuring that products meet stringent specifications and regulatory standards. By employing a systematic approach, they help businesses maintain high-quality benchmarks through the process of checking and testing products to ensure that they meet specifications.
Comprehensive Quality Inspection Services
China Inspection Pro offers a range of quality inspection services tailored to the unique needs of different sectors. Their expertise encompasses everything from pre-production inspections to final product evaluations, ensuring that every phase adheres to established quality control procedures. This commitment enables companies to identify defects early in the manufacturing process, significantly reducing costs associated with returns and rework.
The 4 types of quality control are integral to their methodology: statistical process control, acceptance sampling, continuous improvement processes, and inspection-based assessments. Each type serves a specific purpose in identifying variances from desired product standards. This multifaceted approach ensures that clients receive thorough evaluations based on their specific requirements.
Ensuring Regulatory Compliance and Market Standards
One of the primary goals of China Inspection Pro is to ensure that products comply with both local and international regulations. By adhering to established market standards, they help businesses navigate complex compliance landscapes effectively. This not only protects consumers but also enhances brand reputation by demonstrating a commitment to quality.
Their rigorous quality control tests list includes checks for functionality, safety, durability, and aesthetic appeal—ensuring all aspects are thoroughly vetted before reaching the market. Such diligence minimizes the risk of costly recalls or legal issues stemming from non-compliance with industry regulations. Ultimately, this proactive stance helps businesses build trust with customers who expect nothing less than excellence.
Actionable Recommendations to Enhance Quality
After conducting inspections and assessments, China Inspection Pro provides actionable recommendations aimed at enhancing product quality further. These insights can lead companies towards adopting best practices in their production processes while addressing any identified weaknesses promptly. By implementing these recommendations, businesses can significantly improve their overall operational efficiency.
Additionally, integrating feedback into existing quality control procedures fosters a culture of continuous improvement—a key factor in maintaining competitive advantage within any industry landscape. The focus on ongoing enhancement aligns perfectly with the core principles behind the 4 types of quality control previously mentioned—ensuring organizations remain agile and responsive to market demands over time.
In conclusion, leveraging services like those offered by China Inspection Pro allows companies not only to meet but exceed customer expectations through rigorous adherence to quality standards while fostering innovation within their operations.
Conclusion
In the ever-evolving landscape of business, quality is not just a buzzword; it's a cornerstone of success. Companies that prioritize quality assurance and control can significantly enhance their reputation, reduce costs associated with defects, and ultimately drive customer satisfaction. The process of checking and testing products to ensure that they meet specifications is called quality control, which plays an essential role in maintaining high standards across various industries.
The Importance of Quality in Business Success
Quality serves as the bedrock upon which successful businesses are built. Without robust quality control procedures in place, organizations risk delivering subpar products that can tarnish their brand image and alienate customers. By focusing on quality, companies not only meet customer expectations but often exceed them, leading to increased loyalty and repeat business.
Moreover, implementing effective quality control tests list helps identify potential issues before they escalate into costly problems. This proactive approach saves time and resources while ensuring that products consistently meet or exceed industry standards. Ultimately, prioritizing quality is synonymous with investing in long-term business success.
Integrating QA and QC for Optimal Results
The integration of Quality Assurance (QA) and Quality Control (QC) creates a powerful synergy that can elevate any organization's output. While QA focuses on process improvements to prevent defects from occurring, QC zeroes in on identifying product flaws after production through various quality control examples. Together, these two facets ensure a seamless flow from initial design through to final delivery.
By combining the 4 types of quality control—statistical process control, acceptance sampling, continuous improvement processes, and more—companies can create a comprehensive framework for maintaining excellence throughout their operations. This holistic approach not only enhances product reliability but also fosters a culture of continuous improvement within the organization.
Future Trends in Quality Assurance and Control
As we look ahead, several trends are poised to reshape the landscape of quality assurance and control significantly. One notable trend is the increasing reliance on automation and artificial intelligence to streamline the process of checking and testing products to ensure that they meet specifications is called automated testing solutions. These innovations promise greater efficiency while reducing human error during inspections.
Moreover, sustainability will take center stage as companies adopt eco-friendly practices within their quality control procedures. Consumers are increasingly demanding transparency regarding sourcing materials and manufacturing processes; thus organizations must adapt accordingly or risk losing market share.
In conclusion, staying abreast of these future trends will be crucial for businesses aiming to maintain competitive advantages through superior quality assurance practices.
