Introduction

In today's fast-paced manufacturing landscape, understanding what quality check means is more critical than ever. Quality checks serve as the backbone of production processes, ensuring that every product meets established standards and expectations. Without effective quality control measures, businesses risk delivering subpar goods and services, damaging their reputation and profitability.
Understanding Quality Check and Its Importance
Quality checks are systematic evaluations designed to assess the integrity of products throughout the manufacturing process. They play a pivotal role in maintaining high standards, safeguarding both consumer trust and brand loyalty. By implementing rigorous quality assurance protocols, companies can minimize defects and enhance customer satisfaction.
Defining Key Terms in Quality Assurance
To grasp the full scope of quality assurance, it's essential to define key terms such as QC inspector, non-conformity report, and NPI (New Product Introduction). A QC inspector is responsible for conducting thorough assessments during production phases to ensure compliance with industry standards. Meanwhile, a non-conformity report documents any deviations from these standards, prompting corrective actions that drive continuous improvement.
The Role of Quality Checks in Manufacturing
Quality checks are integral to manufacturing processes as they help identify issues early on—before they escalate into costly problems. These checks encompass various methods such as visual inspection procedures and testing of electronic components to validate product reliability. Furthermore, social compliance auditing ensures that ethical practices are upheld across supply chains while contributing to the overall production of quality goods and services.
What Does Quality Check Mean?

Quality checks are the backbone of any production process, ensuring that products meet established standards before reaching consumers. So, what does quality check mean? Simply put, it's a systematic approach to evaluating products and services against predefined criteria to ensure they are fit for use and satisfy customer expectations.
The Essence of Quality Control
At its core, quality control (QC) is about maintaining high standards throughout the production of quality goods and services. This involves various processes, including regular assessments and inspections, to identify defects or inconsistencies in products. Without effective QC measures in place, manufacturers risk delivering subpar items that can damage their reputation and lead to financial losses.
In manufacturing contexts, understanding what does quality check mean is crucial for maintaining competitive advantage. It often encompasses comprehensive testing of electronic components as well as adherence to industry regulations. Thus, a robust QC system not only safeguards product integrity but also enhances customer satisfaction.
Historical Context of Quality Checks
The concept of quality checks has evolved significantly over the decades—from rudimentary inspections to sophisticated methodologies that incorporate technology and data analytics. Historically, the rise of industrialization brought forth a need for standardized practices in production processes; thus began the formalization of quality assurance techniques. By understanding this historical context, we can appreciate how far we've come in ensuring product reliability through rigorous testing methods.
In earlier times, social compliance auditing was primarily focused on labor conditions rather than product quality itself; however, today's comprehensive approach combines both aspects into a unified framework for assessment. This evolution highlights how essential it is for manufacturers to adapt their strategies according to market demands while still adhering to best practices in QC procedures.
Industry Standards and Best Practices
Industry standards play a pivotal role in defining what does quality check mean across different sectors. Organizations like ISO (International Organization for Standardization) establish guidelines that help companies implement effective QC measures tailored specifically for their industries—be it electronics or textiles. These benchmarks not only foster consistency but also create trust among consumers regarding product safety and efficacy.
Best practices in quality control involve ongoing training for teams responsible for conducting visual inspection procedures as well as employing advanced technologies like automated testing systems where applicable. Furthermore, understanding what is a non-conformity report allows organizations to address discrepancies promptly while also facilitating continuous improvement initiatives within their operations.
In summary, grasping what does NPI mean in manufacturing helps stakeholders appreciate how new product introductions must align with established QC protocols from day one—ensuring that every new item launched meets or exceeds consumer expectations right from its inception.
What is a QC Inspector?
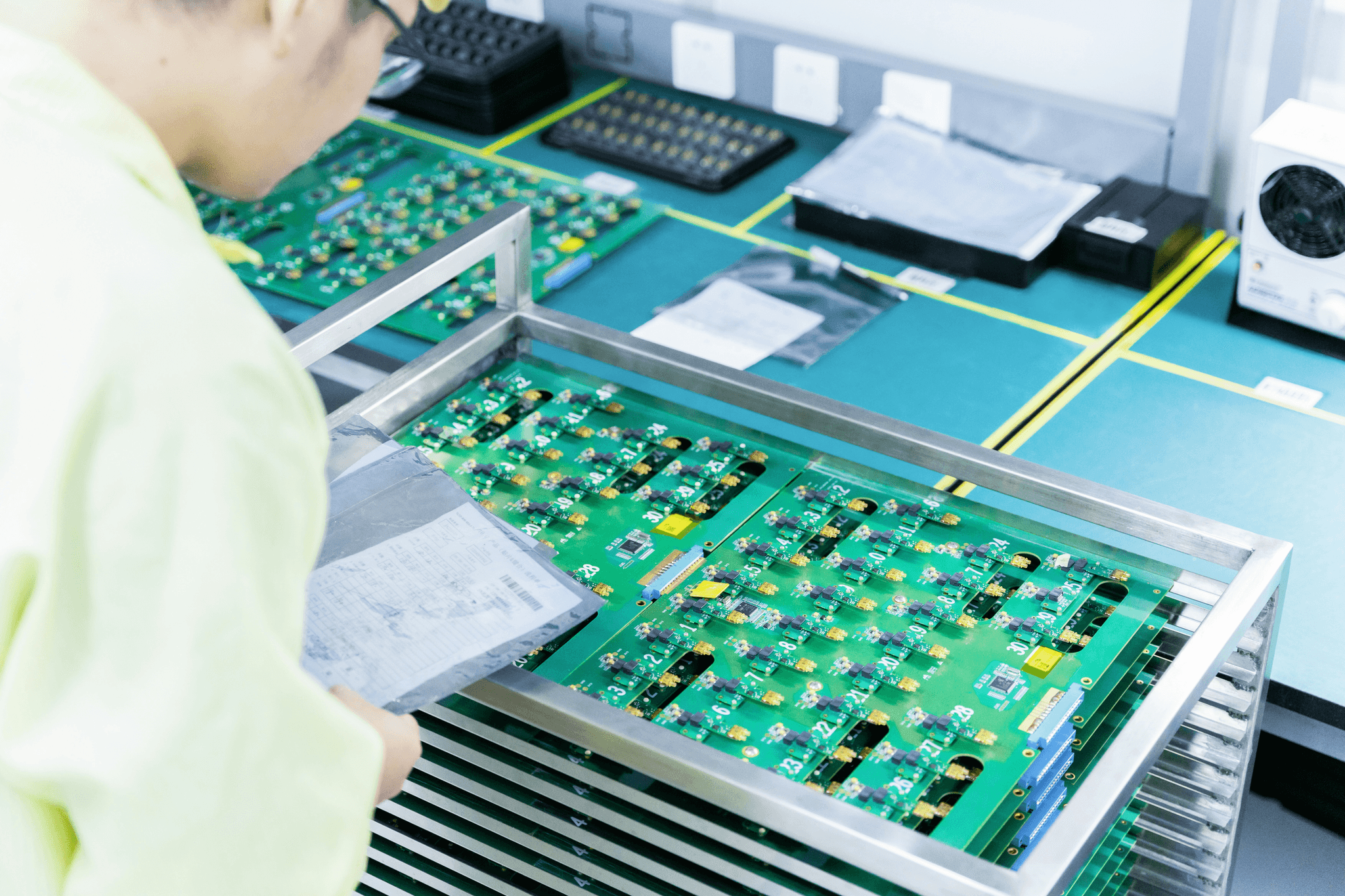
In the realm of manufacturing, understanding what a QC inspector is can be pivotal for ensuring the production of quality goods and services. A QC inspector plays a crucial role in maintaining quality standards throughout the production process, ensuring that every component meets the established specifications. Their duties often encompass various stages of production, from raw material inspection to final product assessment.
The Role of QC Inspectors in Production
The primary role of QC inspectors is to conduct thorough assessments at different phases of production, which directly relates to what does quality check mean. This involves performing visual inspections and testing of electronic components to identify defects or deviations from standards. By implementing social compliance auditing practices, they help ensure that not only are products compliant with safety regulations but also ethically produced.
QC inspectors also document their findings meticulously, which leads us to understand what a non-conformity report entails. When discrepancies arise during inspections, these reports serve as essential tools for tracking issues and fostering continuous improvement. Moreover, by collaborating closely with production teams, they provide invaluable feedback that informs processes and enhances overall product quality.
Skills and Qualifications of a QC Inspector
To effectively fulfill their responsibilities, a QC inspector must possess a unique blend of skills and qualifications tailored for the job at hand. Familiarity with various testing methods for electronics is paramount; inspectors should be adept at using specialized tools and techniques relevant to their industry. Additionally, analytical skills are crucial for interpreting data from inspections and determining whether products meet established criteria.
In terms of qualifications, many employers look for candidates who have completed relevant education or training programs in quality assurance or manufacturing disciplines. Knowledge about visual inspection procedures is often emphasized since it forms the basis for many assessment techniques used in the field. Ultimately, strong communication skills are essential as well; inspectors must convey findings clearly to ensure all team members understand how they relate to NPI (New Product Introduction) processes.
Impact of QC Inspectors on Product Quality
The impact that QC inspectors have on product quality cannot be overstated; they are essentially gatekeepers who uphold industry standards through rigorous checks and balances. By conducting thorough inspections throughout production phases—often leveraging insights from social compliance auditing—they significantly reduce the likelihood of defective products reaching consumers. Their efforts directly correlate with enhanced customer satisfaction and brand reputation by ensuring only high-quality goods enter the market.
Furthermore, through diligent documentation practices—including non-conformity reports—QC inspectors contribute significantly to continuous improvement initiatives within organizations. These reports not only highlight areas needing attention but also foster an environment where learning from mistakes becomes part of the culture—essentially answering what does NPI mean in manufacturing contexts where innovation thrives on past lessons learned.
In summary, understanding the role of a QC inspector sheds light on how vital these professionals are in maintaining high-quality standards across industries while navigating complex challenges like social compliance auditing and electronic component testing.
Testing of Electronic Components
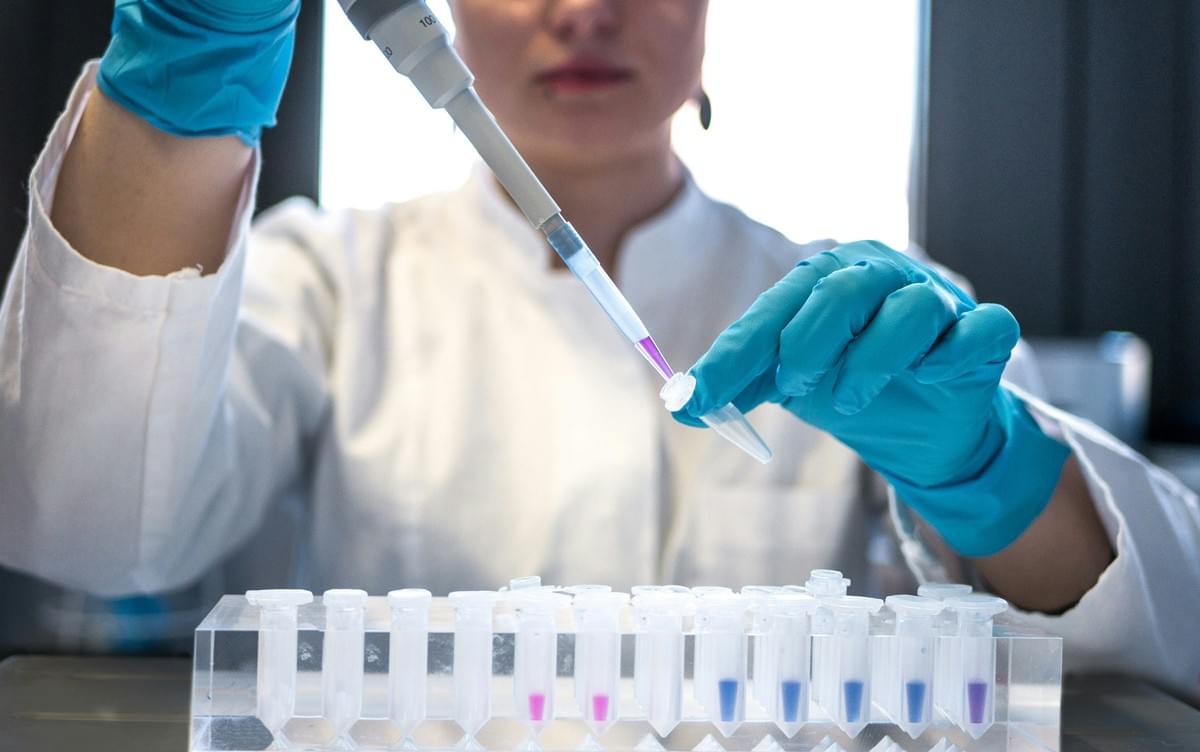

In the fast-paced world of electronics, ensuring that every component functions perfectly is paramount. The testing of electronic components serves as a crucial checkpoint in the manufacturing process, safeguarding against defects that could lead to product failures. This meticulous approach not only enhances the production of quality goods and services but also reinforces consumer trust in electronic products.
Importance of Testing in Electronics
Testing in electronics is not just a box-ticking exercise; it’s vital for maintaining safety and performance standards. When we ask ourselves what does quality check mean, it becomes clear that rigorous testing is at the heart of this concept. By identifying potential issues early on, manufacturers can avoid costly recalls and ensure compliance with industry regulations, ultimately benefiting everyone involved—from producers to end-users.
Common Testing Methods for Electronics
There are several common testing methods employed in the industry to verify component functionality and reliability. Techniques such as functional testing, burn-in testing, and visual inspection procedures play a significant role in quality assurance processes. Each method has its own strengths; for example, functional testing checks if components perform their intended functions while visual inspection procedures help spot any physical defects or discrepancies.
Ensuring Reliability Through Quality Checks
Quality checks are essential for ensuring reliability throughout the lifecycle of electronic components. By implementing thorough inspections and tests—whether through social compliance auditing or detailed non-conformity reports—manufacturers can effectively manage risks associated with product failures. Understanding what NPI means in manufacturing also emphasizes the importance of integrating quality checks from the outset during new product introductions to establish robust standards right from day one.
Social Compliance Auditing
In the realm of quality assurance, social compliance auditing is a critical component that ensures ethical practices within production environments. It serves as a safeguard against labor violations and promotes fair treatment of workers, aligning with the broader objectives of quality checks. By examining various labor standards, these audits help maintain the integrity of supply chains while fostering a culture of accountability.
What is Social Compliance Auditing?
Social compliance auditing refers to the systematic evaluation of a company's adherence to ethical labor practices and standards. This process involves assessing working conditions, employee treatment, and adherence to regulations that support human rights within manufacturing settings. In essence, it is about ensuring that organizations are not just focused on what does quality check mean in terms of products but also in how they treat their workforce.
Importance for Global Supply Chains
The significance of social compliance auditing cannot be overstated when considering global supply chains that span multiple countries and cultures. These audits play an essential role in identifying potential risks related to labor exploitation or unsafe working conditions, which can ultimately impact the production of quality goods and services. By maintaining high standards through regular audits, companies can build trust with consumers who increasingly prioritize ethical sourcing in their purchasing decisions.
How Audits Affect Quality Standards
Audits have a profound effect on quality standards by highlighting areas for improvement not only in product output but also in employee welfare practices. When organizations address findings from social compliance audits, they enhance their overall operational efficiency and commitment to producing quality goods and services. Additionally, incorporating these audits into regular quality check protocols encourages continuous improvement across all aspects of production—from what is non-conformity report management to ensuring robust testing of electronic components.
Visual Inspection Procedure
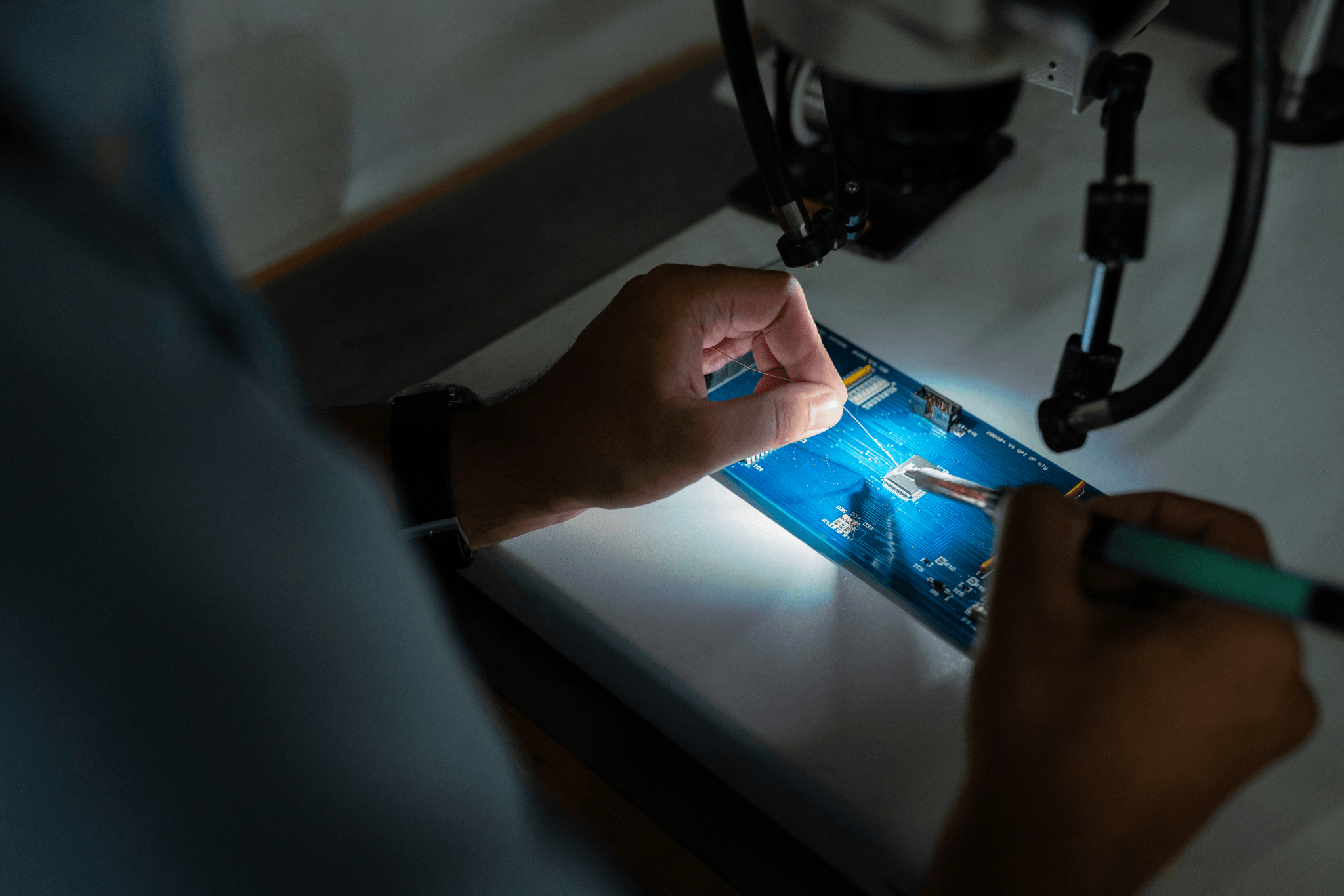

Visual inspection is a fundamental technique in the realm of quality assurance, particularly when it comes to ensuring the production of quality goods and services. This procedure involves examining products or components using the naked eye or magnifying tools to identify defects, inconsistencies, or non-conformities. When we ask ourselves what does quality check mean, visual inspection often serves as a first line of defense against subpar products making it to market.
Overview of Visual Inspection Techniques
There are various visual inspection techniques employed across different industries, including electronics and manufacturing. Common methods include direct visual inspection, where inspectors scrutinize items for visible flaws, and more advanced techniques like automated optical inspection (AOI). Each approach has its own merits; while manual inspections allow for nuanced human judgment, AOI can quickly analyze large volumes of electronic components with impressive accuracy.
The role of a QC inspector is crucial here; they must be adept at using these techniques effectively to ensure that products meet established standards. For instance, in the testing of electronic components, inspectors may look for soldering issues or component misalignments that could affect performance. Thus, understanding what is a QC inspector becomes vital when discussing visual inspection procedures.
Benefits of Visual Inspections in Quality Control
Visual inspections offer numerous benefits that enhance overall quality control processes. Firstly, they are cost-effective and quick; defects can be identified early in production without extensive testing procedures that might delay manufacturing timelines. Additionally, visual inspections help maintain compliance with social compliance auditing standards by ensuring that products meet safety regulations before they reach consumers.
Moreover, these inspections foster a culture of continuous improvement within organizations by identifying recurring issues that need addressing—thus answering what is non-conformity report all about? By documenting these findings through non-conformity reports, companies can implement corrective actions and refine their processes over time. Ultimately, effective visual inspections contribute significantly to the production of quality goods and services.
Case Studies Highlighting Visual Inspection Success
Several case studies underscore the effectiveness of visual inspection procedures across various sectors. For example, an electronics manufacturer faced challenges with defective circuit boards impacting their product launch schedule; implementing rigorous visual inspections allowed them to identify issues early on during testing of electronic components before mass production commenced. This proactive approach not only saved costs but also ensured timely delivery without compromising on quality.
Another instance involved a textile company struggling with fabric defects due to inadequate oversight during manufacturing stages; adopting comprehensive visual inspections led to significant reductions in returns and increased customer satisfaction levels—demonstrating how crucial this procedure is in maintaining high-quality standards aligned with NPI (New Product Introduction) goals. Such examples highlight how integrating robust visual inspection techniques can elevate overall product integrity while reinforcing what does quality check mean within an organization’s framework.
What is a Non-Conformity Report?
A Non-Conformity Report (NCR) is a vital document in manufacturing that highlights instances where products or processes deviate from established standards or specifications. Understanding what a non-conformity report entails is essential for maintaining the integrity of production processes and ensuring the production of quality goods and services. These reports serve as a foundation for identifying issues, facilitating improvements, and ultimately enhancing overall quality assurance practices.
Understanding Non-Conformity Reports in Manufacturing
In the realm of manufacturing, a non-conformity report acts as an official record detailing specific deviations from quality standards. This could relate to anything from the testing of electronic components to discrepancies noted during visual inspection procedures. By pinpointing these non-conformities, organizations can better understand their weaknesses and address them proactively before they escalate into larger problems.
Process of Addressing Non-Conformities
The process of addressing non-conformities begins with the identification and documentation through an NCR. Once a report is filed, it triggers an investigation to assess the root cause—this could involve QC inspectors conducting thorough analyses or implementing social compliance auditing measures to ensure adherence to regulations. After identifying the cause, corrective actions are formulated and executed, which may include revisiting what does quality check mean in practice for future prevention.
Role of Non-Conformity Reports in Continuous Improvement
Non-Conformity Reports play a crucial role in continuous improvement initiatives within manufacturing settings by providing actionable insights into recurring issues. By systematically analyzing these reports, companies can refine their processes related to new product introduction (NPI) while enhancing their overall quality checks framework. Ultimately, this leads not only to improved product reliability but also fosters a culture that prioritizes excellence across all facets of production.
What Does NPI Mean in Manufacturing?
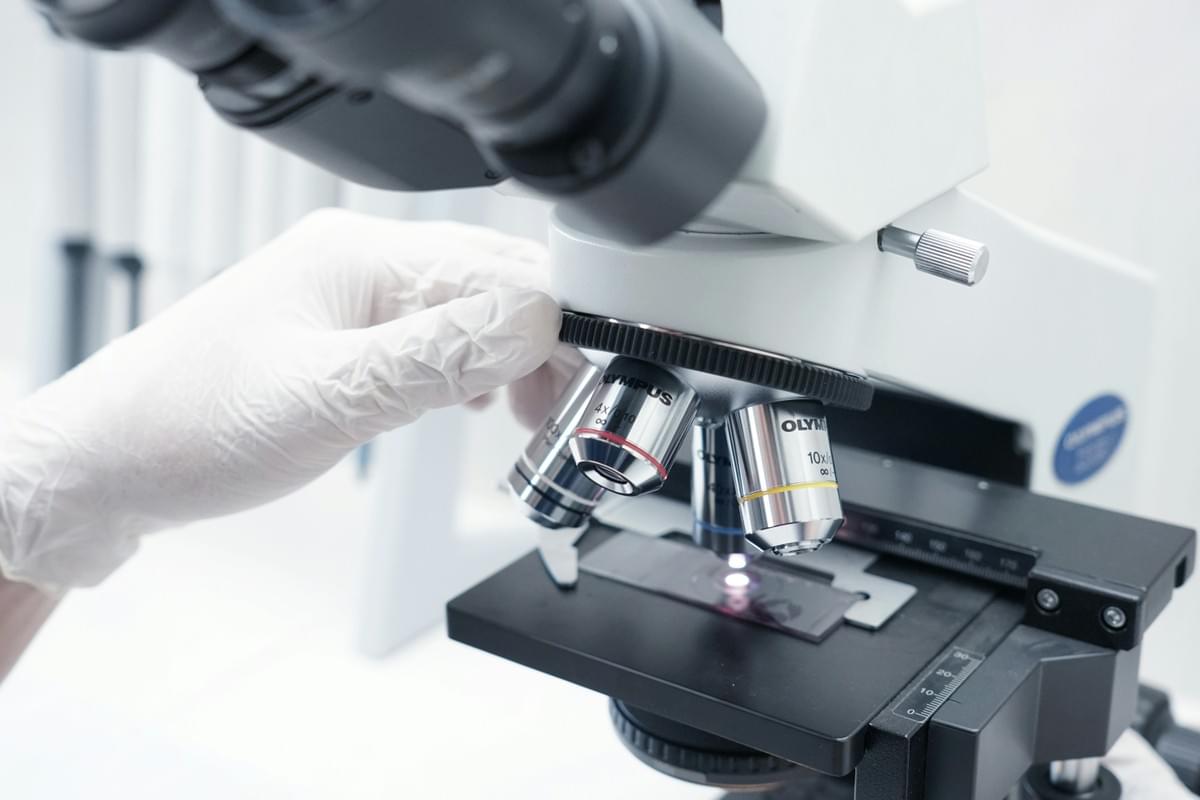

New Product Introduction (NPI) is a critical process in the manufacturing sector that involves bringing a new product to market. It encompasses everything from the initial concept and design phases to production and quality checks. Understanding what does NPI mean in manufacturing is essential for companies aiming to enhance their product offerings while maintaining high standards of quality.
Defining New Product Introduction (NPI)
At its core, NPI refers to the structured approach that organizations use to develop and launch new products. This process not only includes designing and engineering but also integrates testing of electronic components to ensure functionality and reliability. By defining what does quality check mean within the context of NPI, businesses can establish rigorous protocols that guarantee every aspect of the product meets industry standards.
Importance of NPI in Quality Assurance
The importance of NPI in quality assurance cannot be overstated; it serves as a backbone for ensuring that new products are developed with a focus on quality from day one. Effective NPI processes help identify potential issues early, reducing the risk of non-conformities later on, which ties back into understanding what is non-conformity report procedures. In addition, social compliance auditing during the NPI phase ensures that ethical standards are met throughout production, further solidifying trust with consumers.
NPI and Its Relationship with Quality Checks
NPI's relationship with quality checks is integral; these checks are embedded at various stages throughout the introduction process. By implementing visual inspection procedures alongside rigorous testing methods, manufacturers can ensure that they are producing goods that not only meet specifications but also exceed customer expectations for quality goods and services. Ultimately, understanding what does quality check mean in relation to NPI allows companies to streamline their processes while elevating their overall product standards.
Conclusion
Quality checks are the backbone of successful businesses, ensuring that products meet established standards and customer expectations. The phrase what does quality check mean encompasses a wide array of processes designed to maintain high standards throughout production. In an increasingly competitive market, neglecting quality checks can lead to significant losses and damaged reputations.
The Significance of Quality Checks in Business
Quality checks serve as a vital checkpoint in the production process, helping businesses avoid costly errors and maintain customer trust. By understanding what is a QC inspector's role, companies can appreciate how these professionals contribute to maintaining product integrity through rigorous testing protocols. Ultimately, effective quality assurance strategies not only enhance brand reputation but also foster loyalty among consumers.
Enhancing Production of Quality Goods and Services
Incorporating thorough testing of electronic components into the manufacturing process ensures that products function reliably and efficiently. With robust visual inspection procedures in place, manufacturers can identify defects early on, thus enhancing the overall production of quality goods and services. Additionally, social compliance auditing plays an essential role in verifying that ethical practices are upheld during production, further solidifying a company’s commitment to quality.
How China Inspection Pro Elevates Quality Standards
China Inspection Pro exemplifies how organizations can elevate their quality standards through meticulous processes tailored to various industries. By addressing what is non-conformity report findings promptly and effectively, they help clients navigate challenges associated with new product introduction (NPI). Their expertise not only clarifies what does NPI mean in manufacturing but also reinforces the importance of continuous improvement through consistent quality checks.
