Introduction
The inspection process is a crucial aspect of quality control that ensures products meet specific standards before reaching consumers. Understanding the 7 steps of the inspection process can significantly enhance efficiency and effectiveness, ultimately leading to higher customer satisfaction and reduced costs. By familiarizing yourself with each step—from Preparation and Planning to Reporting and Feedback—you can streamline operations and minimize errors.
Understanding the Inspection Process
At its core, the inspection process involves a systematic approach to evaluating products or services against predetermined criteria. The 7 steps of the inspection process include Preparation and Planning, Sampling, Visual Inspection, Functional Testing, Measurement and Specification Verification, Packaging and Labeling Review, and Reporting and Feedback. Each step serves a unique purpose in ensuring that every product meets quality standards before it reaches the market.
Importance of Each Step
Each step in the inspection process holds significant importance in maintaining product quality. For instance, Preparation and Planning sets the foundation by establishing clear objectives that guide subsequent actions. Likewise, Sampling ensures that inspections are representative of overall production quality, while Visual Inspection allows for immediate identification of defects—demonstrating how each phase contributes to a comprehensive evaluation.
How to Make It Easier
Simplifying the inspection process doesn't mean cutting corners; rather, it involves adopting best practices that enhance efficiency without compromising quality. Utilizing effective tools during Sampling or employing checklists during Visual Inspection can streamline tasks significantly. Additionally, investing time in thorough Reporting and Feedback can lead to continuous improvement across all 7 steps of the inspection process—making your job easier while ensuring top-notch results.
Preparation and Planning

Preparation and planning are the cornerstones of an effective inspection process. The 7 steps of the inspection process begin long before you ever set foot on-site; they start with a solid foundation built through careful foresight. By investing time in preparation, you can streamline your efforts in sampling, visual inspection, functional testing, measurement and specification verification, packaging and labeling review, and reporting and feedback.
Setting Clear Objectives
Setting clear objectives is crucial for guiding the entire inspection process. Without defined goals, it’s easy to get sidetracked or miss critical aspects during sampling or visual inspections. Establishing what success looks like at this stage will not only enhance focus but also ensure that all team members are aligned with the intended outcomes.
Gathering Necessary Documents
The next step involves gathering necessary documents that will support your inspection efforts. This includes specifications, previous reports, compliance guidelines, and any relevant regulatory information that could affect your findings during functional testing or measurement verification. Having these documents on hand will facilitate smoother communication within your team and aid comprehension during packaging and labeling review.
Assembling the Right Team
Assembling the right team is an essential part of preparation and planning that can make or break your inspection's success. Each member should bring specialized skills to the table—whether it’s expertise in sampling methods or experience in conducting thorough visual inspections. A well-rounded team ensures that all aspects of the 7 steps of the inspection process are covered effectively while fostering collaboration during reporting and feedback.
Sampling
Sampling is a pivotal stage in the 7 steps of the inspection process, acting as the bridge between preparation and actual evaluation. It helps ensure that inspections are both efficient and effective, allowing teams to focus on quality without overwhelming themselves with every single item. By mastering this phase, you set the groundwork for successful Visual Inspection, Functional Testing, Measurement and Specification Verification, Packaging and Labeling Review, and ultimately Reporting and Feedback.
Choosing the Right Sampling Method
Selecting an appropriate sampling method is crucial in ensuring that your inspection process yields reliable results. There are several methods available—random sampling, systematic sampling, or stratified sampling—each with its own advantages depending on your objectives. Understanding these methods allows you to tailor your approach based on factors like product type or production volume while aligning with the overall goal of thorough Preparation and Planning.
Determining Sample Size
Determining sample size can feel like trying to solve a Rubik's Cube blindfolded—tricky but essential! The right sample size balances accuracy with practicality; too small a sample might miss defects while too large can consume unnecessary resources during Visual Inspection. A well-calculated sample size not only enhances efficiency but also supports effective Functional Testing by ensuring that findings are statistically significant for Measurement and Specification Verification.
Ensuring Representative Samples
Ensuring that samples are representative is like casting actors for a movie—you want to capture the essence of the entire production! This means choosing samples that reflect variations in production conditions or product types to avoid skewed results during inspections. When done right, this step lays a solid foundation for all subsequent phases including Packaging and Labeling Review and ultimately leads to insightful Reporting and Feedback.
Visual Inspection

Visual inspection is a critical component of the 7 steps of the inspection process, serving as the first line of defense against defects and discrepancies. This step allows inspectors to identify issues that may not be immediately apparent through other methods. By honing in on visual cues, teams can effectively address potential problems before they escalate.
Key Elements to Observe
During visual inspection, there are several key elements that inspectors should carefully observe. First and foremost, the overall appearance of the product plays a significant role; any irregularities or inconsistencies can indicate deeper issues within the manufacturing process. Additionally, attention should be paid to specific features such as color, texture, and finish—all of which contribute to a product's quality and compliance with specifications outlined in earlier steps like Preparation and Planning.
Another crucial aspect is checking for alignment and assembly accuracy. Misalignment can lead to functional failures later on, which would necessitate further scrutiny during Functional Testing or Measurement and Specification Verification stages. Lastly, it’s essential to assess packaging integrity; after all, no one wants their pristine products arriving at customers' doors looking like they’ve been through a wrestling match!
Common Visual Defects
When conducting visual inspections, certain defects tend to pop up more frequently than others—these are your red flags! Some common visual defects include scratches on surfaces, incorrect color matching, or even missing components that could hinder performance down the line. These issues often stem from lapses in quality control during previous stages such as Sampling or Preparation and Planning.
Another prevalent concern is improper labeling or packaging that fails to meet industry standards; this not only affects aesthetics but also compliance with Packaging and Labeling Review requirements. Inspectors should also be vigilant for signs of wear or damage that may have occurred during transit—after all, what good is a flawless product if it arrives damaged? By identifying these common defects early on in the 7 steps of the inspection process, teams can save time and resources by addressing them promptly.
Utilizing Effective Checklists
To streamline visual inspections effectively, utilizing well-structured checklists is paramount! A comprehensive checklist serves as both a guide and a safeguard against overlooking critical aspects during this step of the 7 steps of the inspection process. It should encompass key elements observed earlier while also allowing room for notes on any defects encountered.
Incorporating feedback from previous inspections into your checklist enhances its effectiveness over time—this aligns beautifully with Reporting and Feedback principles discussed later in our outline! Furthermore, checklists help maintain consistency across different inspectors; when everyone follows the same criteria during their assessments (like those outlined in Sampling), you’ll achieve more reliable results.
Lastly—and perhaps most importantly—don’t forget to tailor your checklist based on specific products or industries! Customizing your approach ensures thoroughness while keeping efficiency at its best throughout each stage leading up to final approval.
Functional Testing
Functional testing is a critical step in the 7 steps of the inspection process, ensuring that products perform as intended before they reach consumers. By meticulously assessing functionality, businesses can identify potential issues that may not be visible during earlier stages like Visual Inspection or Sampling. This proactive approach not only enhances product quality but also builds trust with customers who rely on functionality for their satisfaction.
Defining Functionality Requirements
To effectively carry out functional testing, it’s essential to clearly define functionality requirements tailored to each product. These requirements set the benchmark against which all subsequent tests will be measured, ensuring alignment with customer expectations and regulatory standards. By doing so, companies can streamline Preparation and Planning efforts and focus on critical aspects that impact performance.
Testing Procedures Explained
Once functionality requirements are established, it's time to dive into testing procedures that will put those requirements to the test. This involves a series of structured methods designed to evaluate whether a product meets its specified criteria under various conditions. From stress tests to usability assessments, these procedures provide invaluable insights into how well a product performs in real-world scenarios and help highlight any shortcomings identified during earlier steps like Measurement and Specification Verification.
Documenting Results Effectively
After conducting functional tests, documenting results effectively is paramount for future reference and continuous improvement. Comprehensive documentation captures key findings, anomalies, and overall performance metrics that inform both immediate actions and long-term strategies within the 7 steps of the inspection process. By maintaining clear records throughout all stages—including Reporting and Feedback—companies can ensure accountability and foster an environment of transparency for stakeholders involved.
Measurement and Specification Verification
Measurement and specification verification is a pivotal step in the 7 steps of the inspection process, ensuring that products meet exact standards. Accurate measurements are crucial not only for quality assurance but also for compliance with regulatory requirements. By focusing on this step, businesses can avoid costly rework and enhance customer satisfaction.
Importance of Accurate Measurements
Accurate measurements serve as the backbone of effective quality control in the inspection process. When products are measured correctly, it ensures that they meet design specifications and functional requirements, which directly impacts performance and safety. Inadequate measurement practices can lead to discrepancies that may compromise product integrity, making this step critical in Preparation and Planning.
Moreover, accurate measurements help identify potential defects early in the Sampling phase, allowing teams to address issues before they escalate. This proactive approach reduces waste during Visual Inspection by minimizing the number of defective items identified later on. Ultimately, ensuring precise measurements fosters trust between manufacturers and consumers while reinforcing brand reputation.
Tools and Techniques Used
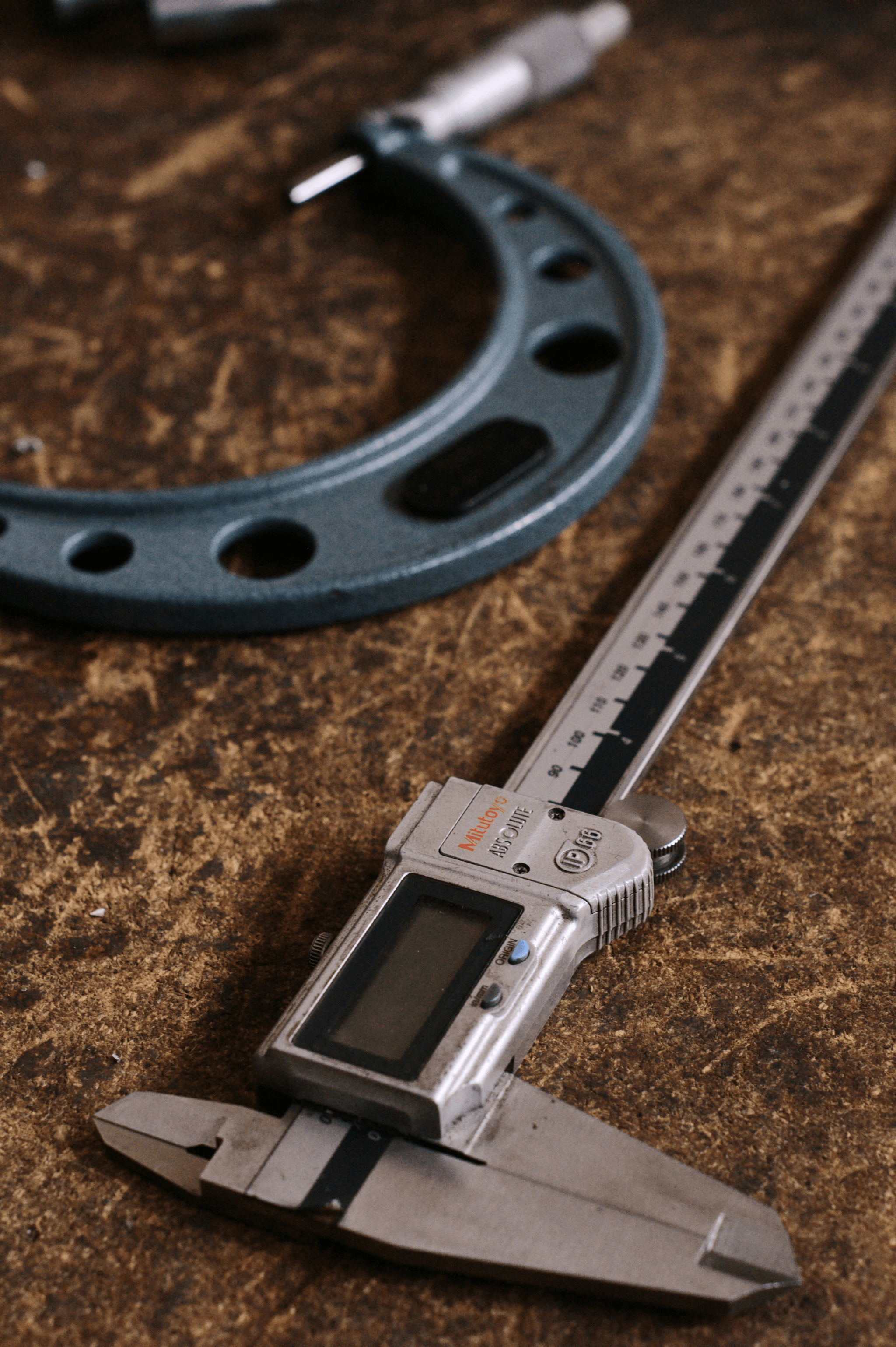
To achieve accuracy in measurement during the inspection process, various tools and techniques come into play. Calipers, micrometers, gauges, and laser measuring devices are commonly employed to obtain precise readings across different dimensions. Each tool serves a specific purpose; for instance, calipers excel at measuring internal dimensions while micrometers offer higher precision for smaller parts.
In addition to traditional tools, digital measuring instruments have gained popularity due to their ease of use and accuracy enhancements. Techniques like statistical process control (SPC) can also be utilized to monitor measurement data over time for consistency across multiple production runs. Integrating these tools effectively supports each stage of Measurement and Specification Verification within the broader context of Functional Testing.
Cross-Referencing Specifications
Cross-referencing specifications is an essential technique that complements accurate measurements throughout the inspection process. It involves comparing measured values against predefined standards or regulatory guidelines to ensure compliance with industry norms during Packaging and Labeling Review as well as Reporting and Feedback phases. This meticulous attention to detail helps identify any deviations from expected results early on.
By cross-referencing specifications at this stage, teams can pinpoint areas needing improvement or adjustment before finalizing products for market release or distribution channels. This practice not only enhances product reliability but also streamlines communication among team members involved in Preparation and Planning stages by creating a clear framework for quality expectations across all 7 steps of the inspection process.
Finally, effective cross-referencing lays a solid foundation for subsequent inspections by providing valuable insights into trends over time—an invaluable resource when conducting future Sampling or Visual Inspection activities.
Packaging and Labeling Review
When it comes to the 7 steps of the inspection process, packaging and labeling review is a critical phase that can make or break product compliance. This step ensures that all products are not only well-protected during transit but also clearly communicate essential information to consumers and retailers alike. Neglecting this part can lead to misunderstandings, product returns, or even safety issues that could have been easily avoided.
Ensuring Compliance with Standards
Compliance with industry standards is paramount in packaging and labeling review. Regulatory bodies often set specific guidelines that products must meet before they can be sold, including safety warnings, ingredient lists, and handling instructions. By adhering to these standards, companies not only avoid potential legal issues but also build trust with their customers.
To ensure compliance effectively, it's crucial to integrate this review into the earlier stages of the inspection process—specifically during Preparation and Planning. This proactive approach helps identify any gaps in documentation or product requirements early on, thereby streamlining subsequent steps like Sampling and Visual Inspection. Remember, a well-prepared package speaks volumes about your brand's commitment to quality.
Importance of Clear Labeling
Clear labeling is more than just a nice-to-have; it's an essential aspect of effective communication between manufacturers and consumers. Labels should provide concise information about the product's contents, usage instructions, expiration dates, and any relevant certifications or warnings. If consumers can't easily understand what they're buying or how to use it safely, you're setting yourself up for dissatisfaction—or worse.
Moreover, clear labeling plays a significant role in enhancing customer confidence during Functional Testing phases as well as after purchase when they rely on accurate information for proper usage. In today's fast-paced market where consumers are bombarded with choices, having clear labels can differentiate your product from competitors who may overlook this important detail during their packaging processes.
Common Packaging Issues
Despite best efforts in the 7 steps of the inspection process—including Packaging and Labeling Review—common issues often arise that can compromise product integrity or consumer satisfaction. One frequent problem is inadequate sealing which may lead to contamination or spoilage; another issue might be improper labeling where essential information is missing or unclear.
These common pitfalls highlight why thorough Measurement and Specification Verification should precede final packaging decisions; ensuring that dimensions align with standards can prevent many headaches later on in the process. Additionally, conducting regular audits during Visual Inspection allows teams to catch these errors early before products hit store shelves or shipping docks—saving time and resources down the line.
In conclusion, incorporating a meticulous approach towards Packaging and Labeling Review within the broader framework of the inspection process not only enhances compliance but also elevates customer experience through clarity and reliability.
Reporting and Feedback
In the realm of inspections, the significance of reporting and feedback cannot be overstated. It serves as the bridge between the inspection process and actionable insights, ensuring that all stakeholders are on the same page regarding findings and recommendations. By mastering this crucial step, you can enhance the overall effectiveness of the 7 steps of the inspection process.
Creating Comprehensive Reports
Creating comprehensive reports is essential for documenting each phase of the inspection process, from Preparation and Planning to Packaging and Labeling Review. A well-structured report should summarize findings from Sampling, Visual Inspection, Functional Testing, Measurement and Specification Verification, and any other relevant steps taken during inspections. Including clear visuals, data points, and a summary of key issues helps stakeholders understand not just what was found but also why it matters.
Moreover, these reports should be tailored to their audience; technical jargon may be appropriate for engineers but could confuse management or clients. When crafting your report, ensure that it highlights both successes in compliance as well as areas needing improvement. This balanced approach fosters an environment where continuous improvement can thrive throughout all 7 steps of the inspection process.
Providing Constructive Feedback
Constructive feedback is a vital component in closing the loop on inspections; it's not just about identifying problems but also about offering solutions for remediation. After completing each step—Sampling through Reporting and Feedback—it's critical to communicate findings clearly so that teams can take appropriate action based on your insights. Remember to focus on behaviors or processes rather than personal attributes to cultivate a positive atmosphere for growth.
Effective feedback should encourage an open dialogue among team members involved in each phase of the inspection process. This collaborative effort ensures that everyone understands their role in addressing issues identified during Visual Inspection or Functional Testing phases specifically. When everyone feels empowered to contribute solutions based on constructive critiques, it enhances teamwork throughout every aspect of your operations.
Importance of Follow-Up
The importance of follow-up cannot be overlooked when discussing Reporting and Feedback within the 7 steps of the inspection process; it's where accountability meets action! Following up on reported issues ensures they are addressed promptly rather than falling into a black hole after initial discussions. Establishing timelines for resolving identified concerns keeps everyone focused on achieving compliance across all stages—from Measurement and Specification Verification to Packaging and Labeling Review.
Moreover, follow-ups provide an opportunity to assess whether implemented changes have effectively resolved previous issues or if further adjustments are necessary. This ongoing evaluation reinforces a culture dedicated to quality assurance throughout every part of your operation while fostering trust among team members involved in various phases like Sampling or Functional Testing processes alike. Ultimately, effective follow-up solidifies improvements made during inspections while paving the way for future successes.
Conclusion

In conclusion, the inspection process is a well-orchestrated symphony of various steps, each playing a crucial role in ensuring quality and compliance. The 7 steps of the inspection process—Preparation and Planning, Sampling, Visual Inspection, Functional Testing, Measurement and Specification Verification, Packaging and Labeling Review, and Reporting and Feedback—work together to create a robust framework that guarantees satisfactory outcomes. Neglecting any step could lead to oversight and potential pitfalls; therefore, understanding each component's significance is paramount.
The Role of Each Step in Success
Each step in the 7 steps of the inspection process contributes uniquely to the overall success of an inspection endeavor. Preparation and Planning set the stage for effective execution by establishing clear objectives and assembling a capable team. Following this foundation with Sampling ensures that results are representative, while Visual Inspection identifies defects before they escalate into larger issues. Functional Testing confirms that products meet their intended use, whereas Measurement and Specification Verification solidifies compliance with industry standards.
Streamlining the Inspection Process
Streamlining the inspection process can significantly enhance efficiency without sacrificing quality or thoroughness. By refining Preparation and Planning efforts to include precise objectives and necessary documents upfront, teams can minimize delays later on. Optimizing Sampling methods ensures that resources are used wisely while maintaining accuracy during Visual Inspection phases; this leads to quicker identification of issues during Functional Testing and Measurement Verification stages.
How China Inspection Pro Can Help
China Inspection Pro offers invaluable support throughout all 7 steps of the inspection process by providing expert guidance tailored to your specific needs. With their extensive experience in Preparation and Planning as well as effective Sampling strategies, they help ensure no detail goes unnoticed during Visual Inspections or Functional Testing procedures. Moreover, their expertise extends to Packaging and Labeling Review as well as comprehensive Reporting and Feedback mechanisms that foster continuous improvement within your organization.
