Introduction
In today’s competitive business landscape, the quality control method serves as a cornerstone for maintaining excellence in products and services. Quality assurance is not just a buzzword; it’s an essential practice that ensures customer satisfaction and operational efficiency. Understanding how quality control integrates with overall business strategies is crucial for any organization aiming to thrive.
Understanding the Quality Control Method
The quality control method encompasses a variety of practices designed to monitor and maintain the quality of products throughout their lifecycle. By implementing effective QC quality control measures, businesses can identify defects early in the production process, minimizing waste and enhancing productivity. This proactive approach not only safeguards product integrity but also fosters a culture of continuous improvement within organizations.
Importance of Quality Assurance in Business
Quality assurance plays a vital role in establishing trust between businesses and their customers, ensuring that products meet established standards consistently. When companies prioritize QA quality practices, they are more likely to see increased customer loyalty and reduced costs associated with returns or rework. In essence, investing in quality and assurance translates into long-term sustainability and profitability for any enterprise.
Overview of Quality Control Systems
Quality control systems are structured frameworks that help organizations implement their QC quality control strategies effectively. These systems encompass various methodologies—ranging from statistical process controls to comprehensive QMS systems—that guide businesses in monitoring performance metrics over time. By adopting robust quality control systems, companies can ensure compliance with industry standards while continuously improving their processes.
The Foundation of Quality Control

Quality control is the backbone of any successful business operation, ensuring that products and services meet specific standards. This section will delve into the fundamental concepts that underpin quality control methods, emphasizing the critical relationship between quality assurance (QA) and quality control (QC). By establishing a solid foundation in these principles, organizations can effectively implement robust QMS systems to enhance their operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Key Definitions in Quality Control
To truly grasp quality control methods, one must first understand some key definitions. Quality control refers to the systematic process of ensuring that products or services meet predefined standards through monitoring and testing. In contrast, quality assurance focuses on preventing defects by improving processes before they occur, thereby enhancing overall quality and assurance in production.
When we talk about QC in a business context, it typically involves activities like inspections, testing, and audits aimed at identifying defects or inconsistencies in products. These activities are crucial for maintaining high-quality standards while minimizing waste and maximizing efficiency. In essence, mastering these key definitions lays the groundwork for effective implementation of both QA and QC practices.
Role of Quality Assurance in QC
Quality assurance plays a pivotal role within the realm of quality control by establishing guidelines that help maintain product integrity throughout production processes. While QC focuses on identifying defects after they occur, QA ensures that those defects are less likely to happen in the first place. This proactive approach not only boosts confidence in product reliability but also enhances customer satisfaction—an essential goal for any business striving for excellence.
The interplay between QA and QC creates a comprehensive framework where continuous improvement is possible; as businesses refine their processes through QA initiatives, they simultaneously strengthen their QC measures. This symbiotic relationship fosters an environment where both quality control methods can thrive harmoniously to produce superior outcomes. Therefore, understanding this role is vital for anyone involved in managing or implementing QMS systems.
Types of Quality Control Methods
There are various types of quality control methods employed by organizations to ensure consistent product output and service delivery. Some widely recognized techniques include Statistical Process Control (SPC), which utilizes statistical tools to monitor processes; Six Sigma methodologies aimed at reducing variability; and Total Quality Management (TQM), which emphasizes continuous improvement across all levels of an organization.
Each method offers unique benefits tailored to different operational needs while sharing common goals: improving efficiency, minimizing waste, and enhancing customer satisfaction through reliable products or services. By selecting appropriate QC methods based on specific industry requirements or challenges faced during production cycles, businesses can create effective strategies that align with their overall objectives related to quality assurance.
In summary, understanding these foundational aspects—key definitions within quality control frameworks; the indispensable role played by QA; along with various types of QC methods—equips organizations with valuable insights necessary for achieving high-quality outcomes consistently.
Quality Control vs. Quality Assurance

In the realm of business, understanding the distinction between quality control (QC) and quality assurance (QA) is crucial for effective management. While both are essential components of a robust quality management system (QMS), they serve different purposes and functions. Quality control focuses on identifying defects in the final products, while quality assurance emphasizes preventing defects throughout the entire production process.
Distinguishing Features of QC and QA
Quality control methods primarily involve testing and inspection to ensure that products meet predefined standards before they reach consumers. This reactive approach is about catching errors after they've occurred, making it a vital part of any QC quality control strategy. On the other hand, quality assurance takes a proactive stance; it involves systematic processes designed to enhance product development and reduce the likelihood of defects occurring in the first place.
The key difference lies in their focus: QC is product-centric, dealing with outputs, while QA is process-centric, focusing on inputs and workflows that lead to those outputs. Understanding these distinctions helps businesses implement effective strategies for both QA quality initiatives and QC methods within their operations. Ultimately, both elements are necessary for achieving high levels of customer satisfaction through consistent delivery of quality products.
How They Complement Each Other
Despite their differences, quality control and quality assurance work hand-in-hand to ensure excellence in production processes. While QA sets up frameworks that aim to prevent issues from arising, QC provides feedback on how effectively those frameworks are working by identifying any flaws or inconsistencies in finished products. This synergy allows organizations to refine their QMS systems continually while also ensuring that end products meet customer expectations.
Moreover, integrating both approaches can lead to significant improvements in overall operational efficiency. For example, when a company implements rigorous QA practices but neglects QC methods, it may find itself producing high-quality items that still fail due to unforeseen defects caught too late in the process. Conversely, relying solely on QC without a solid foundation of QA can result in costly recalls or dissatisfied customers—neither desirable outcomes for any business aiming for success.
Real-world Applications of Quality Control
In practice, many industries leverage both quality control and assurance methods to enhance their operations significantly. For instance, manufacturing companies often employ statistical process control as part of their QC strategy to monitor production processes continuously and identify variances before they escalate into larger problems—this exemplifies an effective use of a quality control method within a comprehensive QMS framework.
Similarly, software development teams utilize QA practices like continuous integration testing alongside traditional QC measures such as user acceptance testing (UAT). This dual approach ensures not only that software meets functional requirements but also adheres to performance benchmarks set by stakeholders—demonstrating how intertwining these two aspects can lead to superior outcomes across diverse sectors.
Ultimately, whether you're talking about automotive manufacturing or tech start-ups looking at qa quality initiatives—the interplay between these two disciplines remains pivotal for driving improvements across all facets of business operations.
Proven Quality Control Methods
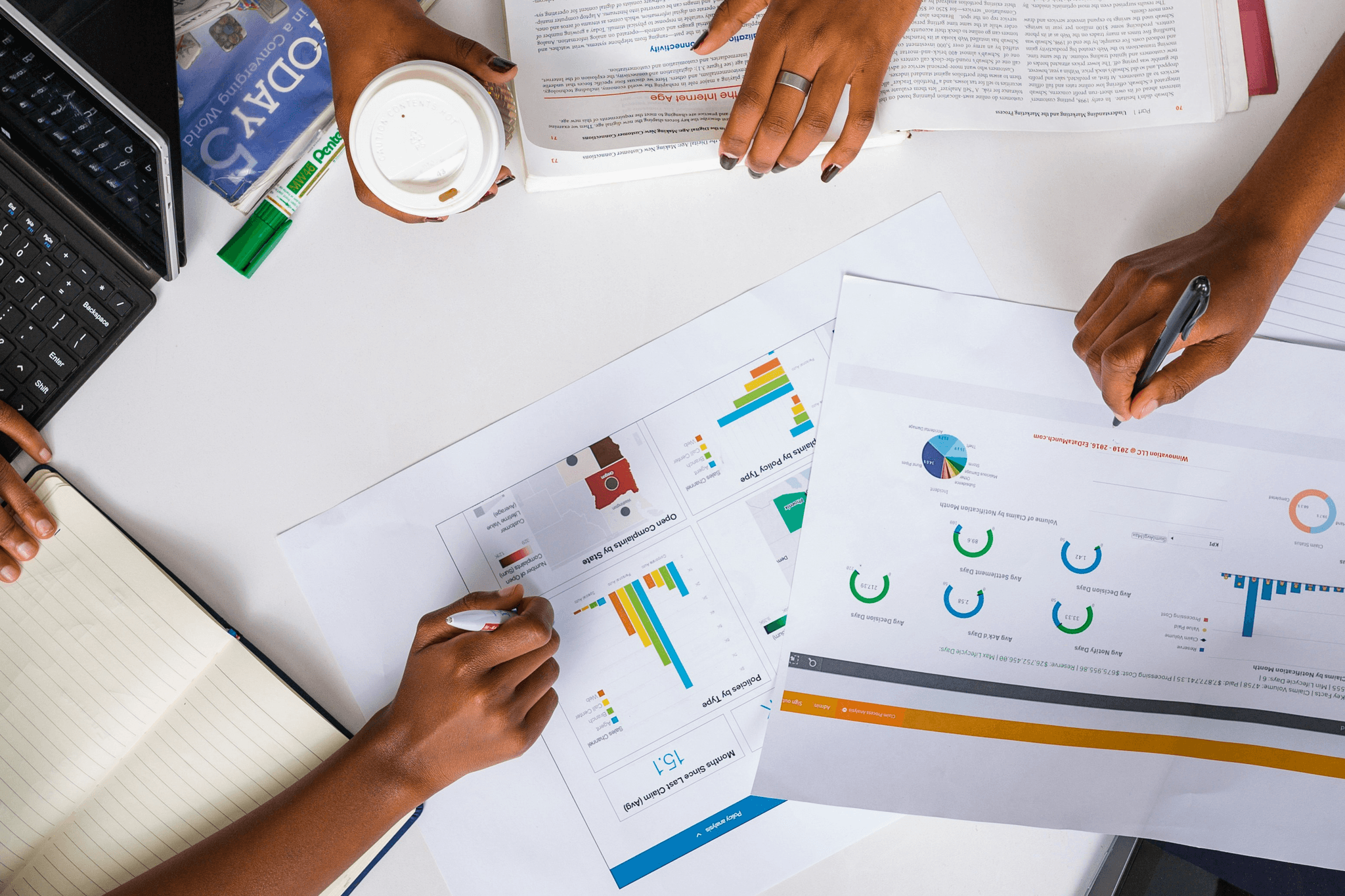

In the realm of quality control, several methods have emerged as champions in ensuring that products and services meet the highest standards. These proven quality control methods not only enhance product reliability but also fortify customer trust through effective quality assurance practices. Understanding these methodologies is crucial for any business aiming to implement robust quality management systems (QMS systems) that stand the test of time.
Statistical Process Control Explained
Statistical Process Control (SPC) is a powerful quality control method that employs statistical techniques to monitor and control processes. By utilizing control charts, businesses can visualize process variations in real-time, allowing them to identify issues before they escalate into significant problems. This proactive approach ensures that quality assurance remains at the forefront of operations, leading to improved efficiency and reduced waste.
SPC focuses on understanding process behavior rather than merely inspecting finished products, which enhances overall quality and assurance in production lines. By analyzing data trends over time, organizations can make informed decisions about process adjustments, ultimately fostering a culture of continuous improvement within their QMS systems. The beauty of SPC lies in its ability to transform data into actionable insights, making it an essential tool for any serious QC quality control initiative.
Six Sigma Methodology Overview
Six Sigma is another highly regarded methodology that emphasizes reducing defects and improving overall process performance through a disciplined approach. This data-driven strategy utilizes specific tools and techniques to identify root causes of problems and eliminate variations in processes—essentially striving for near perfection in every output. As a result, Six Sigma not only enhances product quality but also significantly boosts customer satisfaction levels by ensuring consistent delivery of high-quality goods.
The core principle behind Six Sigma revolves around its DMAIC framework: Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control. This structured approach allows organizations to systematically address issues while integrating effective QA quality practices into their daily operations. By adopting Six Sigma principles within their QMS systems, companies can achieve remarkable enhancements in both efficiency and effectiveness across various departments.
Total Quality Management Essentials
Total Quality Management (TQM) encapsulates a holistic approach towards improving organizational processes through ongoing refinement across all departments—from production to customer service. At its heart lies the belief that every employee plays an integral role in achieving high-quality standards; thus fostering teamwork becomes paramount for success in this philosophy. TQM emphasizes continuous improvement as well as strong leadership commitment to cultivate an environment where quality and assurance are prioritized at every level.
Implementing TQM requires establishing clear objectives aligned with overall business goals while ensuring rigorous training on best practices related to QC quality control methods throughout the organization. With consistent focus on customer needs coupled with employee engagement initiatives, companies can create a culture centered around excellence—one where everyone feels responsible for maintaining high standards of output. In this way, TQM serves not only as a strategy but also as a mindset that drives sustainable success within any QMS system.
Implementing Quality Control Systems
Implementing effective quality control systems is a critical step in ensuring that products and services meet the desired standards of quality and assurance. A well-structured Quality Management System (QMS) not only enhances operational efficiency but also fosters a culture of continuous improvement within an organization. By focusing on the right quality control methods, businesses can significantly reduce defects, increase customer satisfaction, and ultimately boost profitability.
Setting up QMS Systems for Success
Setting up QMS systems for success requires a clear understanding of both quality control and quality assurance principles. First, organizations must define their quality objectives and align them with overall business goals to ensure that all stakeholders are on the same page regarding expectations. Next, it’s essential to select appropriate quality control methods tailored to specific processes or products, ensuring that the chosen QC quality control practices are integrated seamlessly into daily operations.
Additionally, training employees in these methods is vital for fostering a culture of quality and assurance throughout the organization. By empowering team members with knowledge about effective QA practices, businesses can enhance their ability to identify issues early on and implement corrective actions swiftly. Finally, regular monitoring and evaluation of the QMS systems will help organizations adapt to changing market conditions while maintaining high standards in their products or services.
Challenges in Quality Control Implementation
While implementing quality control can yield significant benefits, several challenges may arise during this process that organizations must navigate effectively. One common hurdle is resistance to change from employees who may be accustomed to existing processes; overcoming this requires strong leadership and clear communication about the importance of adopting new QC methods for overall success. Moreover, integrating various aspects of quality assurance into a cohesive system can be complex, particularly in larger organizations with diverse product lines or service offerings.
Another challenge lies in maintaining consistency across different departments or teams when implementing QC practices; without proper training and resources, variations in how these methods are applied could lead to discrepancies in product or service quality. Additionally, companies may struggle with data management when monitoring performance metrics related to their QMS systems; investing in technology solutions can help streamline data collection and analysis processes while facilitating timely decision-making based on insights gained from these metrics.
Best Practices for Effective Quality Management
To achieve effective quality management through robust QMS systems, adopting certain best practices is essential for long-term success. Firstly, establishing clear communication channels among team members ensures everyone understands their roles within the framework of both QA quality initiatives and general organizational goals related to product excellence. This collaborative approach promotes accountability while fostering an environment where feedback is valued—ultimately leading to improved performance across all functions involved in delivering high-quality outputs.
Secondly, continuous training programs should be implemented regularly so employees remain updated on evolving industry standards as well as innovative QC techniques that could enhance productivity levels further down the line. Emphasizing ongoing education reinforces commitment towards achieving excellence through consistent application of proven methodologies like Six Sigma or Total Quality Management (TQM). Lastly—and perhaps most importantly—organizations must cultivate a mindset focused on proactive problem-solving rather than reactive measures; prioritizing prevention over correction allows businesses not only to minimize defects but also create lasting value through superior customer experiences driven by unwavering dedication towards maintaining exceptional standards throughout every stage involved within their supply chains.
Case Studies in Quality Control

Examining real-world applications of quality control methods reveals how companies can effectively implement quality assurance practices to enhance their operations. The case studies presented here illustrate the profound impact of robust QC and QA systems on business success. From automotive giants to tech innovators, these examples highlight the importance of integrating quality and assurance into everyday processes.
Success Story: Toyota Production System
The Toyota Production System (TPS) is a hallmark example of effective quality control methods in action. Renowned for its focus on efficiency, TPS emphasizes continuous improvement (Kaizen) and waste reduction, ensuring that every aspect of production adheres to stringent quality standards. This commitment to quality control has not only set Toyota apart in the automotive industry but has also become a benchmark for implementing QMS systems globally.
At the heart of TPS lies a strong emphasis on employee involvement in the QC process, empowering workers to identify issues and suggest improvements. This participatory approach fosters a culture where quality assurance is everyone's responsibility, leading to higher product reliability and customer satisfaction. By prioritizing both quality control and assurance, Toyota has consistently delivered vehicles that meet rigorous standards while maintaining operational excellence.
Lessons from Apple’s Quality Assurance
Apple Inc.'s approach to QA quality is another exemplary case worth exploring. The tech giant is known for its meticulous attention to detail throughout its product development lifecycle, which includes rigorous testing phases aimed at ensuring high-quality outputs. Apple's commitment to a seamless user experience reflects its understanding that effective quality control methods are crucial for maintaining brand loyalty and market leadership.
One key lesson from Apple’s strategy is the integration of feedback loops within their QMS systems, allowing them to adapt quickly based on user experiences and technological advancements. This proactive stance ensures that any potential issues are addressed before they escalate into larger problems affecting customers worldwide. Ultimately, Apple's success underscores how combining innovative design with robust QC practices can lead to superior products that resonate with consumers.
China Inspection Pro’s Approach to Quality
China Inspection Pro exemplifies an organization dedicated solely to enhancing product quality through comprehensive inspection services tailored for various industries. Their focus on implementing advanced QC methodologies ensures that manufacturers adhere strictly to international standards while minimizing defects in production processes. By leveraging technology alongside traditional inspection techniques, they provide valuable insights into areas needing improvement within clients' QMS systems.
What sets China Inspection Pro apart is their commitment to educating clients about effective QA protocols as part of their service offerings. They emphasize not just identifying faults but also instilling best practices within organizations' existing frameworks—ensuring long-term adherence to both quality control and assurance principles across supply chains. Their holistic approach demonstrates how critical it is for businesses operating in competitive environments to prioritize ongoing education about efficient QC strategies.
Conclusion
In wrapping up our exploration of quality control methods and their indispensable role in business, we find ourselves at a pivotal moment where innovation and tradition intersect. Quality assurance (QA) is evolving, adapting to the needs of modern industries while retaining its core principles. As we look ahead, the future of quality control is not just about maintaining standards but also about embracing new technologies that enhance efficiency and effectiveness.
The Future of Quality Control Methods
The future of quality control methods is bright, marked by a shift towards automation and data-driven decision-making. With advancements in artificial intelligence and machine learning, QC quality control processes are becoming more precise and less prone to human error. Companies are increasingly investing in QMS systems that integrate these technologies to streamline operations and improve overall product quality.
As businesses strive for excellence, they will likely adopt more agile methodologies that allow for real-time feedback and continuous improvement in their quality assurance practices. This means that the traditional concepts of quality control will evolve into dynamic frameworks capable of responding swiftly to market demands. Ultimately, organizations that embrace these changes will lead the charge in setting new benchmarks for quality.
Innovations in Quality Assurance Practices
Innovations in quality assurance practices are reshaping how companies approach their QC strategies. The rise of cloud-based QMS systems allows teams to collaborate seamlessly across locations, ensuring consistent implementation of QA protocols regardless of geography. Moreover, the integration of big data analytics enables businesses to predict potential issues before they arise, enhancing proactive measures within their QC framework.
Another exciting development is the growing emphasis on sustainability within quality assurance practices. Companies are now prioritizing eco-friendly materials and processes as part of their commitment to both product integrity and environmental responsibility. By aligning QA with sustainability goals, organizations can not only improve their brand image but also contribute positively to global efforts against climate change.
Final Thoughts on Quality and Assurance
In conclusion, the interplay between quality control and assurance is crucial for any business aiming for long-term success. The relationship between these two elements ensures not only compliance with industry standards but also fosters a culture dedicated to excellence throughout an organization’s operations. As we continue to innovate within this space, it’s essential that companies remain committed to both maintaining high-quality standards while exploring new avenues for improvement.
Quality control methods will always be integral to business success; however, they must adapt alongside emerging trends in technology and consumer expectations. By prioritizing robust QA practices alongside effective QC strategies, businesses can navigate challenges while delivering exceptional products or services consistently. In this ever-evolving landscape, embracing change while holding onto foundational principles will ensure a bright future for both quality control and assurance alike.
