Introduction

In the realm of manufacturing, a comprehensive understanding of factory audit components is essential for ensuring product quality and compliance. Quality control serves as the backbone of effective audits, guiding manufacturers in implementing robust systems that uphold standards throughout production processes. Furthermore, grasping the nuances of Good Manufacturing Processes (GMP) certification is crucial for organizations striving to achieve excellence and maintain market competitiveness.
Essential Factory Audit Components
Factory audit components encompass a variety of elements that collectively contribute to a successful quality inspection process. These components include documentation review, on-site evaluations, and adherence to established protocols that ensure compliance with industry standards. By focusing on these integral parts, companies can identify areas for improvement and mitigate risks associated with subpar manufacturing practices.
Importance of Quality Control in Audits
Quality control plays a pivotal role in audits by establishing benchmarks against which products are measured and assessed. Without rigorous quality inspection protocols, organizations risk producing defective goods that could lead to customer dissatisfaction or regulatory penalties. By prioritizing quality control during audits, manufacturers can foster a culture of continuous improvement and innovation while safeguarding their reputation in the marketplace.
Understanding GMP Certification
Understanding GMP certification is vital for businesses aiming to streamline their operations while adhering to industry regulations. This certification assures stakeholders that the manufacturer follows stringent guidelines related to production processes, cleanliness, and employee training—factors critical for maintaining product integrity. Ultimately, obtaining GMP certification not only enhances credibility but also serves as a competitive advantage within an increasingly regulated landscape.
Quality Control in Factory Audits
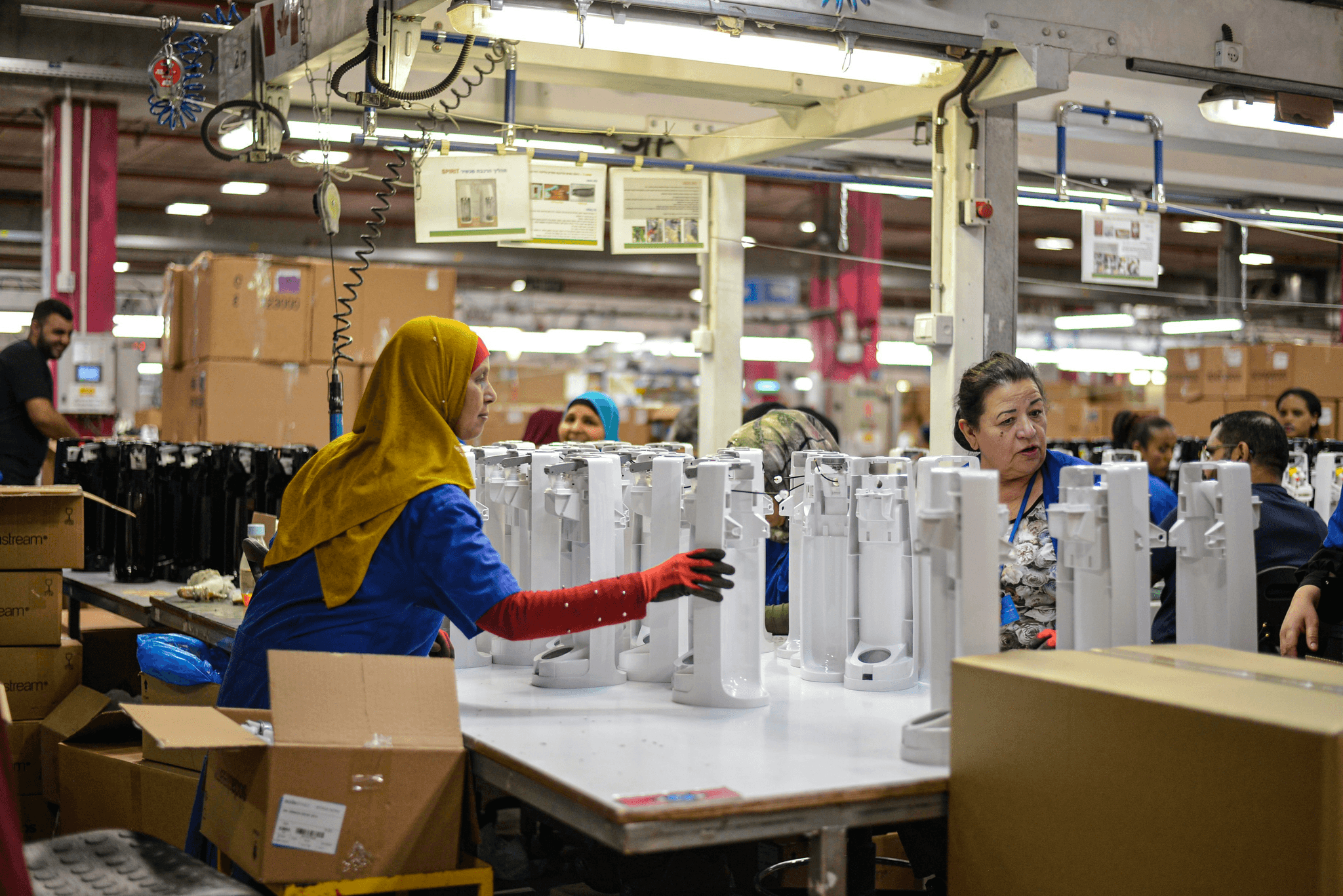

Quality control is the backbone of manufacturing, ensuring that products meet established standards and specifications. In the context of factory audits, quality control plays a pivotal role in identifying discrepancies and areas for improvement. By focusing on essential factory audit components, manufacturers can enhance product quality and maintain compliance with industry regulations.
Role of Quality Control in Manufacturing
Quality control is integral to the manufacturing process, serving as a safeguard against defects and inefficiencies. It involves systematic monitoring and evaluation of various production stages to ensure adherence to good manufacturing processes (GMP). By implementing robust quality control measures, manufacturers can not only improve product reliability but also foster customer trust and satisfaction.
In a typical factory audit, quality control mechanisms are assessed to determine their effectiveness in maintaining product standards. This includes evaluating inspection protocols, testing methods, and employee training programs that ensure compliance with GMP certification requirements. Ultimately, a strong quality control framework contributes significantly to reducing waste and optimizing operational efficiency.
Key Quality Control Metrics
To gauge the effectiveness of quality control processes during factory audits, it’s essential to track specific metrics that provide insight into performance levels. Common key performance indicators (KPIs) include defect rates, yield percentages, and customer complaints—each offering valuable information about product quality over time. By regularly monitoring these metrics, manufacturers can identify trends that inform necessary adjustments in their production practices.
Another vital metric is first-pass yield (FPY), which measures the percentage of products manufactured correctly without rework or defects on the first attempt. High FPY indicates effective quality inspection processes aligned with GMP standards; conversely, low FPY may signal underlying issues requiring immediate attention during audits. Additionally, tracking non-conformance reports allows organizations to address recurring problems proactively.
Best Practices for Quality Inspection
Implementing best practices for quality inspection is crucial for any manufacturer aiming for excellence in their output while adhering to GMP certification standards. One effective approach is adopting a risk-based inspection strategy that prioritizes high-risk areas or products based on historical data or potential impact on safety and efficacy. This targeted focus enables more efficient use of resources during factory audits.
Moreover, leveraging technology such as automated inspection systems can significantly enhance accuracy while minimizing human error during inspections. Utilizing tools like statistical process control (SPC) helps monitor production processes continuously and provides real-time data analysis for informed decision-making regarding quality improvements. Finally, regular training sessions for employees involved in inspections ensure they remain knowledgeable about current best practices related to both quality control and GMP compliance.
Good Manufacturing Processes and Compliance

In the realm of manufacturing, Good Manufacturing Processes (GMP) serve as the backbone for ensuring product quality and safety. These processes encompass a set of guidelines and practices designed to minimize risks involved in production, which is crucial when assessing factory audit components. By adhering to these standards, manufacturers can significantly enhance their quality control measures and establish a solid foundation for successful audits.
Overview of Good Manufacturing Processes
Good Manufacturing Processes are systematic practices that ensure products are consistently produced and controlled according to quality standards. This includes everything from raw material sourcing to final product inspections, emphasizing the importance of quality inspection at every stage. By implementing GMP, factories can streamline operations while minimizing errors that could compromise product integrity.
The essence of GMP lies in its comprehensive approach—covering equipment maintenance, employee training, sanitation procedures, and documentation practices. Each element plays a vital role in maintaining high-quality production standards and ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements. Thus, understanding GMP is essential for any organization aiming to excel in factory audits.
Benefits of Adhering to GMP Standards
Adhering to GMP standards offers numerous benefits that extend beyond mere compliance; it fosters a culture of quality control within organizations. When factories implement these processes diligently, they reduce the likelihood of defects or contamination in their products, leading to increased customer satisfaction and trust. Moreover, consistent adherence to GMP can yield significant cost savings by minimizing waste and rework associated with poor-quality products.
Another advantage is enhanced marketability; companies boasting GMP certification often find it easier to enter new markets or secure contracts with discerning clients who prioritize safety and quality assurance. Additionally, such compliance not only prepares businesses for rigorous factory audits but also boosts their reputation as reliable manufacturers committed to excellence. In today's competitive landscape, investing in good manufacturing processes is not just beneficial—it's essential.
How GMP Certification Affects Audits
GMP certification profoundly impacts how factory audits are conducted by establishing a clear framework against which performance can be measured. With certified processes in place, auditors can focus their attention on verifying compliance rather than identifying fundamental flaws within the manufacturing system itself—a significant time-saver during inspections. This allows for more thorough evaluations of other critical factory audit components like operational efficiency and employee training programs.
Furthermore, holding a valid GMP certification signals a commitment to high-quality production practices that resonate well with auditors; it reflects an organization’s proactive stance towards maintaining industry standards and regulations. Consequently, this leads not only to smoother audit experiences but also potentially favorable outcomes during assessments—like reduced scrutiny or expedited review times due to demonstrated reliability in operations.
In summary, embracing good manufacturing processes through effective adherence can transform how businesses approach both production quality and regulatory compliance during factory audits.
Effective Quality Inspection Strategies
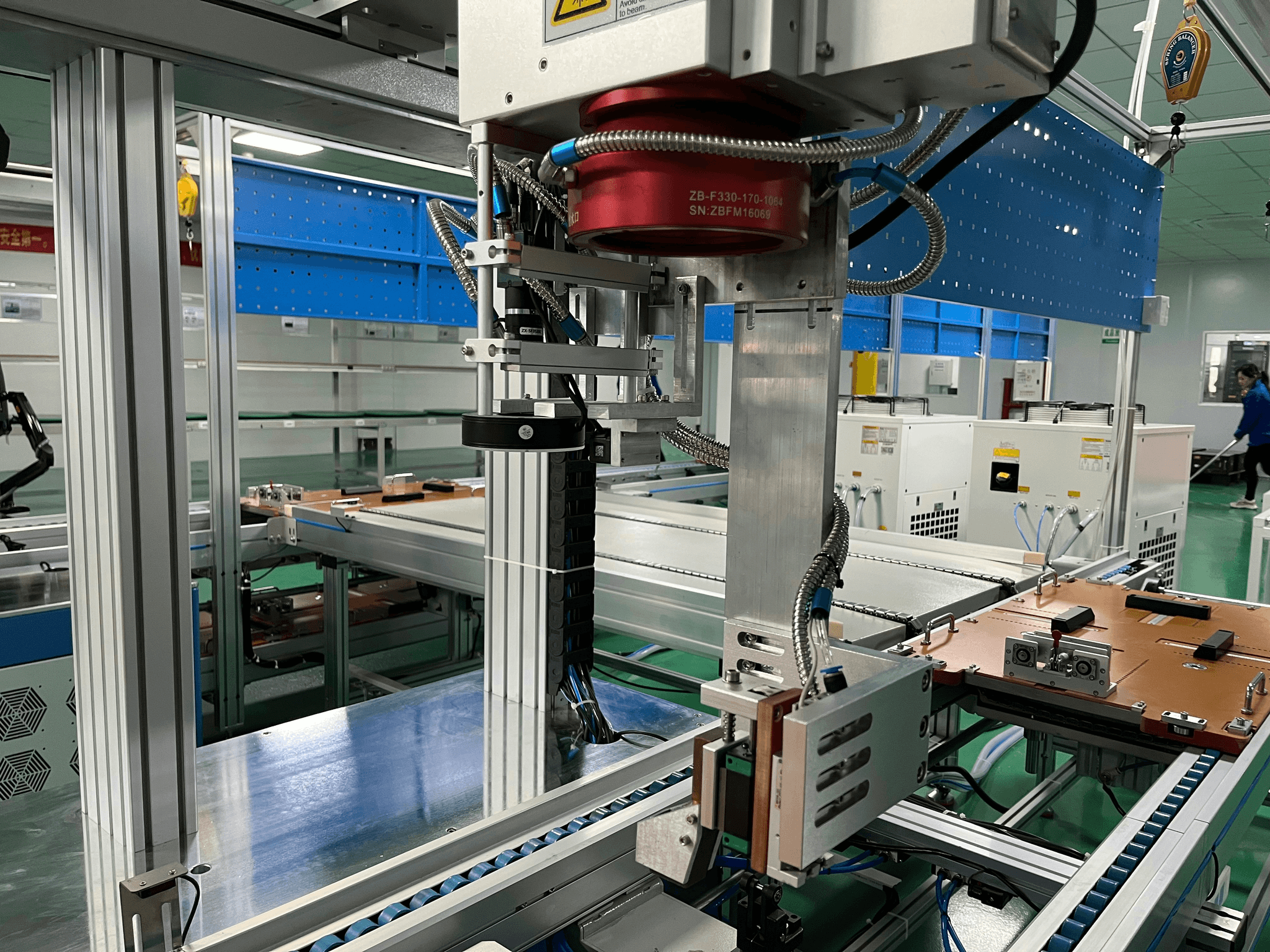
Quality inspection is the backbone of a successful manufacturing process, ensuring that products meet stringent standards before reaching consumers. By implementing effective quality inspection strategies, companies can uphold their reputation and maintain compliance with good manufacturing processes (GMP). The right techniques and tools not only streamline the inspection process but also enhance overall quality control in factory audits.
Techniques for Conducting Quality Inspections
When it comes to conducting quality inspections, a systematic approach is crucial. Start by defining clear criteria based on the essential factory audit components, which include product specifications and regulatory requirements. Utilizing techniques such as random sampling and visual inspections can help identify defects early in the production cycle, minimizing waste and ensuring adherence to GMP certification standards.
Moreover, employing standardized checklists during inspections can significantly improve consistency across different teams and shifts. This practice ensures that all aspects of quality control are covered thoroughly, reducing the chances of oversight. Training personnel on these techniques fosters a culture of quality awareness throughout the organization, leading to improved outcomes in factory audits.
Tools and Technology for Quality Assessment
In today's digital age, leveraging technology for quality assessment has become indispensable. Advanced tools such as automated inspection systems and data analytics software can enhance accuracy in evaluating product quality against established criteria derived from good manufacturing processes (GMP). These technologies allow for real-time monitoring of production lines, enabling quick adjustments when deviations occur.
Additionally, utilizing mobile applications for on-the-go inspections can streamline communication between teams while providing instant access to critical information regarding factory audit components. By integrating these modern tools into your quality control strategy, you not only increase efficiency but also bolster your compliance with GMP certification requirements. Embracing innovation in this area ultimately leads to better-quality products and higher customer satisfaction.
China Inspection Pro: A Trusted Partner
When it comes to navigating the complexities of factory audits and ensuring rigorous quality control measures are in place, partnering with an experienced service provider like China Inspection Pro can be invaluable. This organization specializes in offering comprehensive solutions tailored to meet specific needs related to good manufacturing processes (GMP) compliance and quality inspection protocols. Their expertise ensures that all essential factory audit components are meticulously addressed during inspections.
China Inspection Pro employs seasoned inspectors who utilize both traditional methods and cutting-edge technology for thorough evaluations of manufacturing facilities worldwide. With their support, businesses can confidently uphold their commitment to delivering high-quality products while adhering strictly to GMP certification standards. Ultimately, collaborating with trusted partners enhances your ability to maintain consistent quality control throughout your supply chain.
Conclusion

Wrapping up our exploration of factory audit components, it's clear that quality control is not just a box to check; it’s the backbone of successful manufacturing. The significance of quality control lies in its ability to ensure products meet the highest standards, which ultimately leads to customer satisfaction and brand loyalty. By integrating robust quality inspection processes, manufacturers can identify potential issues before they escalate, safeguarding their reputation and bottom line.
Recap of Quality Control Significance
Quality control is pivotal in maintaining the integrity of manufacturing processes and products. It encompasses various factory audit components designed to assess compliance with established standards and practices. When manufacturers prioritize quality control, they not only enhance their operational efficiency but also instill confidence in their customers regarding product reliability.
Importance of GMP Compliance
Adhering to Good Manufacturing Processes (GMP) is essential for any organization aiming for excellence in production. GMP compliance ensures that every aspect of manufacturing—from raw materials to finished products—meets stringent safety and quality standards. This adherence not only facilitates smoother factory audits but also plays a crucial role in obtaining GMP certification, which can significantly elevate a company's credibility in the marketplace.
Final Thoughts on Quality Inspection Strategies
Implementing effective quality inspection strategies is vital for any manufacturer looking to thrive in today's competitive landscape. By employing advanced tools and technologies alongside traditional methods, businesses can enhance their quality assessment capabilities significantly. Ultimately, a commitment to continuous improvement through rigorous inspections will yield long-term benefits, fostering an environment where high-quality production becomes the norm rather than the exception.
