Introduction
In the ever-evolving landscape of food production, understanding GMP in the food industry is crucial for ensuring quality and safety. Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) serve as a backbone for food safety regulations, providing a structured approach to maintaining high standards throughout the manufacturing process. As we delve into this topic, we'll uncover how GMP standards shape the industry and protect consumers from potential hazards.
Understanding GMP in the Food Industry
Good Manufacturing Practices are essential guidelines that ensure products are consistently produced and controlled according to quality standards. In the food industry, GMP encompasses everything from raw material sourcing to packaging and distribution, aiming to minimize risks and enhance product integrity. By adhering to these practices, manufacturers can confidently answer questions like What are the 5 principles of GMP? while fostering a culture of safety.
The Importance of Food Safety Regulations
Food safety regulations are designed to protect public health by ensuring that food products meet specific safety criteria before reaching consumers' plates. These regulations often reference GMP as a foundational element in their framework, highlighting its significance in preventing contamination and ensuring product quality. When manufacturers ask themselves What is the main purpose of GMP?, they recognize that compliance with these regulations is not just about legality but also about safeguarding consumer trust.
How GMP Standards Shape the Industry
GMP standards play an instrumental role in shaping best practices across the global food supply chain, influencing everything from ingredient sourcing to end-product testing. By establishing clear protocols, these standards encourage consistency and reliability within production processes while minimizing variability that could lead to unsafe products. Moreover, understanding What are the GMP standards for food? helps companies align their operations with international expectations, paving the way for market expansion and customer loyalty.
What is GMP?
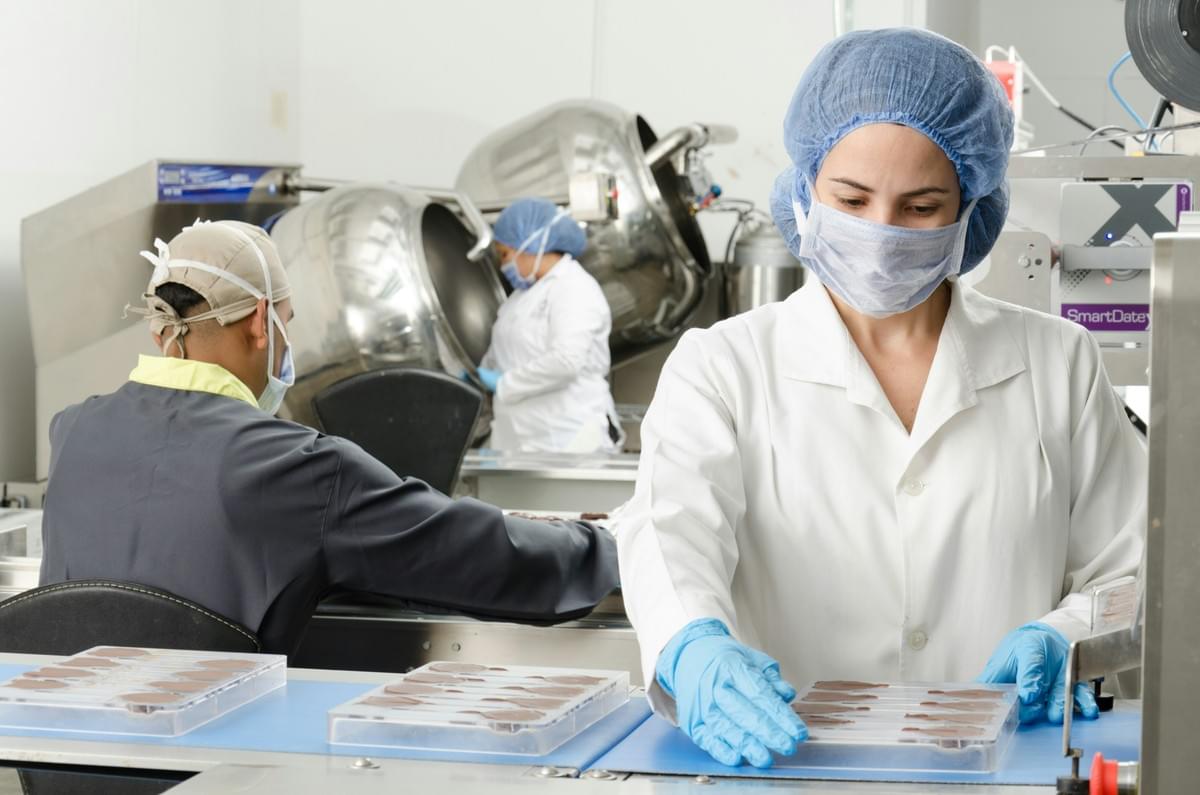

Good Manufacturing Practices, commonly known as GMP, are essential guidelines that ensure the consistent production of quality food products. In the food industry, GMP plays a critical role in safeguarding public health by establishing standards for cleanliness, equipment maintenance, and employee training. Understanding what GMP entails helps stakeholders navigate the intricate landscape of food safety regulations and quality assurance.
Definition and Origins of GMP
GMP refers to a system that ensures products are consistently produced and controlled according to quality standards. The origins of GMP can be traced back to the pharmaceutical industry in the 1960s when regulatory bodies recognized the need for stringent manufacturing practices to prevent contamination and errors. Over time, these principles were adapted for various sectors, including the food industry, leading to a more comprehensive understanding of what constitutes safe and effective production processes.
Core Components of GMP
The core components of GMP encompass several critical areas: sanitation practices, equipment maintenance, personnel training, and documentation procedures. These elements work together to create an environment where food safety is prioritized at every stage—from raw material sourcing to final product distribution. By adhering to these core components, companies can effectively minimize risks associated with contamination or quality degradation while ensuring compliance with established regulations.
Key Differences Between GMP and Other Standards
While many standards exist in the realm of food safety—such as Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point (HACCP) or ISO certifications—GMP focuses specifically on operational processes rather than end-product testing alone. Unlike HACCP which identifies specific hazards at different stages of production, GMP provides a broader framework aimed at maintaining overall quality throughout manufacturing operations. Understanding these key differences helps businesses decide how best to integrate various standards like HACCP with their existing GMP practices for optimal safety outcomes.
What are the 5 Principles of GMP?

In the realm of food safety, understanding the five principles of GMP is crucial for ensuring quality and compliance in the food industry. These principles serve as a foundation for establishing effective practices that not only meet regulatory standards but also enhance consumer trust. By adhering to these principles, organizations can significantly mitigate risks associated with food production.
Overview of GMP Principles
The five principles of GMP encompass a range of practices aimed at promoting safe and high-quality food products. They include: proper personnel training, maintaining clean and hygienic environments, implementing robust documentation procedures, ensuring consistent equipment maintenance, and conducting regular audits and inspections. Collectively, these principles help answer the question: What are the 5 principles of GMP? They form an essential part of any comprehensive strategy to uphold food safety and quality in the ever-evolving landscape of the gmp in food industry.
Applying Principles in Food Manufacturing
Applying these five principles within food manufacturing processes is vital for operational success. For instance, proper personnel training ensures that employees understand their roles in maintaining hygiene standards and product quality; this directly addresses what is the main purpose of GMP—enhancing safety and reducing risks in production environments. Additionally, by regularly documenting processes and conducting routine audits, manufacturers can create a culture of accountability that aligns with both GMP standards for food and HACCP guidelines.
Real-World Examples of GMP Implementation
Real-world examples illustrate how companies successfully implement these five principles to enhance their operations within gmp in food industry contexts. For example, a large dairy producer might conduct monthly training sessions to reinforce hygiene protocols among staff while also performing regular equipment maintenance checks to prevent contamination risks—showcasing an effective application of these core principles. Another example includes a snack manufacturer that utilizes detailed documentation practices to track ingredient sourcing and processing steps, demonstrating how adherence to what are the 5 principles of GMP can lead to improved product quality and consumer trust.
What are the GMP Standards for Food?
In the realm of food production, Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) serve as a crucial framework to ensure safety and quality. The GMP standards for food vary significantly across different regions, reflecting local regulations and cultural considerations. Understanding these specific standards is essential for businesses aiming to comply with legal requirements while maintaining high-quality products.
Specific Standards in Different Countries
GMP in the food industry is not a one-size-fits-all approach; each country has established its own set of guidelines tailored to its unique needs. For instance, the European Union has stringent regulations that focus on hygiene and traceability, while countries like Japan emphasize traditional methods alongside modern practices. These variations highlight how what constitutes best practices can differ based on regional priorities and consumer expectations.
Overview of FDA and USDA Guidelines
In the United States, both the FDA (Food and Drug Administration) and USDA (United States Department of Agriculture) play pivotal roles in establishing GMP standards for food products. The FDA outlines comprehensive guidelines that cover everything from facility cleanliness to employee training, ensuring that all aspects of production adhere to safety protocols. Meanwhile, the USDA focuses specifically on meat, poultry, and egg products, enforcing rigorous inspection processes to guarantee compliance with GMP principles.
Role of International Standards like ISO
Internationally recognized standards such as ISO 22000 provide a global framework for implementing GMP in food manufacturing processes. These standards help harmonize practices across borders, making it easier for companies to operate internationally while ensuring consistent quality and safety in their products. By adhering to these international guidelines alongside national regulations like those from the FDA or USDA, businesses can enhance their credibility and consumer trust within the global market.
What is the Main Purpose of GMP?
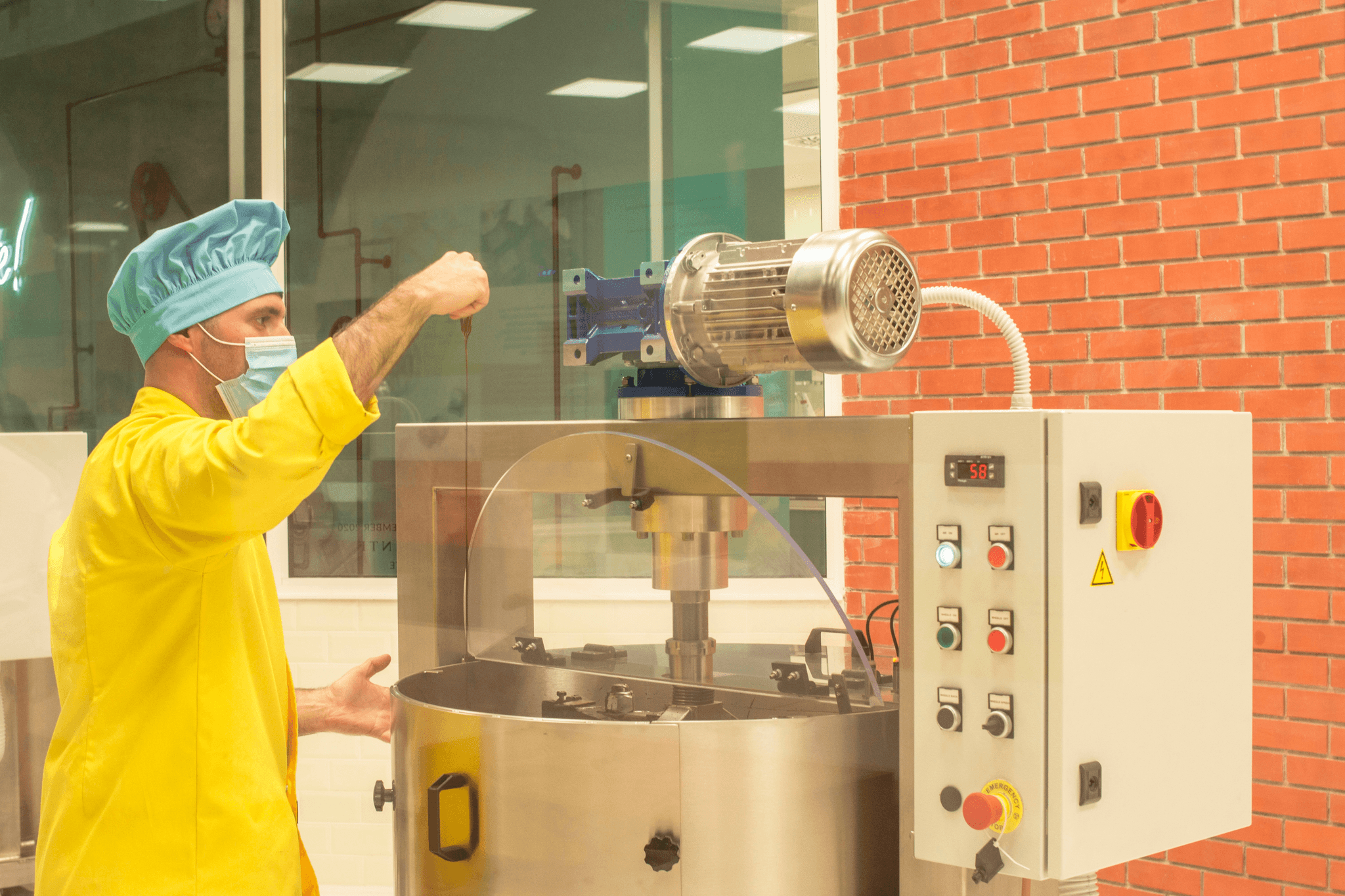

The main purpose of GMP in the food industry is to ensure that food products are consistently produced and controlled according to quality standards. By adhering to these guidelines, manufacturers can enhance food safety and quality, reduce risks during production, and ultimately build consumer trust in their products. This trifecta not only benefits the producers but also safeguards public health.
Enhancing Food Safety and Quality
One of the primary goals of GMP is enhancing food safety and quality, which is crucial in the ever-evolving landscape of the food industry. By implementing strict hygiene practices, proper equipment maintenance, and thorough employee training, companies can minimize contamination risks that could compromise product integrity. This focus on quality assurance not only protects consumers but also aligns with what are the GMP standards for food across various regulatory bodies.
Reducing Risks in Food Production
Reducing risks in food production is another cornerstone of what is the main purpose of GMP. Through systematic processes such as risk assessments and regular audits, manufacturers can identify potential hazards before they escalate into serious issues. This proactive approach not only mitigates dangers associated with foodborne illnesses but also addresses operational inefficiencies—ensuring that what are the 5 principles of GMP are effectively applied throughout production.
Building Consumer Trust in Food Products
Building consumer trust in food products hinges on transparency and accountability—two elements strongly emphasized by GMP practices. When consumers see a commitment to high-quality standards backed by rigorous testing and compliance with regulations like HACCP (Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point), they feel more confident about their purchases. In a world where information travels fast, demonstrating adherence to what is Haccp and GMP in the food industry becomes essential for maintaining brand loyalty.
What is HACCP and GMP in the Food Industry?

In the realm of food safety, two acronyms dominate the conversation: HACCP and GMP. While both frameworks aim to ensure food safety and quality, they serve distinct yet complementary roles in the food industry. Understanding their relationship is crucial for anyone involved in food production or regulation.
Understanding the Relationship Between HACCP and GMP
GMP, or Good Manufacturing Practices, lays down the foundational standards for hygiene, quality control, and operational procedures in the food industry. It focuses on ensuring that products are consistently produced according to quality standards. On the other hand, HACCP (Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point) builds upon those foundations by identifying specific hazards that could compromise food safety during production processes.
The synergy between HACCP and GMP is vital; while GMP provides a broad framework for safe manufacturing practices, HACCP hones in on critical points where risks can arise. Together, they create a robust system that not only adheres to what are the GMP standards for food but also addresses potential hazards proactively. This dynamic duo ensures that manufacturers can effectively manage risks while maintaining high-quality products.
How HACCP Enhances GMP Implementation
HACCP enhances GMP implementation by providing a structured approach to identifying and mitigating risks at various stages of production. By integrating what are the 5 principles of GMP into its framework, HACCP allows companies to focus on critical control points where failures could lead to contamination or product defects. This targeted approach not only improves compliance but also elevates overall product quality.
Furthermore, implementing HACCP within a GMP framework helps organizations systematically document processes and monitor performance metrics more effectively. This documentation becomes invaluable during audits or inspections by regulatory bodies such as the FDA or USDA—key players who enforce what are the GMP standards for food across different regions. In this way, companies can build consumer trust by demonstrating their commitment to rigorous safety measures.
Case Studies of Successful HACCP and GMP Integration
Numerous companies have successfully integrated both HACCP and GMP into their operations with remarkable results. For instance, a large poultry processing plant adopted these frameworks together which led to a significant reduction in contamination rates—showing how effective this combination can be when executed properly. By adhering closely to what is Haccp and gmp in the food industry practices alongside strict adherence to what is the main purpose of GMP?, they were able to enhance their reputation as a safe producer.
Another example involves a dairy manufacturer that implemented these systems after facing several compliance issues with health regulations. By establishing stringent controls based on both frameworks, they not only improved product safety but also streamlined operations—demonstrating how beneficial this integration can be across various sectors within the industry.
In conclusion, understanding how HACCP enhances existing good manufacturing practices gives companies an edge in ensuring both compliance with regulations and consumer satisfaction through safe products.
Conclusion
In wrapping up our exploration of GMP in the food industry, it's clear that these standards are not just bureaucratic hurdles but essential frameworks that ensure food safety and quality. From understanding what GMP entails to recognizing its core principles, we see how they shape manufacturing practices across the globe. The relationship between GMP and HACCP further emphasizes the importance of a comprehensive approach to food safety, ensuring consumers receive products that meet rigorous standards.
Recap of Key GMP Concepts in Food
To summarize, GMP in the food industry encompasses a set of practices aimed at ensuring consistent quality and safety in food production. We delved into what are the 5 principles of GMP, highlighting aspects such as hygiene, training, and documentation that form the backbone of effective manufacturing processes. Additionally, we explored what are the GMP standards for food across various regions, showcasing how regulations can differ yet all aim to protect consumer health.
Importance of Third-Party Inspections like China Inspection Pro
Third-party inspections play a pivotal role in reinforcing compliance with GMP standards for food by providing an unbiased evaluation of manufacturing practices. Organizations like China Inspection Pro offer critical oversight that ensures companies adhere to both local and international regulations while enhancing trust among consumers. In a world where transparency is paramount, these inspections help safeguard against potential lapses in quality or safety within the complex supply chains typical of today's global market.
Future of GMP in the Global Food Industry
Looking ahead, the future of GMP in the global food industry appears promising yet challenging as new technologies emerge and consumer expectations evolve. As we continue to ask ourselves what is HACCP and GMP in the food industry and how they interact with one another, it becomes increasingly important to innovate while maintaining rigorous standards for safety and quality. Ultimately, as awareness grows around these concepts, we can anticipate a stronger commitment from producers worldwide to uphold these essential principles.
