Introduction
In the fast-paced world of electronics, ensuring product quality is not just a luxury—it's a necessity. Electronic quality control serves as the backbone of any successful manufacturing process, helping to guarantee that products meet stringent standards before they reach consumers. By implementing effective quality management strategies, companies can minimize defects and enhance customer satisfaction.
Understanding the Importance of Quality Control
Quality control (QC) is pivotal in maintaining the integrity and reliability of electronic products. It encompasses various processes designed to identify defects and ensure that every component meets predefined specifications. Without robust QC measures, manufacturers risk producing faulty products that can lead to costly recalls and damage their reputation in an increasingly competitive market.
The Role of Quality Management in Electronics
Quality management plays a crucial role in shaping the overall production landscape within the electronics sector. By integrating quality assurance practices throughout every stage of manufacturing, companies can foster a culture of excellence that prioritizes defect prevention over mere detection. This proactive approach not only streamlines operations but also enhances product consistency and reliability.
Key Players in Electronic Quality Control
The realm of electronic quality control involves several key players who work collaboratively to uphold high standards. Quality assurance specialists are at the forefront, employing various QC inspection techniques to assess product integrity before it reaches consumers' hands. Additionally, engineers, production managers, and supply chain professionals all contribute to establishing a comprehensive framework for effective quality management within their organizations.
Fundamentals of Electronic Quality Control
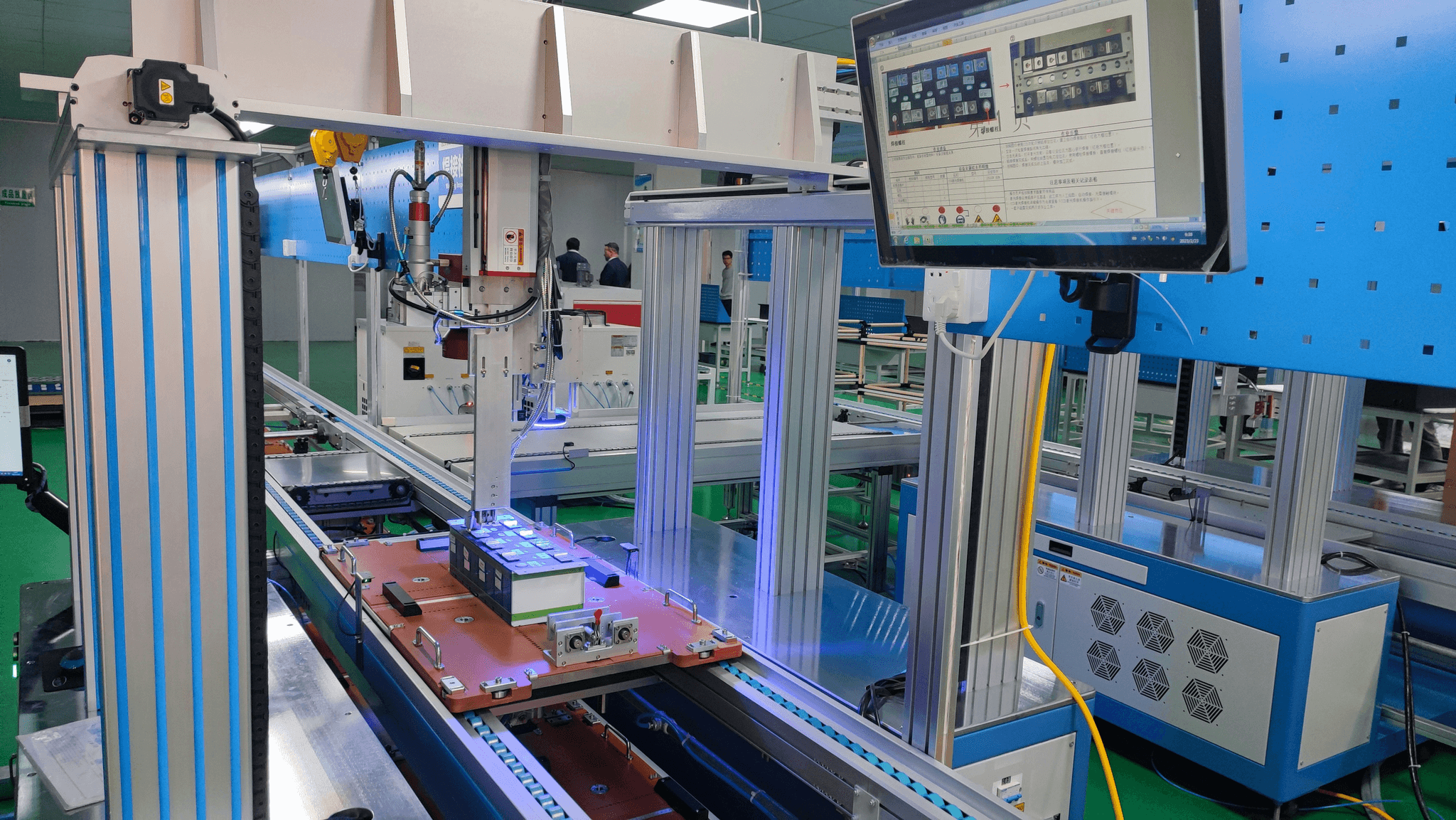
Understanding the fundamentals of electronic quality control (QC) is essential for manufacturers aiming to deliver products that meet or exceed customer expectations. Quality control in electronics encompasses a range of processes and practices designed to ensure that every component and product adheres to stringent quality standards. By implementing effective quality management strategies, companies can enhance their operational efficiency and build a reputation for reliability.
Defining Quality Control in Electronics
Quality control in electronics refers to the systematic processes that manufacturers employ to ensure their products are free from defects and function as intended. This involves not just inspecting finished goods, but also monitoring the production process itself, which includes raw materials, assembly procedures, and final testing. Effective QC practices help identify issues early on, reducing waste and ensuring that customers receive high-quality electronic products.
In this context, the role of a quality assurance specialist becomes crucial; they are responsible for developing protocols and performing QC inspections at various stages of production. These specialists utilize specific benchmarks and metrics to assess product quality consistently. By defining clear criteria for what constitutes acceptable quality, businesses can streamline their QC processes while enhancing overall product reliability.
Essential QC Techniques and Tools
There are several essential techniques and tools utilized in electronic quality control that help maintain high standards throughout manufacturing processes. Common methods include statistical process control (SPC), failure mode effects analysis (FMEA), and root cause analysis (RCA). Each technique plays a vital role in identifying potential failures before they occur, ensuring that corrective actions can be taken swiftly.
Moreover, adopting advanced tools such as automated inspection systems or software solutions can significantly enhance the efficiency of QC inspections. These technologies allow for real-time monitoring of production lines, detecting anomalies faster than traditional methods could achieve. The integration of these tools into a comprehensive quality management system enables organizations to maintain consistency while continuously improving their QC efforts.
The Lifecycle of QC in Manufacturing
The lifecycle of QC in manufacturing involves several key stages: planning, execution, assessment, and feedback loops aimed at continuous improvement. Initially, manufacturers must establish clear objectives regarding what constitutes acceptable levels of quality within their operations—this sets the foundation for effective electronic quality control practices throughout production cycles.
During execution, various QC inspections are conducted at different phases—from incoming material checks through final product evaluations—to ensure compliance with established standards. After assessments are made based on these inspections, feedback is gathered from both customers and internal teams; this information is invaluable for refining processes further.
Ultimately, by understanding the lifecycle of QC in manufacturing—and how it interconnects with broader concepts like quality management—companies can create robust systems that not only reduce defects but also foster an environment where innovation thrives alongside reliability.
The Process of Quality Inspection
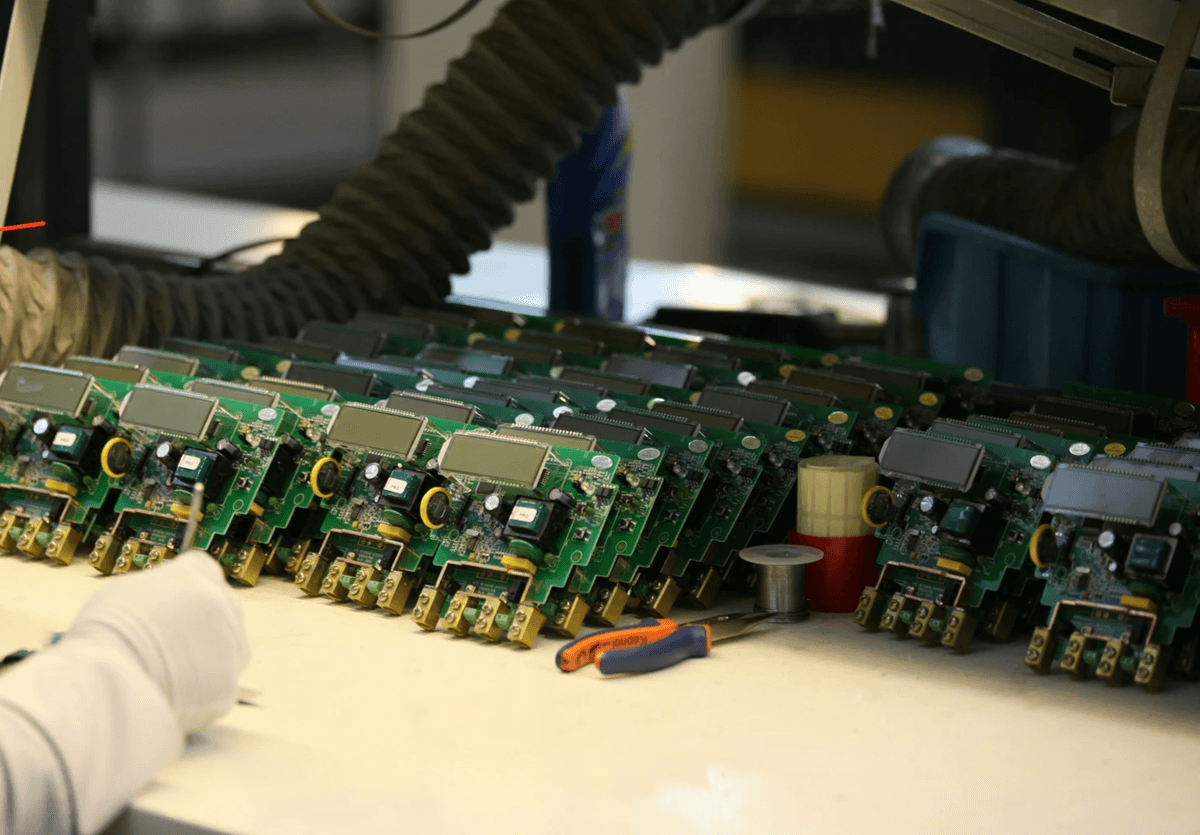
The process of quality inspection is a critical component in electronic quality control, ensuring that products meet established standards before reaching the consumer. Quality inspections serve as a safeguard against defects, enhancing overall quality management by identifying issues early in the manufacturing process. This proactive approach not only reduces costs associated with returns and repairs but also boosts customer satisfaction and brand reputation.
Types of QC Inspections in Electronics
In the realm of electronics, various types of QC inspections play pivotal roles in maintaining high-quality standards. Incoming inspection checks raw materials and components for compliance with specifications before they enter production, while in-process inspections monitor assembly stages to catch defects on the spot. Finally, outgoing inspections ensure that finished products adhere to quality benchmarks before they are shipped out, making every stage essential for effective electronic quality control.
Role of Quality Assurance Specialists
Quality assurance specialists are the unsung heroes behind successful QC inspections in electronics manufacturing. Their expertise lies not just in identifying flaws but also in developing robust quality management systems that minimize risks throughout production cycles. By analyzing data and implementing best practices, these specialists ensure that every product meets stringent quality standards while fostering a culture of continuous improvement within their teams.
Importance of Pre-Shipment Inspections
Pre-shipment inspections are arguably one of the most crucial steps in electronic quality control, serving as the final checkpoint before products hit store shelves or customers' doorsteps. These inspections help verify that all items meet agreed-upon specifications and performance criteria, significantly reducing post-sale issues such as returns or complaints from customers about product defects. By investing time and resources into thorough pre-shipment QC inspection processes, manufacturers can build trust with their clients while safeguarding their brand's reputation.
Strategies for Effective Quality Management
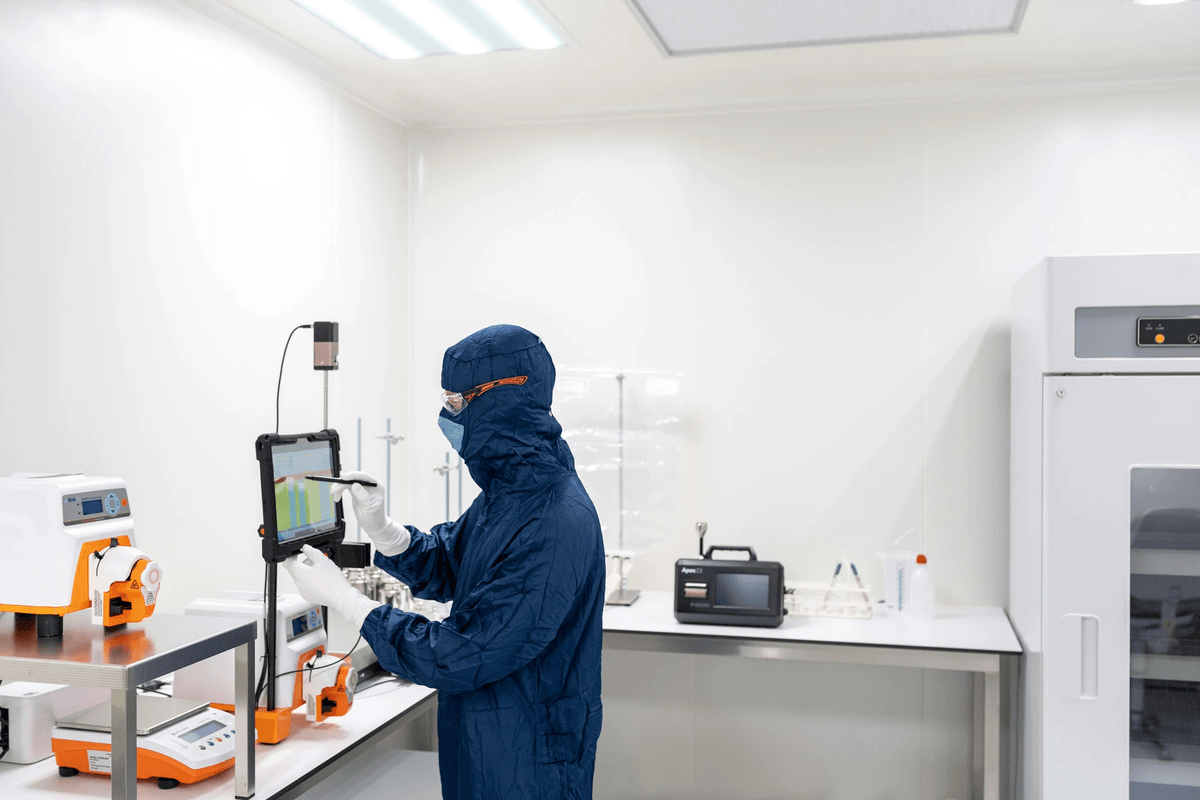

In the fast-paced world of electronics, effective quality management is not just a nicety; it’s a necessity. Emphasizing best practices in quality management systems can streamline processes and enhance overall product quality. By adopting a proactive approach to electronic quality control, manufacturers can minimize defects and maximize customer satisfaction.
Best Practices in Quality Management Systems
Implementing robust quality management systems (QMS) is crucial for any organization involved in electronic quality control. This includes establishing clear procedures, regular audits, and comprehensive documentation that supports consistent qc inspection processes. Engaging all stakeholders—from production teams to top management—ensures that everyone understands their role in maintaining the high standards of quality and quality management.
Moreover, integrating technology into QMS can lead to improved efficiency and accuracy in tracking defects or non-conformities. Utilizing software tools that facilitate data collection and analysis allows teams to make informed decisions based on real-time information. Ultimately, these best practices not only enhance product reliability but also foster a culture of continuous improvement within the organization.
Continuous Improvement and Feedback Loops
Continuous improvement should be at the heart of any effective electronic quality control strategy. Establishing feedback loops among different teams helps identify areas for enhancement while reinforcing accountability within the qc inspection process. Regularly reviewing performance metrics ensures that organizations remain agile and responsive to both internal challenges and market demands.
Incorporating methodologies such as Six Sigma or Lean Manufacturing can significantly contribute to refining processes over time. These frameworks encourage teams to analyze root causes of defects systematically, leading to more sustainable solutions rather than quick fixes. By fostering an environment where feedback is welcomed and acted upon, companies can maintain high standards of excellence in their products.
Training and Development for QC Teams
Investing in training and development for QC teams is essential for sustaining high-quality outcomes in electronics manufacturing. Quality assurance specialists play a pivotal role; therefore, equipping them with the latest skills ensures they are prepared to tackle evolving challenges in electronic quality control effectively. Regular workshops, certifications, and on-the-job training keep staff updated on industry standards and innovative qc inspection techniques.
Moreover, creating mentorship programs within organizations fosters knowledge sharing among experienced professionals and newcomers alike. This not only enhances individual skill sets but also builds a cohesive team environment focused on achieving common goals related to quality management. Ultimately, well-trained QC personnel are crucial assets that drive continuous improvement efforts across all facets of production.
Case Studies: Successful Quality Control

In the realm of electronic quality control, examining the practices of industry leaders provides invaluable insights into effective quality management strategies. Companies like Apple and Samsung have mastered the art of quality assurance, ensuring their products meet high standards before reaching consumers. Additionally, organizations such as China Inspection Pro offer specialized services that enhance QC inspection processes across various sectors.
Lessons from Apple’s Quality Assurance Practices
Apple's approach to quality control is nothing short of legendary, setting a benchmark for electronic quality control in the tech industry. Their rigorous testing protocols ensure that every product undergoes extensive qc inspections at multiple stages of production, leaving no room for errors. The company emphasizes a culture of quality management where every employee is encouraged to contribute to maintaining high standards throughout the manufacturing process.
One key lesson from Apple's practices is their commitment to continuous improvement and innovation in quality assurance methods. By leveraging advanced technologies and data analytics, Apple can quickly identify defects and implement corrective measures effectively. This proactive stance not only enhances product reliability but also fosters customer loyalty through consistent delivery of top-notch devices.
How Samsung Ensures Product Quality
Samsung has developed a robust framework for ensuring product quality that combines cutting-edge technology with meticulous qc inspection processes. Their comprehensive quality management system encompasses everything from supplier evaluation to final product testing, ensuring that each component meets stringent standards before assembly. This holistic approach allows Samsung to deliver high-quality electronics while minimizing risks associated with defects.
The company also invests heavily in training its quality assurance specialists, equipping them with the necessary skills and knowledge to identify potential issues early on in production. Regular workshops and seminars keep teams updated on best practices in electronic quality control, fostering an environment where excellence is expected and celebrated. By prioritizing employee development alongside technological advancements, Samsung maintains its reputation as a leader in product reliability.
Insights from China Inspection Pro’s Services
China Inspection Pro specializes in providing tailored solutions for businesses looking to enhance their electronic quality control efforts without breaking the bank. Their services include comprehensive qc inspections tailored specifically for electronics manufacturers aiming to uphold high standards while navigating complex supply chains efficiently. By employing experienced inspectors who understand local regulations and international compliance requirements, they help clients mitigate risks associated with poor-quality products.
One significant insight gleaned from China Inspection Pro's operations is the importance of pre-shipment inspections in maintaining product integrity before it reaches consumers’ hands. These inspections serve as a final checkpoint where any discrepancies can be identified and rectified promptly—saving companies from costly recalls or reputational damage later on. Moreover, their emphasis on transparent communication ensures that clients are always informed about inspection results and potential areas for improvement within their own processes.
Challenges and Solutions in Quality Control
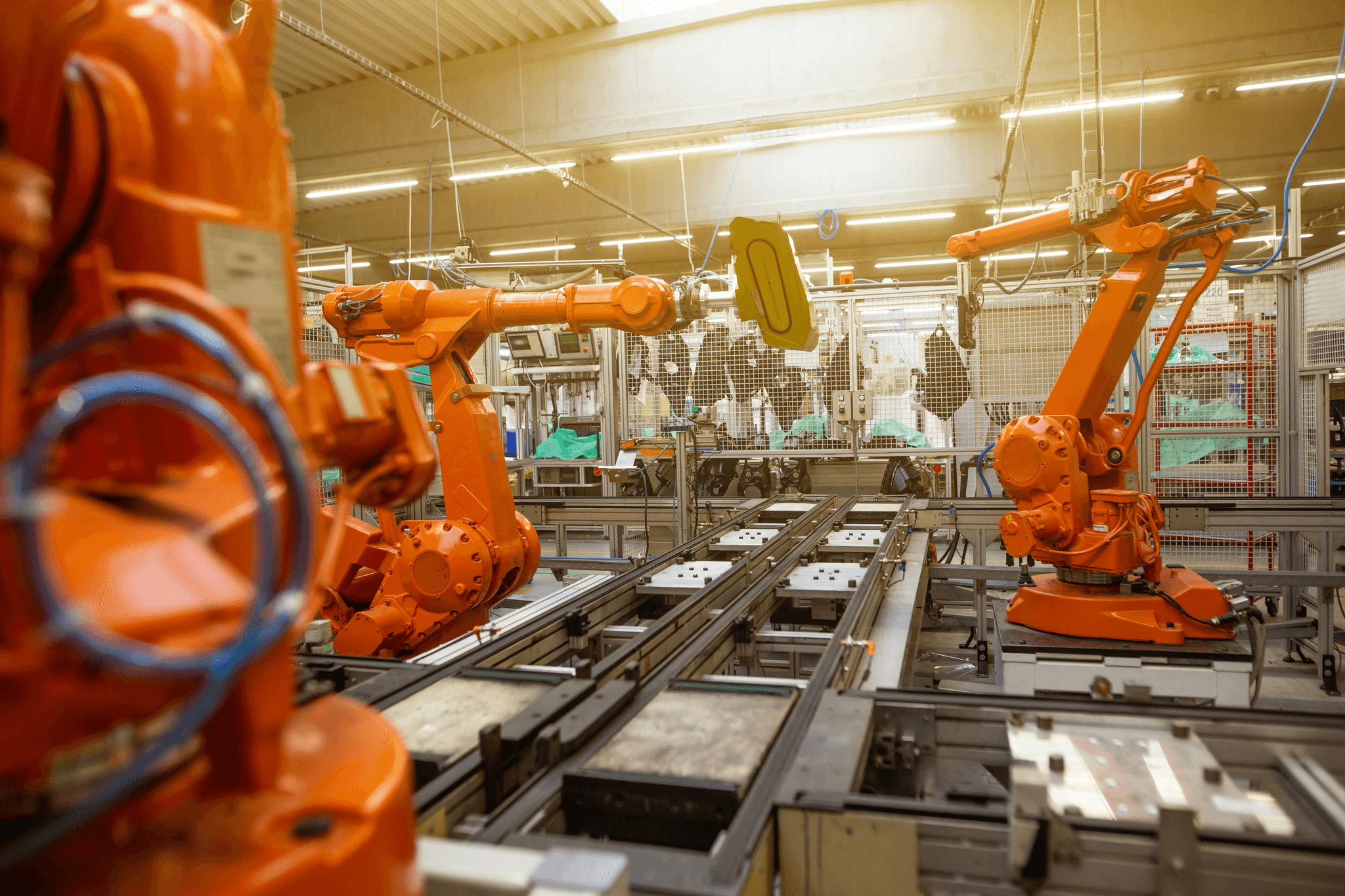
In the fast-paced world of electronics manufacturing, quality control (QC) faces numerous challenges that can impact product reliability and customer satisfaction. From rapid technological advancements to increasingly complex supply chains, maintaining high standards is no small feat. However, by identifying these hurdles and implementing innovative solutions, manufacturers can enhance their electronic quality control processes significantly.
Common QC Challenges in Electronics Manufacturing
One of the most pressing challenges in electronic quality control is the sheer complexity of modern devices. As products incorporate more intricate components and software, ensuring that every element meets quality management standards becomes increasingly difficult. Additionally, manufacturers often grapple with varying regulations across different markets, which complicates compliance efforts for quality assurance specialists tasked with maintaining product integrity.
Another significant challenge is the rising pressure to reduce production costs while still delivering high-quality products. Many companies find themselves cutting corners or relying on less reliable suppliers to save money, which can lead to defects and ultimately harm their reputation in the market. Furthermore, a lack of skilled personnel trained in QC inspection methods exacerbates these issues, as experienced professionals are essential for effective quality management.
Lastly, adapting to rapid changes in consumer expectations poses a challenge for electronic manufacturers striving for excellence in QC practices. The demand for faster turnaround times without compromising quality creates a delicate balance that requires constant vigilance and improvement strategies from organizations dedicated to maintaining effective quality assurance systems.
Innovative Solutions for Quality Assurance
To tackle these challenges head-on, many companies are adopting innovative solutions that leverage technology to enhance electronic quality control processes. Automation plays a crucial role here; advanced robotics and AI-powered inspection tools streamline QC inspections by quickly identifying defects that human inspectors might overlook. This not only boosts efficiency but also ensures consistent adherence to stringent quality management protocols.
Moreover, embracing data analytics allows manufacturers to gain deeper insights into their production processes and identify potential areas of improvement proactively. By analyzing historical data on defects and failures during the QC inspection phase, organizations can implement targeted corrective actions before problems escalate into larger issues affecting product launches or customer satisfaction.
Training programs focused on upskilling employees are also vital for overcoming challenges in electronic quality control. By investing in continuous education for their workforce—especially those working as quality assurance specialists—manufacturers can cultivate a culture of excellence where staff members are knowledgeable about the latest QC techniques and tools available within the industry.
The Future of Quality Control in a Digital Age
As we look ahead into an increasingly digital future, electronic quality control will likely continue evolving alongside technological advancements such as IoT (Internet of Things) devices and smart manufacturing systems. These innovations promise greater connectivity among machines throughout production lines; this interconnectedness will enable real-time monitoring of product performance against predefined standards set forth by robust quality management frameworks.
Additionally, machine learning algorithms will play an essential role in predicting potential failures before they occur—transforming traditional reactive approaches into proactive strategies within QC practices across various sectors within electronics manufacturing. This shift towards predictive maintenance could revolutionize how companies manage their resources while ensuring compliance with rigorous standards upheld by industry leaders.
Ultimately, building trust through effective electronic quality control measures will remain paramount as consumers demand higher levels of transparency regarding product origins and manufacturing practices moving forward into this digital age—a future where innovation meets responsibility head-on.
Conclusion
As we wrap up our exploration of electronic quality control, it's clear that the journey toward impeccable product quality is paved with innovation and diligence. The integration of advanced technologies and methodologies in quality management not only enhances product reliability but also paves the way for a more efficient manufacturing process. By prioritizing quality assurance, companies can ensure their products meet consumer expectations and stand out in a competitive market.
Enhancing Product Quality through Innovation
Innovation is at the heart of enhancing electronic quality control, where cutting-edge tools and techniques redefine what it means to achieve excellence. From automated QC inspections to sophisticated data analytics, these advancements empower manufacturers to detect defects early in the production lifecycle, ensuring that only top-notch products reach consumers. Embracing innovation not only boosts efficiency but also fosters a culture of continuous improvement within organizations committed to quality management.
Building Trust with Quality Assurance Practices
Trust is a cornerstone in any relationship, including that between manufacturers and consumers; effective quality assurance practices are essential for building this trust. By consistently delivering high-quality products backed by rigorous QC processes, companies can cultivate loyalty among their customer base while enhancing their reputation in the market. A dedicated quality assurance specialist plays a pivotal role in this endeavor by meticulously overseeing every aspect of production to ensure compliance with established standards.
The Path Forward for Electronics Manufacturers
Looking ahead, electronics manufacturers must navigate a rapidly evolving landscape where digital transformation is paramount for sustaining competitive advantage. Implementing robust strategies for electronic quality control will be crucial as they adapt to new technologies and consumer demands while maintaining high standards of product integrity. By committing to ongoing training for QC teams and adopting innovative solutions to common challenges, manufacturers can secure their position as leaders in the realm of quality management.
