Introduction
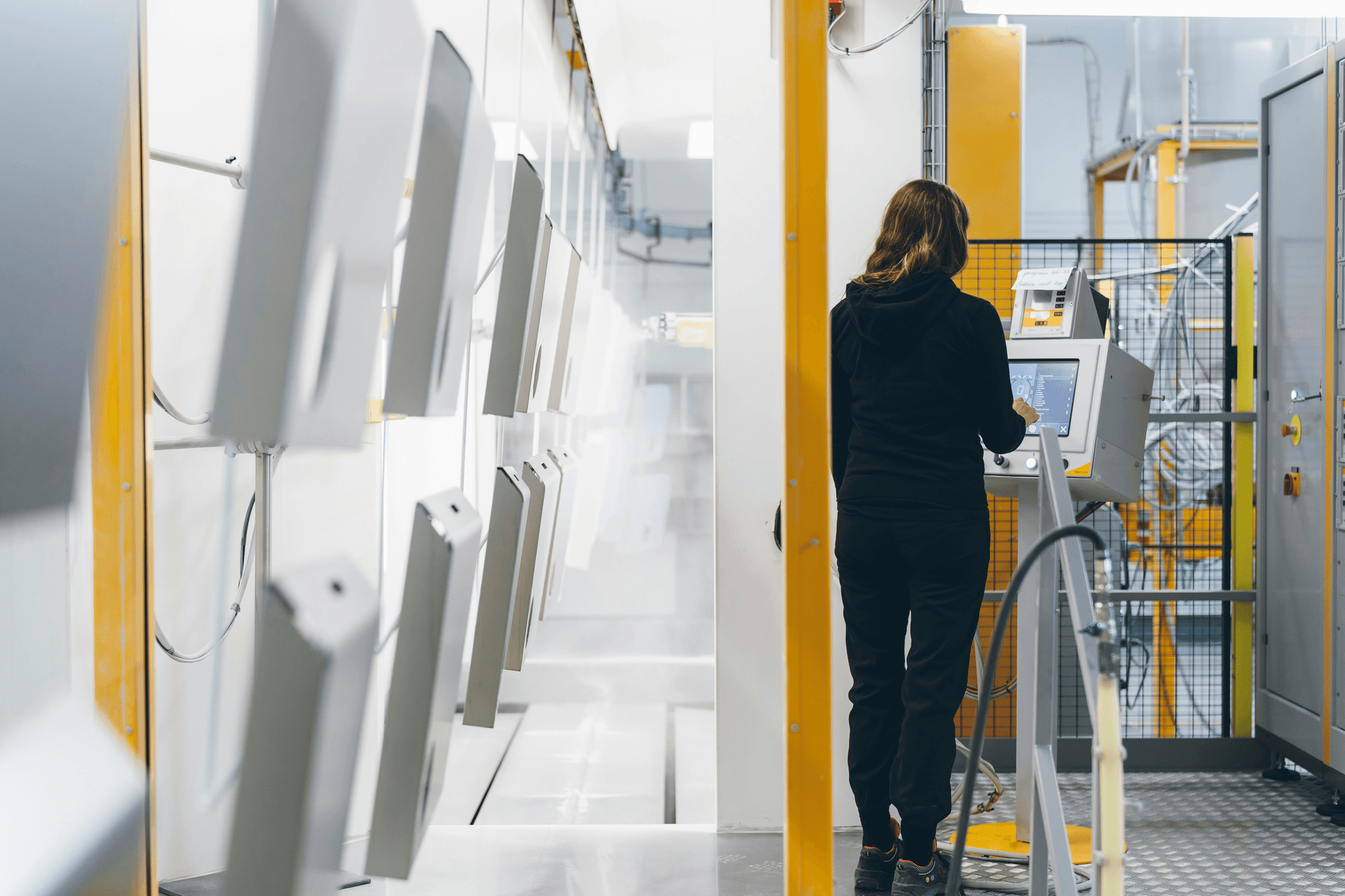

In the ever-evolving landscape of manufacturing, quality control and inspection stand as critical pillars that ensure products not only meet but exceed customer expectations. Understanding quality control fundamentals is essential for any organization aiming to thrive in a competitive market. By embracing effective quality management practices, manufacturers can significantly enhance their operational efficiency and product reliability.
Understanding Quality Control Fundamentals
Quality control encompasses a set of processes aimed at maintaining the desired level of quality in manufactured products. It involves systematic inspections, testing, and monitoring to identify any deviations from established standards. By grasping these fundamentals, organizations can better implement robust quality control measures that foster consistency and excellence across all production stages.
Importance of Quality Control in Manufacturing
The importance of quality control in manufacturing cannot be overstated; it directly impacts customer satisfaction, brand reputation, and overall business success. Effective quality control not only minimizes defects but also reduces waste and rework costs, leading to increased profitability. In an era where consumers are more discerning than ever, prioritizing quality in manufacturing practices is vital for sustaining competitive advantage.
Overview of Effective Quality Inspection Strategies
To achieve high standards in product output, manufacturers must adopt effective quality inspection strategies tailored to their specific needs. This includes integrating both pre-production and final inspection techniques to catch potential issues early on while ensuring compliance with industry regulations. Leveraging technology in these inspection processes enhances accuracy and efficiency—ultimately reinforcing the commitment to quality and control within the organization.
Defining Quality Control in Manufacturing

Quality control is a critical component in the manufacturing landscape, acting as a safeguard to ensure that products meet specified standards and customer expectations. It intertwines with quality inspection to create a robust framework that enhances product reliability and performance. Understanding the nuances of quality control helps organizations streamline their manufacturing practices while minimizing defects and maximizing efficiency.
Key Principles of Quality Control
At the heart of effective quality control are several key principles that guide manufacturing practices. These include consistency, measurement, and improvement, which collectively contribute to maintaining high standards throughout production processes. By embedding these principles into daily operations, companies can foster an environment where quality and control become second nature.
Another essential principle is customer focus; understanding what customers value allows manufacturers to tailor their quality control efforts accordingly. This alignment ensures that products not only meet internal specifications but also resonate with market demands, enhancing overall satisfaction. Furthermore, integrating data-driven decision-making into quality control jobs empowers teams to identify trends and proactively address potential issues before they escalate.
Role of Quality Management Systems
Quality Management Systems (QMS) serve as the backbone for effective quality control in manufacturing environments. A well-implemented QMS provides structured processes for monitoring and improving product quality while ensuring compliance with industry regulations. By leveraging these systems, organizations can systematically manage their quality control efforts from design through production to final inspection.
Moreover, QMS facilitates communication across departments by establishing clear protocols for reporting defects or non-conformities during the production cycle. This transparency not only aids in immediate problem-solving but also contributes to long-term improvements in manufacturing practices through continuous feedback loops. As a result, businesses can cultivate a culture focused on both quality and efficiency—an essential balance for success in today's competitive marketplace.
Differences Between Quality Assurance and Quality Control
While often used interchangeably, quality assurance (QA) and quality control (QC) serve distinct purposes within the realm of manufacturing management. QA is proactive; it focuses on preventing defects by establishing processes designed to ensure product integrity before they reach the production line. In contrast, QC is reactive—it involves identifying defects after production through rigorous testing and inspection methods.
Understanding these differences is crucial for companies aiming to enhance their overall approach to product development and delivery. By integrating both QA and QC strategies into their operations, manufacturers can create a comprehensive framework that emphasizes both prevention and detection of issues related to product quality management. Ultimately, this dual approach leads not only to improved products but also fosters trust between manufacturers and consumers concerning product reliability.
Quality Control Techniques and Tools
In the realm of manufacturing, quality control techniques and tools are essential for ensuring that products meet specified standards. These methodologies not only enhance product reliability but also streamline production processes, ultimately leading to greater customer satisfaction. By understanding and implementing these techniques, businesses can minimize defects and improve overall quality control and inspection outcomes.
Statistical Process Control Methods
Statistical Process Control (SPC) is a vital technique in quality control that utilizes statistical methods to monitor and control manufacturing processes. By analyzing data collected from production, SPC helps identify variations that could indicate potential issues before they escalate into significant problems. This proactive approach not only enhances quality management but also reduces waste, making it a cornerstone of effective manufacturing practices.
SPC employs tools like control charts to visualize process performance over time, allowing for quick identification of trends or shifts in quality levels. When implemented correctly, these methods can significantly reduce variability in production processes, resulting in more consistent product quality. Ultimately, mastering SPC is crucial for anyone pursuing quality control jobs within the manufacturing sector.
Six Sigma and Lean Manufacturing Practices
Six Sigma is another powerful methodology aimed at improving product quality by identifying and eliminating defects through a data-driven approach. This technique focuses on reducing process variation to achieve near-perfect results—specifically aiming for no more than 3.4 defects per million opportunities. When combined with Lean Manufacturing practices, which emphasize waste reduction and efficiency improvement, organizations can create a robust framework for both quality management and operational excellence.
Lean principles complement Six Sigma by streamlining processes while maintaining high standards of quality control and inspection throughout the production cycle. Together, these methodologies foster an environment where continuous improvement becomes ingrained in the company culture, promoting a commitment to excellence across all levels of operation. As industries evolve, professionals skilled in Six Sigma and Lean practices will find themselves increasingly sought after for various quality control jobs.
The Value of Failure Mode Effects Analysis
Failure Mode Effects Analysis (FMEA) is an essential tool used within the realm of quality control to identify potential failure modes within a system or process before they occur. By systematically evaluating each component's potential failure points and their impacts on overall performance, organizations can prioritize risks effectively—thereby enhancing their ability to implement corrective actions proactively. FMEA not only aids in improving product reliability but also strengthens the foundations of effective quality management systems.
Incorporating FMEA into the design phase or during process development ensures that manufacturers maintain high standards throughout their operations while minimizing risks associated with defects or failures later down the line. This forward-thinking approach is crucial for establishing robust protocols around both product design and manufacturing practices focused on safety and efficiency. Ultimately, FMEA serves as a critical tool for professionals dedicated to upholding rigorous standards within their respective fields of expertise related to quality control.
Implementing Quality Control Processes
Implementing effective quality control processes is essential for any manufacturing operation aiming to enhance product quality and maintain customer satisfaction. A well-structured quality control program not only identifies and mitigates defects but also fosters a culture of continuous improvement. By focusing on quality control and inspection, manufacturers can ensure that their products meet established standards consistently.
Steps to Establish a Quality Control Program
Establishing a robust quality control program begins with defining clear objectives aligned with overall business goals. This involves setting specific metrics for success, such as defect rates or customer satisfaction scores, which will guide the quality control efforts throughout the manufacturing process. Next, it's crucial to develop standardized operating procedures that outline each step of the quality inspection process, ensuring everyone on the team understands their roles in maintaining quality and control.
Once procedures are in place, it's time to implement training sessions for all employees involved in quality control jobs. This ensures they are well-equipped with the necessary skills and knowledge about both the tools used in inspections and the principles of effective quality management. Regular reviews and updates of these programs will help adapt to any changes in manufacturing practices or regulatory requirements.
Training for Quality Control Jobs
Training plays a pivotal role in successful implementation of a quality control program; it empowers employees with the expertise needed to perform their tasks effectively. Comprehensive training should cover various aspects of quality inspection techniques, including statistical process control methods and failure mode effects analysis (FMEA). By investing in employee development, companies can cultivate a workforce that is not only adept at identifying issues but also proactive in suggesting improvements.
Moreover, ongoing training sessions should be organized to keep staff updated on new technologies or methodologies within the realm of quality management systems. This commitment to continuous education helps reinforce the importance of maintaining high standards within all manufacturing processes. As employees become more skilled at their roles, they contribute significantly towards enhancing overall product quality through diligent application of best practices.
Continuous Improvement through Quality Feedback
A critical aspect of implementing effective quality control processes is establishing channels for continuous feedback regarding product performance and inspection results. Regularly collecting data from inspections allows manufacturers to identify trends or recurring issues that may require immediate attention or long-term solutions focused on improving overall production efficiency. By analyzing this feedback, companies can make informed decisions that drive product enhancements while minimizing waste.
In addition to internal feedback mechanisms, seeking input from customers can provide invaluable insights into how products are perceived once they reach the market. Engaging customers through surveys or direct communication fosters trust while allowing manufacturers to understand areas needing improvement better—this cycle creates an environment where both product excellence and customer satisfaction thrive together harmoniously under robust quality management protocols.
Lastly, fostering an organizational culture centered around continuous improvement encourages everyone involved—from line workers up through management—to take ownership over their roles concerning both production output and adherence to established standards for both quality control and inspection practices alike.
Quality Inspection Best Practices
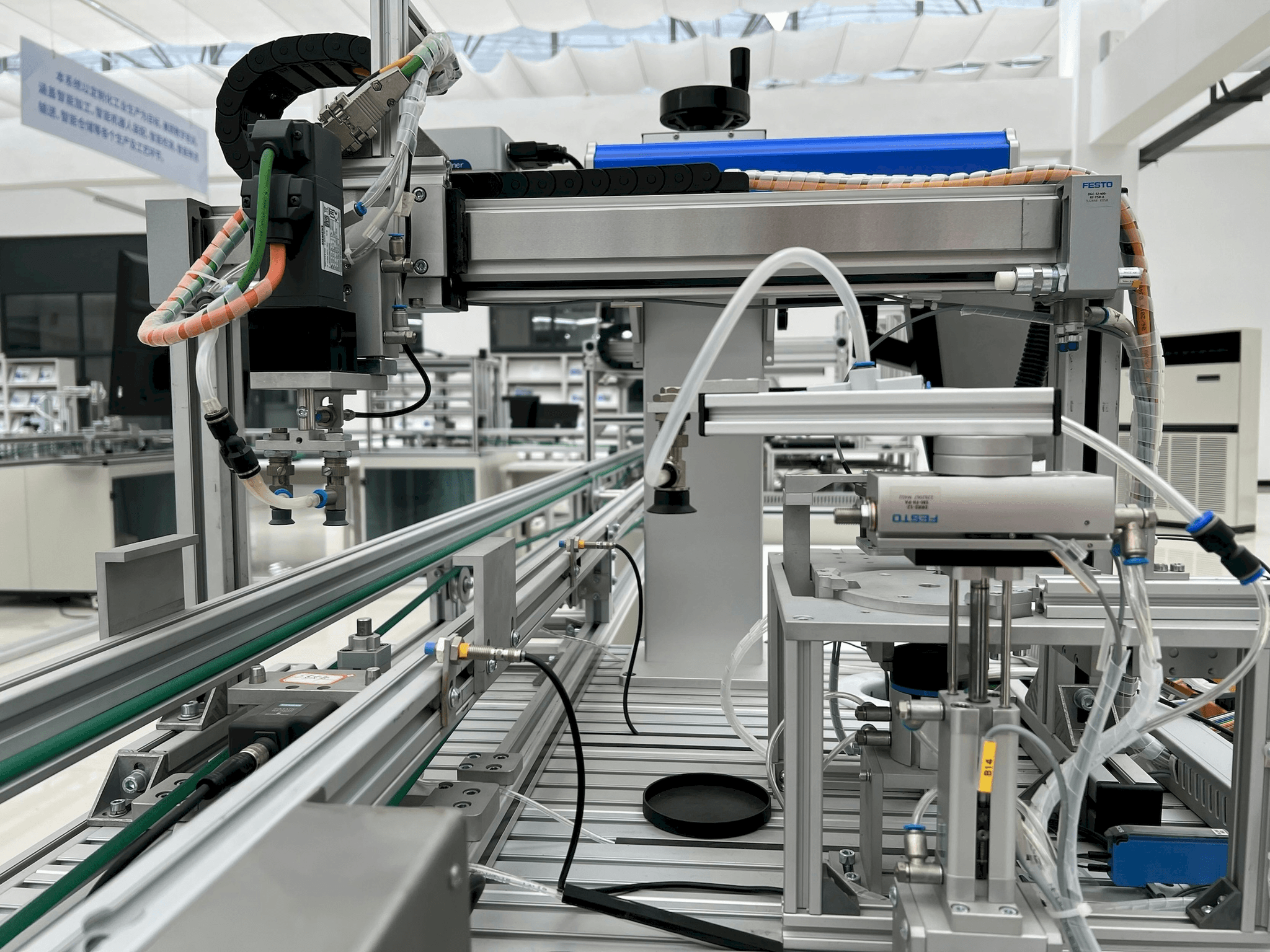
In the realm of manufacturing, quality control and inspection are non-negotiable pillars that uphold product integrity and customer satisfaction. Implementing best practices in quality inspection not only ensures compliance but also fosters a culture of continuous improvement. This section delves into the essential aspects of quality inspection that can significantly enhance overall manufacturing practices.
Importance of Pre-production Quality Inspection
Pre-production quality inspection is a critical step in the manufacturing process that often gets overlooked. By assessing materials and components before production begins, manufacturers can identify potential issues early on, saving time and resources down the line. This proactive approach to quality control reduces the risk of defects, ensuring that only high-quality materials enter the production phase.
Furthermore, engaging in pre-production inspections helps establish strong relationships with suppliers by setting clear expectations for quality and control from the outset. It also provides an opportunity for manufacturers to educate their partners about their specific standards, fostering a collaborative environment focused on achieving excellence. Ultimately, prioritizing pre-production quality inspection lays a solid foundation for effective quality management throughout the entire production cycle.
In-line vs. Final Inspection Techniques
In-line inspections occur during various stages of production, allowing for real-time feedback and immediate corrections if any discrepancies arise. This technique minimizes waste and enhances efficiency by addressing potential issues before they escalate into larger problems.
On the other hand, final inspections take place after production is complete but before products are shipped out to customers. While this method acts as a safety net to catch any remaining defects, it may lead to higher costs if significant issues are discovered at this late stage. Striking a balance between in-line and final inspections allows manufacturers to optimize their approach to quality control while ensuring that products meet stringent standards before reaching consumers.
Leveraging Technology in Quality Control and Inspection
In today's fast-paced manufacturing environment, leveraging technology in quality control and inspection has become indispensable for maintaining high standards of product integrity. Advanced tools such as automated inspection systems and data analytics software streamline processes while providing valuable insights into performance metrics related to quality management. By utilizing these technologies, manufacturers can enhance accuracy during inspections while reducing human error associated with traditional methods.
Moreover, integrating technology enables real-time monitoring of production lines through IoT devices that track performance indicators continuously—allowing teams to respond swiftly when deviations occur from established norms. Embracing digital solutions not only improves efficiency but also empowers employees working within quality control jobs by equipping them with tools that enhance their capabilities in identifying areas for improvement quickly. Ultimately, investing in technological advancements strengthens overall efforts toward achieving optimal levels of both quality control and inspection.
Challenges in Quality Control
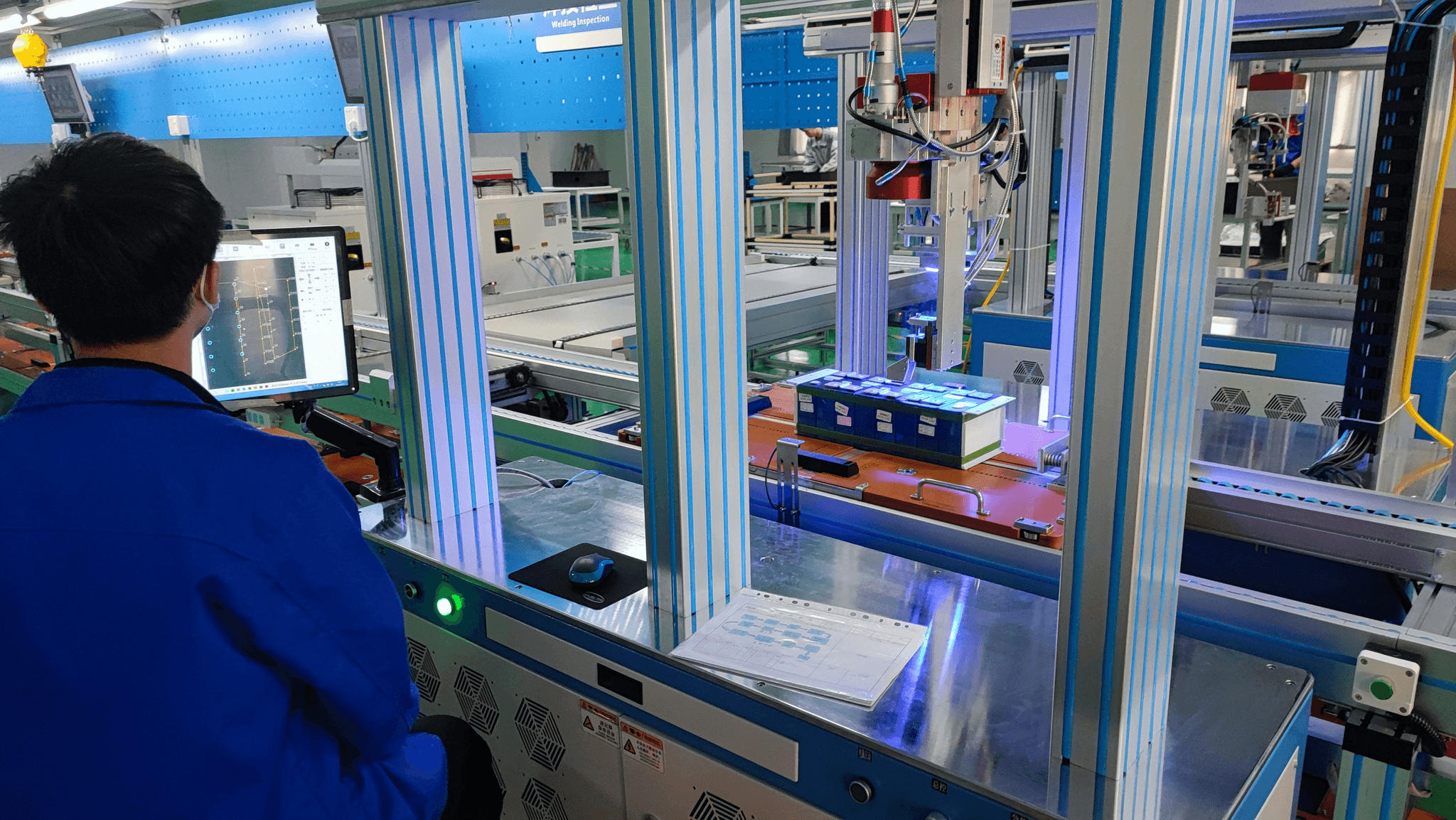
Quality control and inspection processes are essential for maintaining high standards in manufacturing, yet they face several challenges that can hinder effectiveness. Common issues in manufacturing quality often stem from inconsistent practices, lack of training, and inadequate communication between teams. These factors can lead to defects, increased costs, and ultimately a decline in customer satisfaction.
Common Issues in Manufacturing Quality
In the realm of quality control, common issues such as equipment malfunction, human error, and insufficient documentation can wreak havoc on production lines. For instance, when employees are not adequately trained for their quality control jobs, they may overlook critical aspects of quality inspection. Additionally, variations in raw materials can introduce inconsistencies that undermine even the best manufacturing practices.
Another prevalent challenge is the resistance to change within organizations. Employees may be accustomed to traditional methods of quality management and might resist adopting new strategies or technologies that could enhance quality control and inspection processes. This reluctance can stifle innovation and prevent companies from achieving optimal levels of efficiency and product integrity.
Navigating Regulatory Standards and Compliance
Regulatory standards play a crucial role in shaping effective quality control practices across industries; however, navigating these often-complex guidelines can be daunting for manufacturers. Compliance with regulations requires a thorough understanding of both local and international laws concerning product safety and quality assurance measures. Failure to adhere to these standards not only jeopardizes product integrity but also exposes companies to legal repercussions.
Moreover, staying updated with evolving regulations demands continuous training for employees involved in quality management systems. This is where many organizations falter—failing to provide adequate resources for ongoing education leaves teams ill-prepared to meet compliance requirements effectively. As a result, companies risk falling behind their competitors who prioritize robust regulatory adherence alongside effective quality control.
The Role of China Inspection Pro in Quality Assurance
China Inspection Pro has emerged as a pivotal player in addressing challenges related to quality control and inspection within the manufacturing sector. By offering comprehensive services that encompass pre-production checks through final inspections, they help ensure products meet stringent international standards before reaching consumers’ hands. Their expertise allows manufacturers to streamline their processes while enhancing overall product quality through rigorous evaluation methods.
Additionally, China Inspection Pro leverages technology-driven solutions that facilitate real-time monitoring of production lines—an invaluable asset for businesses striving for excellence in their manufacturing practices. By utilizing data analytics tools alongside traditional inspection techniques, they provide actionable insights that empower organizations to refine their approaches towards both quality management and compliance with industry regulations.
Ultimately, as manufacturers continue facing challenges within the realm of quality control, partnerships with specialized agencies like China Inspection Pro will become increasingly vital for sustaining competitive advantage while ensuring top-notch product delivery.
Conclusion
In the ever-evolving landscape of manufacturing, quality control and inspection stand as pillars of success. The future of quality control lies in embracing new technologies and methodologies that enhance efficiency while ensuring product excellence. As industries adapt to changing demands, a robust quality management system will be essential for maintaining high standards in manufacturing practices.
The Future of Quality Control in Manufacturing
The future of quality control is increasingly intertwined with advancements in artificial intelligence and machine learning, promising more accurate inspections and data analysis. Companies are recognizing that investing in innovative tools can streamline their quality control processes, reducing human error and increasing reliability. As we move forward, integrating these technologies into existing frameworks will redefine how we approach quality control jobs across the sector.
Enhancing Product Quality through Best Practices
To truly enhance product quality, manufacturers must adopt best practices that prioritize both prevention and detection of defects through effective quality inspection techniques. Implementing rigorous training programs ensures that employees understand the importance of their roles within the broader context of quality and control. By fostering an environment where continuous improvement is celebrated, organizations can consistently elevate their standards and outcomes.
Building a Culture of Quality and Control
Creating a culture centered around quality and control requires commitment from all levels of an organization—from leadership to frontline workers. Encouraging open communication about challenges faced in achieving high-quality outputs fosters collaboration and innovation among teams involved in quality control and inspection processes. Ultimately, when every employee feels responsible for maintaining high standards, it leads to improved morale and exceptional products that resonate with consumers.
