Introduction
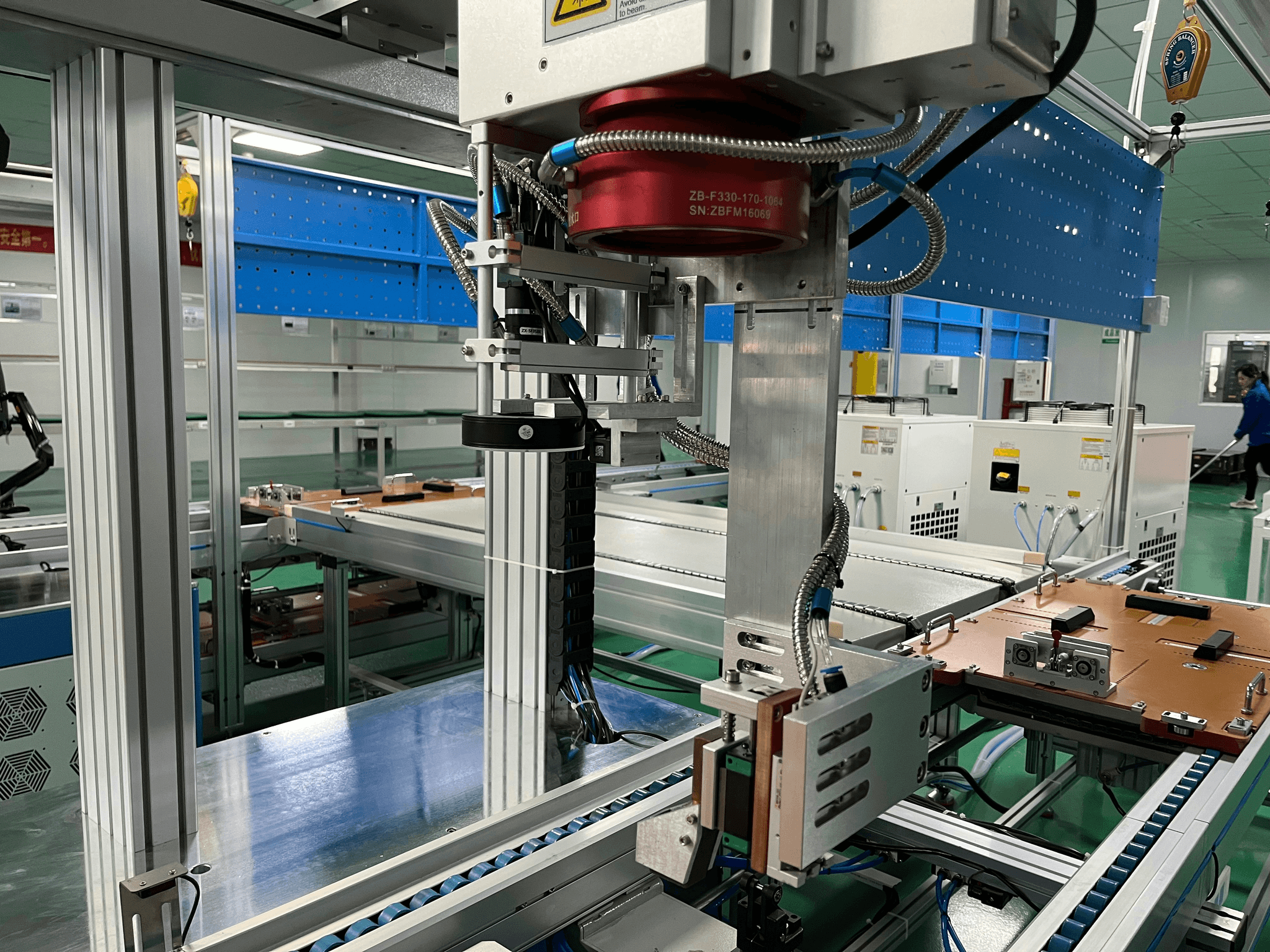
In the intricate dance of manufacturing, understanding the nuances between inspection and quality control is paramount. While both play crucial roles in ensuring product excellence, they serve distinct functions within the broader framework of quality assurance. By grasping these differences, businesses can enhance their processes and ultimately deliver superior products.
Understanding Inspection vs Quality Control
Inspection and quality control often get tossed around as interchangeable terms, but they embody different aspects of the quality assurance spectrum. Inspection is primarily focused on examining products to ensure they meet predetermined standards; it's about catching defects before they become a problem. On the other hand, quality control (QC) encompasses a broader range of activities aimed at preventing defects throughout the manufacturing process, ensuring that every stage adheres to established quality benchmarks.
The Role of Quality Assurance
Quality assurance (QA) serves as the backbone of effective manufacturing practices by establishing systematic processes that guarantee product integrity. It goes beyond mere inspection and QC by emphasizing proactive measures to prevent issues from arising in the first place. By implementing robust QA strategies, organizations can foster a culture of continuous improvement that not only enhances product quality but also boosts operational efficiency.
Why It Matters in Manufacturing
The significance of inspection and quality control cannot be overstated in today’s competitive manufacturing landscape. Effective QA practices lead to reduced waste, lower costs, and improved customer satisfaction—key ingredients for success in any industry. As customers become increasingly discerning about product quality, manufacturers must prioritize comprehensive inspection and QC measures to maintain their reputation and market position.
Defining Inspection and Quality Control
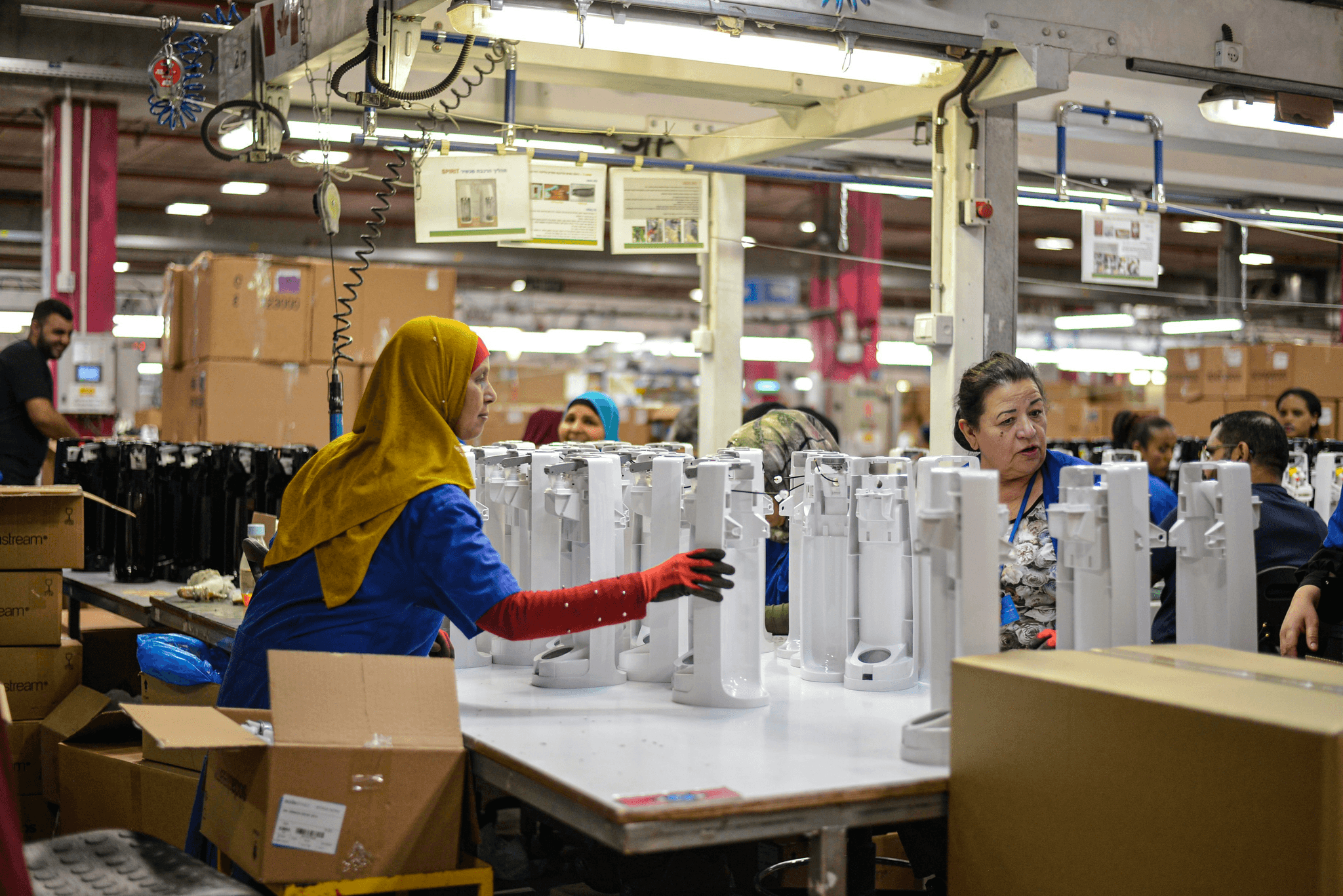

In the realm of manufacturing, understanding the distinction between inspection and quality control is essential. While both are integral to maintaining high standards, they serve different purposes within the broader framework of quality assurance. By defining these concepts, we can better appreciate their roles in ensuring product excellence and customer satisfaction.
What is Inspection?
Inspection refers to the systematic examination of products or processes to ensure they meet specified standards and requirements. This process often involves visual checks, measurements, or tests conducted at various stages of production. Ultimately, inspection acts as a safety net that catches defects before they escalate into larger issues—an essential component of effective quality control.
Understanding Quality Control Process
Quality control (QC) encompasses a series of activities designed to monitor and manage product quality throughout the manufacturing process. This includes establishing benchmarks for acceptable quality levels, conducting inspections at critical points, and implementing corrective actions when deviations occur. An effective QA quality assurance strategy integrates these elements to create a robust framework that not only identifies defects but also fosters continuous improvement.
The Importance of Quality in Manufacturing
Quality in manufacturing isn't just about meeting specifications; it's about building trust with customers and maintaining brand integrity. High-quality products lead to increased customer satisfaction, repeat business, and positive word-of-mouth referrals—all vital for long-term success. By prioritizing inspection and quality control measures within their operations, manufacturers can enhance their reputation while minimizing costs associated with returns or rework due to poor-quality outputs.
The Goals of Inspection and Quality Control

In the realm of manufacturing, the goals of inspection and quality control (QC) are paramount for ensuring that products meet established standards and customer expectations. Quality assurance (QA) serves as a backbone for these processes, providing a structured approach to identifying and rectifying issues before they escalate into costly problems. By focusing on these goals, businesses can enhance their operational efficiency while promoting a culture of quality and assurance throughout their organization.
Ensuring Compliance and Standards
One primary goal of inspection and quality control is to ensure compliance with industry standards and regulations. This involves conducting thorough inspections at various stages of production to verify that materials, processes, and final products adhere to specified guidelines. By implementing robust QA quality systems, companies can minimize risks associated with non-compliance, which often leads to legal ramifications or product recalls.
Moreover, maintaining compliance not only protects the company from potential fines but also fosters trust among consumers who expect high-quality products. Regular inspections help uphold industry standards by identifying deviations early in the production process. Ultimately, effective QC practices contribute significantly to building a reputation for reliability in the marketplace.
Detecting Defects Before Production
Another essential goal of inspection and quality control is detecting defects before they reach the consumer. Early identification of flaws allows manufacturers to address issues promptly rather than waiting until after production is complete—an approach that can save time and resources in the long run. This proactive stance is where QA assurance shines; it empowers teams to implement corrective measures swiftly when defects are identified during inspections.
By employing various methods such as visual inspections or statistical process control techniques, companies can pinpoint areas needing improvement before they escalate into major problems. The result? A smoother production process with fewer interruptions due to defective items slipping through the cracks—ultimately leading to increased efficiency across operations.
Boosting Customer Satisfaction
Boosting customer satisfaction is perhaps one of the most significant goals tied to effective inspection and quality control practices. When customers receive high-quality products that meet their expectations consistently, they are more likely to develop brand loyalty—a crucial factor in today’s competitive market landscape. Implementing rigorous QC measures ensures that every item delivered aligns with customer requirements while minimizing returns due to defects or dissatisfaction.
Furthermore, positive experiences directly correlate with enhanced brand reputation; satisfied customers often share their experiences through word-of-mouth referrals or online reviews—free marketing gold! In this way, investing time into comprehensive QA quality assurance strategies ultimately pays off by cultivating lasting relationships with consumers who appreciate commitment towards delivering excellence consistently.
Methods of Inspection and Quality Control
In the realm of manufacturing, effective inspection and quality control are vital to ensuring that products meet established standards. Various methods are employed to achieve this, each playing a crucial role in the overarching framework of quality assurance. Understanding these methods helps businesses maintain high levels of quality and assurance throughout their production processes.
Visual Inspection Techniques
Visual inspection techniques are among the most fundamental methods in inspection and quality control. This approach involves trained personnel examining products or components for visible defects, ensuring that they adhere to quality standards. While it may seem straightforward, the effectiveness of visual inspections relies heavily on the skills and experience of the inspectors involved.
These techniques can be enhanced through structured guidelines and checklists, helping inspectors identify common issues quickly. For example, using standardized criteria ensures consistency across multiple inspections, reinforcing overall quality assurance efforts. Additionally, integrating visual inspection with other methods can significantly boost the reliability of qc quality control processes.
Incorporating visual aids like magnifying glasses or digital imaging tools can further elevate these inspections' capabilities. As a result, manufacturers can catch defects early in production, ultimately driving customer satisfaction higher through improved product reliability.
Statistical Process Control
Statistical process control (SPC) is another powerful method used in both inspection and quality control that leverages data analysis to monitor production processes. By utilizing statistical techniques to evaluate process performance, manufacturers can identify variations that may indicate potential issues before they escalate into significant problems. This proactive approach not only enhances product quality but also streamlines operations by minimizing waste.
SPC involves collecting data from various stages of production and analyzing it using control charts to visualize trends over time. When deviations from established norms occur, immediate corrective actions can be taken—this is where qa assurance shines as a critical component in maintaining consistent output levels while adhering to compliance standards. Moreover, SPC fosters a culture of continuous improvement within organizations by encouraging teams to analyze their processes regularly.
The implementation of SPC requires training staff on how to interpret data effectively; this investment pays off as employees become more adept at recognizing patterns that affect overall product quality. In turn, this knowledge contributes significantly to achieving better outcomes in both qc quality control measures and broader manufacturing goals.
The Role of Technology in Quality Assurance
Technology has revolutionized the landscape of inspection and quality control by introducing innovative tools designed to enhance accuracy and efficiency in qa quality assurance practices. Automated systems such as robotic arms equipped with sensors can conduct inspections at speeds far surpassing human capabilities while maintaining high precision levels—reducing human error significantly during the process.
Moreover, software solutions enable real-time monitoring and analysis of production lines through advanced algorithms that assess data continuously for any anomalies or deviations from set parameters related to product specifications or compliance requirements. This level of automation not only improves operational efficiency but also allows teams more time for strategic decision-making concerning qc quality control initiatives.
As technology advances further into areas like artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML), its impact on inspection methods will only grow stronger—enabling predictive maintenance strategies based on historical data trends rather than reactive approaches after issues arise. Embracing these technological advancements will ensure businesses remain competitive while consistently delivering high-quality products aligned with customer expectations regarding both safety standards and overall performance.
The Impact of Inspection and Quality Control on Business
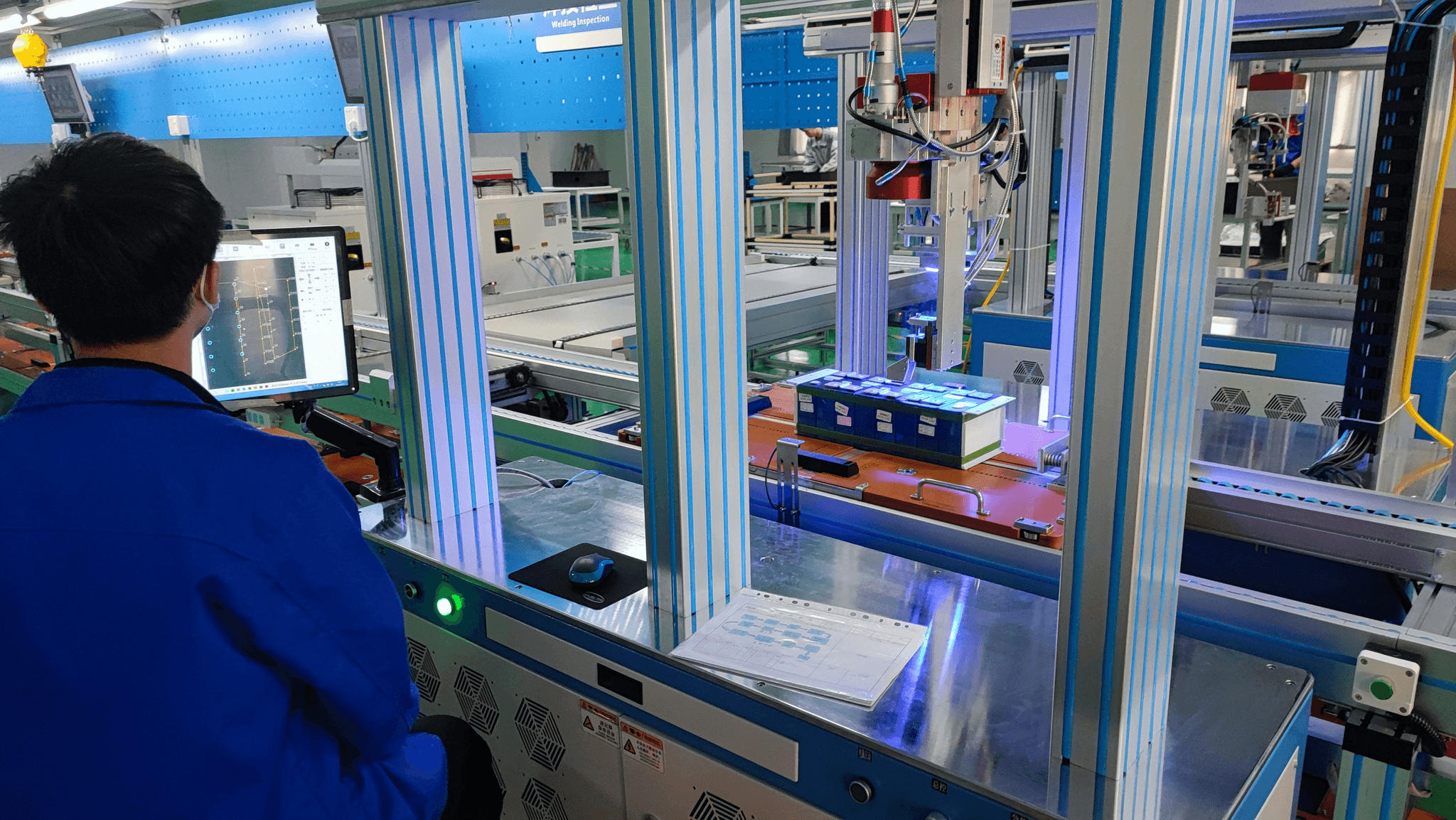
In the competitive landscape of manufacturing, the impact of inspection and quality control (QC) cannot be overstated. Effective quality assurance (QA) practices not only streamline operations but also lead to significant cost savings. By prioritizing QA quality measures, businesses can avoid costly recalls and defects that might tarnish their reputation.
Cost Savings Through Effective QC
Implementing robust inspection and quality control processes can yield substantial cost savings for manufacturers. When companies invest in effective QC measures, they reduce waste, minimize rework, and ultimately lower production costs. Moreover, by detecting defects early through rigorous inspection techniques, businesses can prevent expensive post-production fixes that could have been avoided with proper QA quality assurance.
The long-term financial benefits of maintaining high standards in quality control are clear; fewer defects mean less downtime and a smoother production flow. This efficiency translates into increased profitability as resources are utilized more effectively. Therefore, embracing a culture of quality and assurance not only enhances operational efficiency but also safeguards the bottom line.
Enhancing Brand Reputation
A commitment to thorough inspection and quality control significantly enhances a brand's reputation in the market. Consumers today are more discerning than ever; they seek products that meet high-quality standards consistently. By prioritizing QA assurance practices, companies signal to customers that they value excellence, leading to increased trust and loyalty.
When brands deliver products that exceed customer expectations due to effective QC processes, word-of-mouth marketing becomes a powerful ally. Satisfied customers are likely to share their positive experiences with others, boosting brand visibility and credibility in an increasingly crowded marketplace. Ultimately, investing in robust inspection methods contributes not just to product integrity but also fortifies the overall brand image.
Case Study: China Inspection Pro
To illustrate the profound impact of inspection and quality control on business success, consider China Inspection Pro (CIP), a leading provider of QA services in Asia. With a focus on comprehensive QC solutions tailored for various industries, CIP has helped numerous companies enhance their product standards while reducing operational costs significantly. Their meticulous approach to inspection ensures compliance with international regulations while fostering trust between manufacturers and consumers alike.
Through its innovative use of technology in QA quality assurance processes—such as automated inspections—CIP has set new benchmarks for efficiency within the industry. By sharing data-driven insights with clients regarding potential areas for improvement in their production lines, they've enabled businesses to make informed decisions about their operations swiftly. This case study exemplifies how effective qc quality control practices can lead not only to improved financial outcomes but also foster long-lasting client relationships built on trust.
Best Practices for Effective Inspection and Quality Control
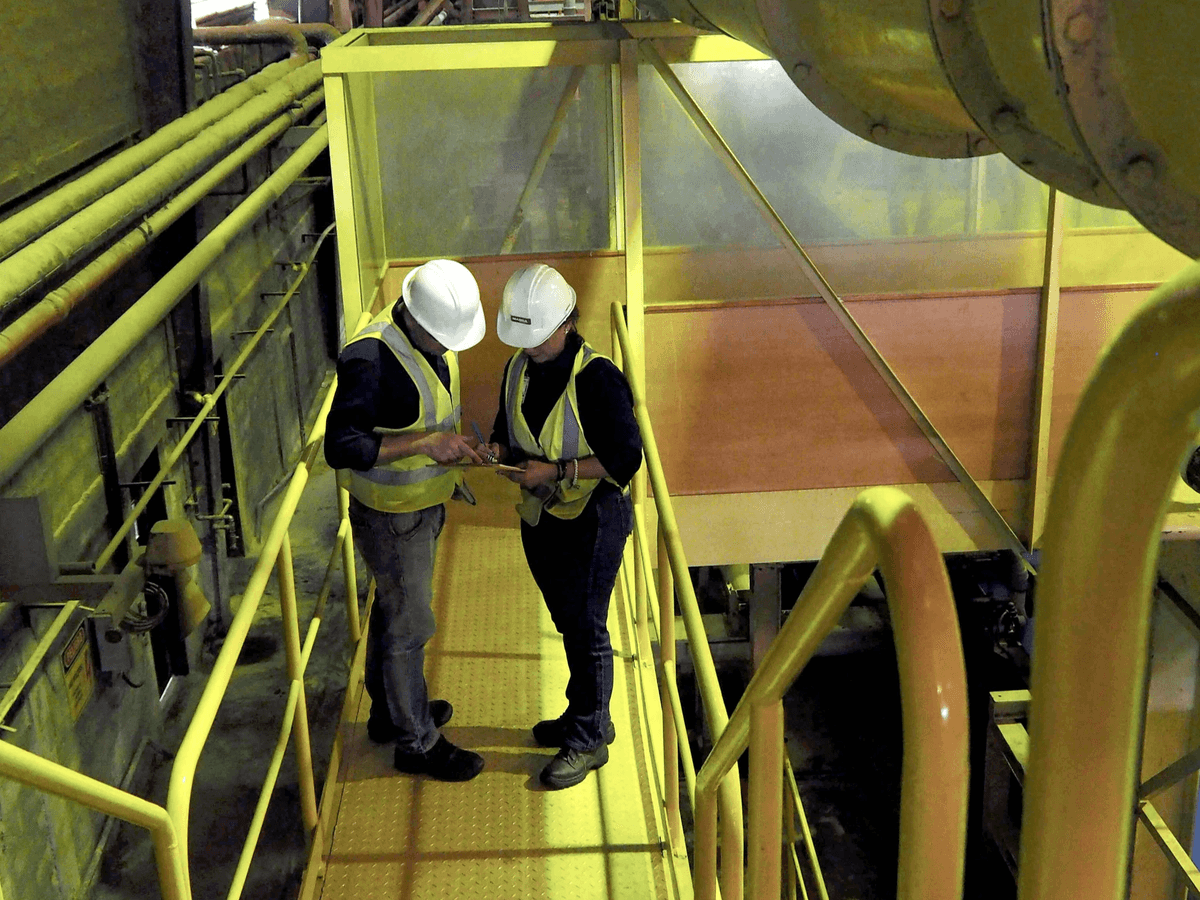

In the realm of manufacturing, effective inspection and quality control (QC) are paramount to ensuring products meet established standards. Implementing best practices not only enhances the efficiency of quality assurance (QA) processes but also fosters a culture of continuous improvement. Here, we explore essential strategies that can elevate your organization’s approach to quality and assurance.
Training Staff for Quality and Assurance
The backbone of any successful inspection and quality control system is a well-trained workforce. Investing in comprehensive training programs equips staff with the necessary skills to identify defects and understand QA quality processes thoroughly. Regular workshops on inspection techniques, QC methods, and the importance of quality assurance help cultivate an environment where every employee feels responsible for maintaining high standards.
Moreover, ongoing education ensures that team members stay updated on industry trends and technological advancements related to quality control. This knowledge empowers them to make informed decisions that align with your company's commitment to excellence in QA assurance. Ultimately, a well-trained staff not only improves inspection outcomes but also boosts morale as employees take pride in their contributions to product quality.
Implementing Continuous Improvement Strategies
Continuous improvement is a cornerstone philosophy in both inspection and quality control practices. By adopting methodologies like Lean or Six Sigma, organizations can systematically enhance their QC processes while minimizing waste and inefficiencies. Regularly reviewing performance metrics allows teams to identify areas needing improvement, ensuring that QA quality remains at the forefront.
Moreover, fostering an organizational culture that encourages feedback plays a crucial role in driving continuous improvement strategies forward. Employees should feel empowered to suggest changes based on their firsthand experiences during inspections or while managing QC tasks. This collaborative approach not only leads to more innovative solutions but also strengthens team cohesion around shared goals of maintaining high-quality standards.
Leveraging Data for Better Decision-Making
In today's data-driven world, leveraging analytics is vital for effective inspection and quality control processes. By collecting and analyzing data from various stages of production, organizations can gain valuable insights into trends affecting product quality over time. This information enables managers to make informed decisions regarding process adjustments or resource allocation aimed at enhancing overall QA assurance.
Additionally, implementing advanced technologies such as machine learning can further improve data analysis capabilities within QC frameworks. Predictive analytics can help identify potential defects before they occur by recognizing patterns from historical data related to inspections or production runs. As companies harness the power of data analytics in their QA efforts, they position themselves for sustained success through improved decision-making regarding product integrity.
Conclusion
In wrapping up our discussion on inspection and quality control, it’s crucial to recognize the distinctive roles these processes play in ensuring product integrity. While inspection focuses on examining products to identify defects, quality control encompasses a broader spectrum of activities aimed at maintaining standards throughout the manufacturing process. Understanding these differences not only clarifies their individual contributions but also highlights how they work in tandem to uphold quality assurance.
Key Differences Between Inspection and QC
Inspection is often seen as a final checkpoint where products are scrutinized for defects before they reach consumers, serving as a safety net for quality assurance. In contrast, quality control involves ongoing processes that ensure every step of production meets predetermined standards and specifications. By distinguishing between inspection and QC, businesses can better allocate resources and implement strategies that enhance overall quality and assurance efforts.
The Essential Role of Quality Assurance
Quality assurance acts as the backbone of any successful manufacturing operation by establishing systematic processes that prevent defects from occurring in the first place. It ensures that both inspection and quality control are effectively integrated into the production workflow, creating a culture of continuous improvement. Without a robust QA framework, companies risk not only product failure but also damage to their reputations and customer trust.
Future Trends in Inspection and Quality Control
As we look ahead, advancements in technology are set to revolutionize inspection and quality control practices across industries. From AI-driven analytics to real-time monitoring systems, these innovations will enhance qa quality assurance efforts by providing deeper insights into production processes. The future will likely see a shift towards more proactive approaches in qc quality control, emphasizing prevention over detection—an evolution that promises higher efficiency and greater customer satisfaction.
