Introduction
In a world where food is both a basic necessity and a cultural cornerstone, the significance of food quality control cannot be overstated. Ensuring that every bite is safe, nutritious, and delicious is not just good practice; it’s essential for public health and trust in the food industry. As consumers become more discerning and regulations tighten, the need for robust food quality control measures has never been greater.
The Importance of Food Quality Control
Food quality control serves as the backbone of any successful food production operation. It encompasses everything from sourcing raw materials to final product packaging, ensuring that safety standards are met at every stage. With rising global concerns over foodborne illnesses and contamination, effective quality control systems are crucial to maintaining consumer confidence in our food supply.
Common Challenges in Food Safety
Despite its importance, the path to effective food quality control is fraught with challenges. Issues such as supply chain inconsistencies, inadequate training of staff, and evolving regulatory requirements can hinder even the most well-intentioned efforts. These challenges necessitate a proactive approach to identify vulnerabilities and implement solutions that safeguard both products and consumers alike.
Overview of Best Practices in Quality Control
To navigate these challenges successfully, businesses must adopt best practices in food quality control that are both comprehensive and adaptable. This includes strategies like establishing clear protocols for inspections, fostering strong supplier relationships, and continuously training employees on safety standards. By embracing these practices, organizations can not only comply with regulations but also enhance their reputation for delivering high-quality products.
Understanding Food Quality Control
Food quality control is the backbone of the food industry, ensuring that products meet established standards for safety and quality. It encompasses a range of processes designed to monitor and maintain the integrity of food products from farm to table. The significance of food quality control cannot be overstated; it protects consumer health, enhances brand reputation, and ensures compliance with regulatory requirements.
Definition and Significance
At its core, food quality control refers to the systematic approach used to ensure that food products are safe for consumption and meet specific quality criteria. This involves various practices aimed at preventing contamination, ensuring freshness, and maintaining consistency in flavor and texture. The significance of effective food quality control lies in its ability to safeguard public health while also boosting consumer confidence in brands that prioritize safety.
Key Components of Quality Control
Effective food quality control comprises several key components that work together harmoniously. These include raw material inspection, process monitoring, product testing, and traceability systems. Each element plays a vital role in identifying potential issues before they escalate into larger problems, ultimately helping businesses uphold their commitment to high standards in food safety.
Regulatory Standards and Compliance
Navigating the maze of regulatory standards is essential for any business involved in food production or distribution. Compliance with guidelines set by organizations such as the FDA or USDA ensures that products not only meet safety benchmarks but also align with industry best practices for food quality control. Adhering to these regulations is crucial not just for avoiding penalties but also for fostering trust among consumers who expect nothing less than safe and high-quality products.
Implementing Effective Quality Management Systems

In the realm of food quality control, implementing effective quality management systems is crucial for ensuring safety and consistency. These systems not only help organizations meet regulatory standards but also enhance customer trust and satisfaction. By embedding quality management practices into their operations, companies can mitigate risks and improve overall performance.
ISO 22000 and Its Impact
ISO 22000 is an internationally recognized standard that outlines the requirements for a food safety management system (FSMS). This framework integrates principles from HACCP (Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point) and focuses on continuous improvement, making it a cornerstone in food quality control. By adopting ISO 22000, organizations can demonstrate their commitment to food safety, which ultimately leads to enhanced consumer confidence and market competitiveness.
The impact of ISO 22000 extends beyond compliance; it fosters a culture of proactive risk management within an organization. Companies that implement this standard often experience reduced incidents of contamination and improved operational efficiency. As a result, they not only protect consumers but also bolster their brand reputation in a highly competitive marketplace.
The Role of HACCP in Food Safety
HACCP plays a pivotal role in food quality control by identifying potential hazards at every stage of production—from raw materials to finished products. This systematic approach allows businesses to establish critical control points where measures can be taken to prevent or minimize risks associated with food safety. The implementation of HACCP is not just about compliance; it’s about creating safer products for consumers while optimizing processes.
By focusing on preventive measures rather than reactive responses, HACCP significantly reduces the likelihood of contamination events occurring in the first place. Training staff on HACCP principles further enhances its effectiveness as employees become more aware of potential hazards during their daily tasks. Ultimately, integrating HACCP into an organization's culture reinforces its commitment to maintaining high standards in food quality control.
Continuous Improvement Strategies
Continuous improvement strategies are essential for maintaining excellence in food quality control over time. Organizations should adopt methodologies such as Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) or Six Sigma to regularly assess processes and outcomes related to product safety and quality. By fostering a mindset focused on ongoing enhancement, companies can adapt swiftly to changes in regulations or consumer expectations.
Engaging employees at all levels in continuous improvement initiatives is vital for success; when staff members feel empowered to contribute ideas, innovation flourishes within the organization. Regular audits and feedback loops also serve as mechanisms for identifying areas needing attention while celebrating successes along the way—creating a balanced approach toward progress in food quality control efforts.
In conclusion, implementing effective quality management systems like ISO 22000 and HACCP while embracing continuous improvement strategies sets the foundation for robust food safety practices that resonate with consumers’ needs today.
Importance of Supplier Quality Assurance
Supplier quality assurance is a cornerstone of effective food quality control, ensuring that the ingredients entering the production line meet safety and quality standards. A robust supplier evaluation process can help mitigate risks associated with food safety breaches, which can have dire consequences for both consumers and brands alike. By prioritizing supplier quality, companies can maintain their reputation and ensure consistent product excellence.
Evaluating Suppliers and Ingredients
When it comes to food quality control, evaluating suppliers and their ingredients is paramount. Companies must conduct thorough assessments of potential suppliers, looking into their sourcing practices, certifications, and past performance regarding food safety standards. This meticulous vetting process helps to identify reliable partners who share a commitment to maintaining high-quality ingredients that align with regulatory requirements.
Additionally, ongoing evaluations are essential as market conditions change and new suppliers emerge. Regular audits of suppliers not only ensure compliance but also foster a culture of accountability in the supply chain. By investing time in these evaluations, businesses can significantly reduce the risk of contamination or subpar ingredient sourcing that could jeopardize overall food quality control.
Establishing Clear Communication Channels
Clear communication channels between manufacturers and suppliers are vital for effective food quality control. Open lines of communication facilitate quick resolution of issues related to ingredient specifications or delivery schedules, minimizing disruptions in production processes. Moreover, fostering transparency encourages collaboration on best practices for maintaining product integrity throughout the supply chain.
Regular meetings or check-ins with suppliers can help reinforce expectations regarding food safety protocols and ingredient standards while allowing for feedback on both sides. This two-way dialogue builds trust and ensures that all parties remain aligned on shared goals concerning product quality. Ultimately, strong communication enhances supplier relationships and contributes positively to overall food quality control efforts.
Case Study: Starbucks and Supplier Relations
Starbucks exemplifies the significance of supplier quality assurance through its rigorous approach to sourcing ingredients globally while maintaining high standards in food quality control. The company has developed a comprehensive Supplier Code of Conduct that outlines expectations regarding ethical sourcing practices, environmental sustainability, and adherence to health regulations. By holding suppliers accountable to these criteria, Starbucks fosters relationships built on trust while ensuring consistent product excellence across all locations.
Additionally, Starbucks collaborates closely with its coffee farmers through programs aimed at improving agricultural practices while promoting social responsibility within communities where they source their beans. This not only strengthens supplier relations but also enhances the overall integrity of their products—a win-win scenario for everyone involved! As such examples show us how crucial it is for companies to prioritize supplier quality assurance as part of their broader strategy in achieving exceptional food quality control.
Training and Engaging Employees

In the realm of food quality control, employees play a pivotal role in ensuring that standards are met consistently. Their engagement and expertise can significantly influence the overall effectiveness of quality management systems. By investing in training and fostering a culture of accountability, organizations can enhance their food safety protocols.
The Role of Staff in Quality Control
Staff members are on the front lines of food quality control, directly interacting with products and processes daily. Their awareness and understanding of quality standards are crucial for identifying potential issues before they escalate into more significant problems. Empowering employees to take ownership of their roles not only boosts morale but also enhances the integrity of food safety practices throughout the organization.
Best Practices for Training Programs
Effective training programs should be tailored to meet the specific needs of each employee while reinforcing the importance of food quality control. Incorporating hands-on learning experiences, such as simulations or workshops, can significantly improve retention rates and practical application skills. Regularly updating training materials to reflect current regulations and industry best practices ensures that staff remain informed about evolving standards.
Employee Engagement Techniques
Engaging employees in discussions about food quality control fosters a sense of community and shared responsibility within an organization. Techniques such as recognition programs, team-building activities, and open forums for feedback can create an environment where staff feel valued and motivated to contribute to quality initiatives actively. By encouraging collaboration across departments, businesses can cultivate a culture that prioritizes excellence in food safety.
Leveraging Technology for Quality Control
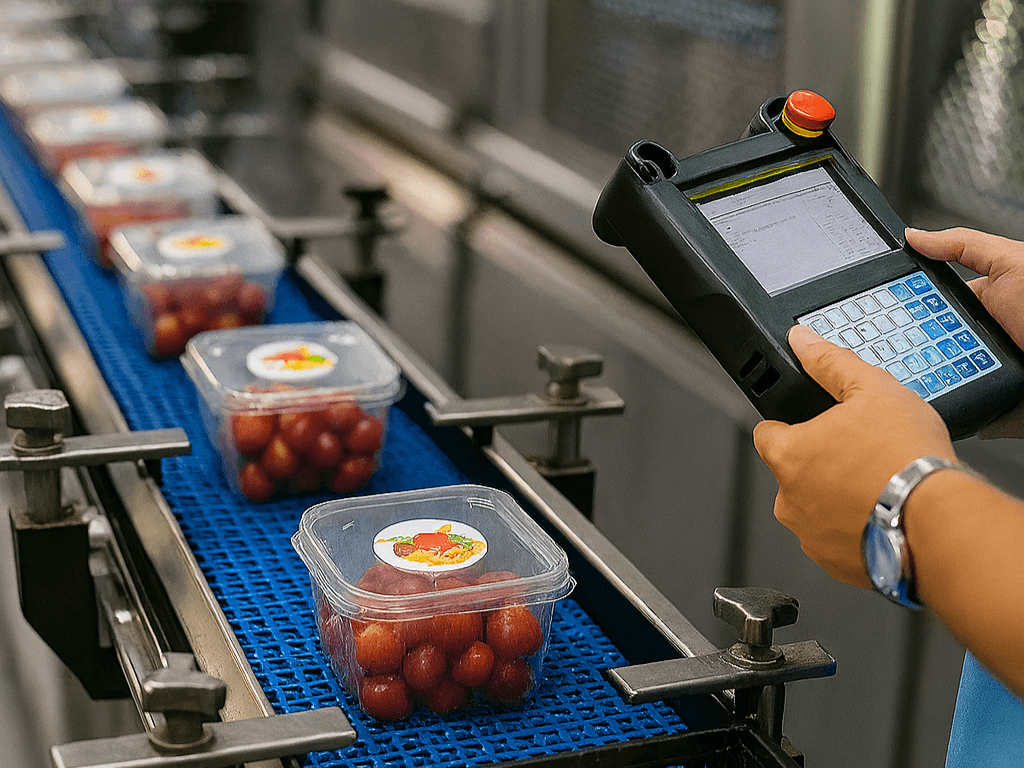
In today's fast-paced world, leveraging technology for food quality control is not just beneficial; it's essential. With the myriad of challenges facing the food industry, from supply chain disruptions to consumer demands for transparency, technology offers innovative solutions that enhance quality management systems. By integrating advanced tools and methodologies, companies can ensure that their food products meet stringent safety standards while maintaining high-quality levels.
Automation in Food Production
Automation has revolutionized food production processes, enabling businesses to maintain consistency and efficiency in their operations. Automated systems can monitor various aspects of production, from ingredient measurements to packaging processes, ensuring adherence to food quality control protocols. This reduces human error and allows staff to focus on more strategic tasks, ultimately leading to better quality assurance across the board.
Moreover, automation facilitates real-time monitoring and reporting of production metrics, which is crucial for maintaining compliance with regulatory standards. By employing automated technologies such as robotics and conveyor systems, companies can streamline workflows while enhancing the accuracy of their quality control measures. As a result, businesses can significantly improve their overall productivity without sacrificing the integrity of their products.
Utilizing Data Analytics for Quality
Data analytics has emerged as a game-changer in the realm of food quality control by providing insights that drive informed decision-making. By collecting and analyzing data from various stages of production—such as ingredient sourcing, processing conditions, and final product testing—companies can identify trends and potential issues before they escalate into larger problems. This proactive approach not only enhances product safety but also fosters continuous improvement in quality management practices.
Furthermore, predictive analytics allows organizations to anticipate fluctuations in demand or potential supply chain disruptions related to ingredient availability or safety recalls. With these insights at hand, businesses can adjust their operations accordingly to ensure consistent product availability while adhering to strict food quality control requirements. Ultimately, harnessing data analytics leads to smarter resource allocation and optimized processes that elevate overall product quality.
Partnering with China Inspection Pro for Inspections
Partnering with specialized organizations like China Inspection Pro adds an extra layer of assurance when it comes to maintaining high standards in food quality control. This partnership enables companies to access expert inspections that assess compliance with both local regulations and international standards—critical factors when dealing with global suppliers or markets. By leveraging such expertise during audits or inspections, businesses can identify weaknesses in their supply chain that might compromise food safety.
Additionally, working closely with inspection professionals helps establish benchmarks for supplier performance based on rigorous assessments tailored specifically for the food industry’s unique challenges. This collaboration fosters a culture of accountability among suppliers while ensuring that ingredients meet stringent criteria before reaching production lines. Consequently, this strategic alliance enhances overall confidence in product integrity while reinforcing commitment towards exemplary food quality control practices across all levels.
Conclusion
In the ever-evolving landscape of food quality control, the future holds promising advancements that will redefine industry standards. As consumer awareness grows, the demand for transparency and safety in food production will drive companies to adopt more robust quality management systems. The integration of innovative technologies and stringent regulatory frameworks will be pivotal in shaping a safer food supply chain.
The Future of Food Quality Control
Looking ahead, food quality control is poised to embrace cutting-edge technologies such as artificial intelligence and blockchain to enhance traceability and accountability. These innovations will not only streamline processes but also empower consumers with real-time information about their food sources. As we navigate this future, a proactive approach to quality assurance will be essential in mitigating risks associated with food safety.
Building a Culture of Quality
Creating a culture of quality within organizations is crucial for achieving consistent excellence in food quality control. This involves fostering an environment where every employee feels responsible for maintaining high standards and understands their role in the process. By prioritizing communication, collaboration, and continuous learning, companies can cultivate a workforce that is not only engaged but also committed to upholding the integrity of their products.
Embracing Innovation in Food Safety
To stay ahead of potential threats, embracing innovation in food safety practices is no longer optional; it’s a necessity. Companies must leverage advancements such as real-time monitoring systems and predictive analytics to identify issues before they escalate into larger problems. By adopting these innovative approaches, businesses can ensure that their commitment to food quality control remains unwavering while simultaneously meeting the evolving expectations of consumers.
