Introduction
In the rapidly evolving world of technology, electronic component testing has become a fundamental aspect of ensuring reliability and performance in various applications. Whether it’s a simple resistor or a complex integrated circuit, each electronic component plays a crucial role in the functionality of devices we use daily. By understanding the importance of testing circuit board components, we can enhance quality control and prevent costly failures down the line.
Importance of Electronic Component Testing
The significance of electronic component testing cannot be overstated; it serves as the backbone for maintaining product integrity and longevity. Proper testing methods for electronic components help identify defects early in the manufacturing process, reducing waste and ensuring that only high-quality products reach consumers. Moreover, thorough testing instills confidence in both manufacturers and end-users regarding the reliability of their electronic parts.
Understanding Electronic Components and Their Functions
To appreciate the nuances of electronic component testing, one must first grasp what these components are and their respective functions within a circuit. Electronic components like resistors, capacitors, inductors, integrated circuits, sensors, and actuators all serve distinct purposes that contribute to overall system performance. By understanding how these electronic parts interact with one another, engineers can better design tests that accurately assess their functionality.
Overview of Testing Methods for Electronic Components
There is an array of testing methods for electronic components that cater to different aspects of performance evaluation. Functional testing ensures that each component operates as intended under specified conditions, while in-circuit testing allows for early detection of issues during assembly. Additionally, automated test equipment streamlines the process by providing efficiency and consistency across large volumes of products—making it an invaluable asset in modern manufacturing environments.
Types of Electronic Components
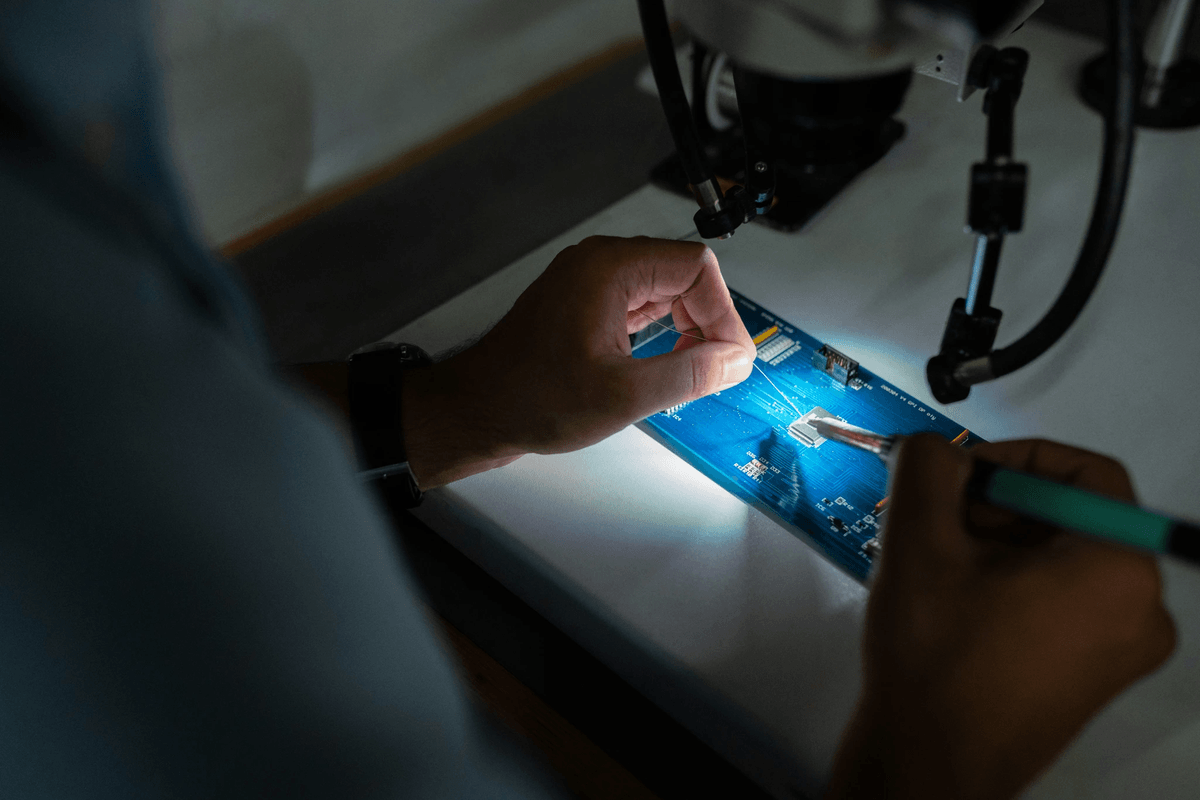
When diving into the world of electronic component testing, it’s crucial to understand the various types of electronic components that make up our circuits. These components are the building blocks of any electronic device, each serving a unique function and playing an essential role in overall performance. From passive elements like resistors and capacitors to sophisticated integrated circuits, the diversity is vast and fascinating.
Resistors, Capacitors, and Inductors
Resistors, capacitors, and inductors form the trio of passive components that are fundamental in circuit design and testing methods for electronic components. Resistors limit current flow while capacitors store electrical energy for later release; both are vital for managing voltage levels within a circuit. Inductors, on the other hand, store energy in a magnetic field when electrical current passes through them—each component plays its part in ensuring smooth operation during electronic component testing.
Testing circuit board components like resistors involves checking their resistance values against specified tolerances to ensure they function correctly within their designated roles. Capacitor testing often requires measuring capacitance values and assessing leakage currents to confirm reliability under operational conditions. Inductors can be tested by evaluating their inductance values and checking for any short circuits or open connections that could lead to performance issues.
Integrated Circuits and Their Impact
Integrated circuits (ICs) revolutionized electronics by combining multiple functions into a single chip, significantly reducing size while increasing performance capabilities. These tiny powerhouses contain numerous transistors that manage everything from simple logic operations to complex processing tasks found in modern devices. Given their complexity, effective electronic component testing becomes paramount; even a minor defect can lead to catastrophic failure.
Testing methods for electronic components involving ICs often include functional tests that assess whether they perform as intended under various conditions—think of it as putting them through an obstacle course! In-circuit testing is also vital here; it allows engineers to identify faults without removing ICs from their boards—a huge time-saver when dealing with intricate designs filled with numerous connections.
Sensors and Actuators
Sensors and actuators represent another critical category of electronic parts that bridge the gap between physical phenomena and digital systems. Sensors detect changes in environmental conditions—like temperature or motion—and convert these changes into signals interpretable by other devices or systems. Actuators take this one step further by converting electrical signals back into physical action, such as moving a motor or opening a valve.
Incorporating effective electronic component testing techniques is essential for both sensors and actuators to ensure accuracy and responsiveness over time. Testing circuit board components like sensors may involve calibrating their output signals against known standards while examining response times under different conditions. For actuators, functionality tests confirm they respond correctly when powered up—essentially making sure they do what they're told without throwing any tantrums!
Essential Testing Tools and Equipment
Multimeters: The Swiss Army Knife
Multimeters are often considered the Swiss Army knife of electronic component testing; their versatility is unmatched. These handy devices measure voltage, current, and resistance, making them indispensable for diagnosing issues with various electronic parts. Whether you're checking a resistor's value or troubleshooting power supply problems, a good multimeter is your best friend in the world of testing methods for electronic components.
The best multimeters come equipped with features like auto-ranging and data hold functions, which simplify measurements and improve accuracy. They can also test continuity and diodes, adding to their already impressive arsenal of capabilities. With a reliable multimeter at your side, you’ll be well-equipped to tackle any challenge that comes your way in testing circuit board components.
Oscilloscopes: Visualizing Circuit Action
While multimeters provide numerical data on electrical parameters, oscilloscopes take it a step further by allowing you to visualize circuit action in real-time. These devices display waveforms on a screen, enabling you to see how signals change over time—essential for analyzing complex electronic components like integrated circuits or sensors. With an oscilloscope, you can identify issues such as signal distortion or timing errors that might not be apparent from simple measurements alone.
Modern oscilloscopes come with advanced features such as digital storage capabilities and built-in analysis tools that enhance your ability to diagnose problems quickly and accurately. They also allow for triggering on specific events within a signal waveform—perfect for catching intermittent faults in testing methods for electronic components. In short, if you want to truly understand how your circuit board components behave under different conditions, an oscilloscope is an invaluable tool.
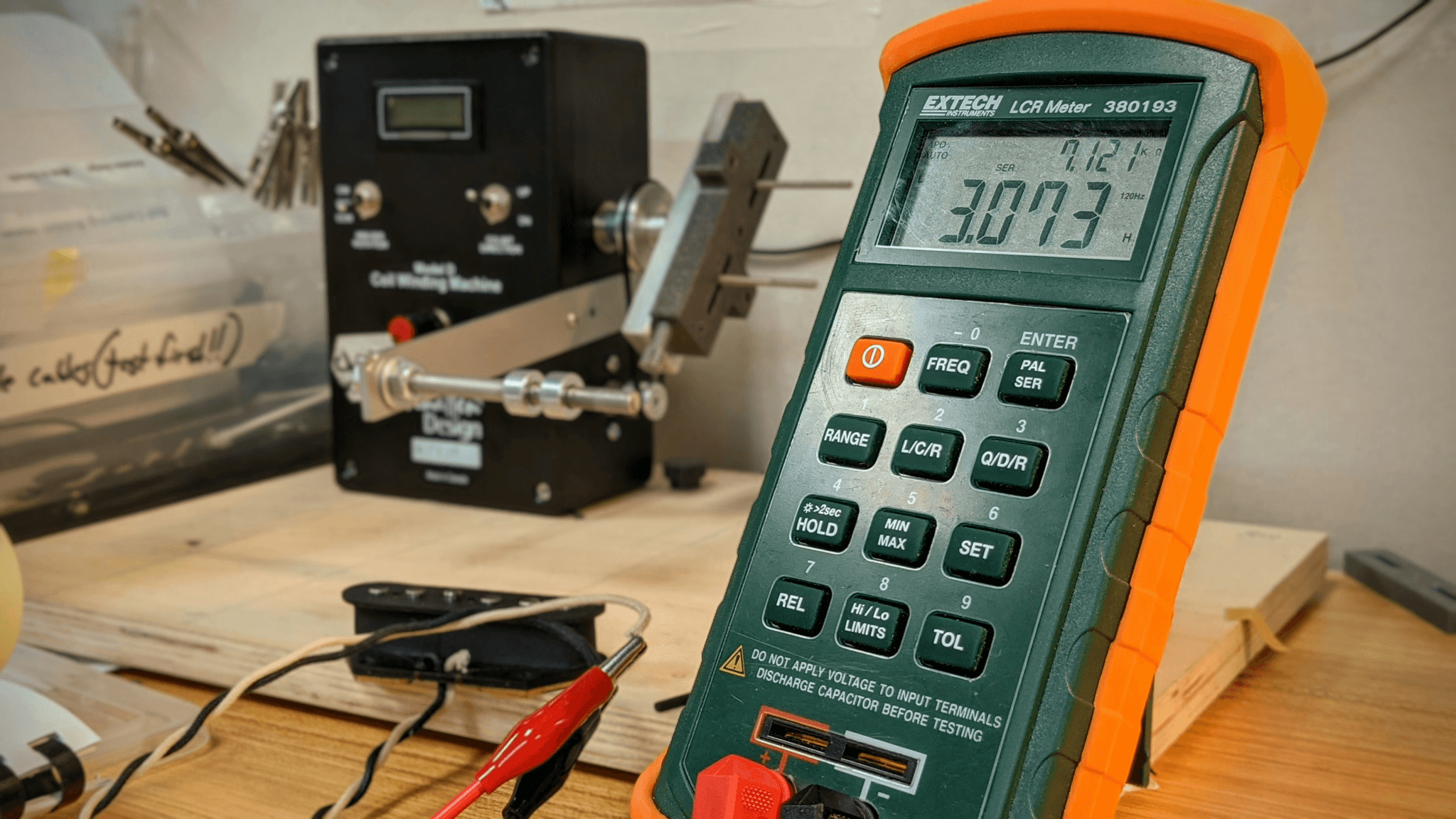
LCR Meters for Passive Components
When it comes to passive components like resistors, capacitors, and inductors, LCR meters shine as specialized instruments designed specifically for measuring inductance (L), capacitance (C), and resistance (R). These meters provide accurate readings crucial for assessing the performance of passive electronic parts during testing circuit board components. Unlike standard multimeters that may offer basic readings, LCR meters delve deeper into component characteristics like equivalent series resistance (ESR) or quality factor (Q).
Using an LCR meter can help identify faulty capacitors or resistors before they cause significant issues in a circuit design—a proactive approach that's essential in today's fast-paced electronics industry. Moreover, these meters often feature automatic measurement functions that save time while ensuring precision during tests—key elements when employing efficient testing methods for electronic components. For anyone serious about maintaining high-quality standards in their projects or products involving passive elements, investing in an LCR meter is undoubtedly worthwhile.
Testing Methods for Electronic Components

When it comes to electronic component testing, the methods you choose can greatly influence the effectiveness of your results. From ensuring that each electronic part functions as intended to identifying potential issues before they escalate, the right testing methods for electronic components are crucial. This section will delve into three primary approaches: functional testing, in-circuit testing, and automated test equipment.
Functional Testing: Ensuring Performance
Functional testing is like putting your electronic components through a rigorous workout to ensure they perform at their best. This method involves applying power and signals to the circuit board and observing whether the output matches expected results. By using functional testing techniques, engineers can validate that each electronic part operates correctly under various conditions, thereby ensuring reliable performance in real-world applications.
One of the key advantages of functional testing is its ability to identify problems that may not be apparent during visual inspections or simpler tests. For example, it can reveal issues such as incorrect voltage levels or response times that could lead to product failure down the line. Ultimately, this approach not only helps in maintaining quality control but also boosts consumer confidence in the functionality of electronic components.
In-Circuit Testing: Spotting Issues Early
In-circuit testing (ICT) is like having a backstage pass to your circuit board's inner workings—allowing you to spot issues before they become show-stoppers. This method involves probing individual components while they are still on the circuit board and checking for faults such as shorts or opens without removing them from their positions. In-circuit testing is particularly effective for detecting manufacturing defects early in production, saving time and costs associated with rework later on.
By employing ICT during assembly processes, manufacturers can significantly reduce the risk of defective products reaching consumers. It also allows for quicker iterations in design changes since faults can be identified almost immediately after assembly rather than waiting until functional tests are performed later on. Consequently, this early detection method enhances overall efficiency and reliability in electronic component testing.
Automated Test Equipment for Efficiency
Automated test equipment (ATE) takes electronic component testing up a notch by incorporating technology that speeds up and standardizes the evaluation process across multiple units simultaneously. Using software-controlled systems allows testers to run complex sequences quickly and accurately while minimizing human error—a win-win scenario! ATE is particularly beneficial when dealing with high volumes of production where consistency is key.
The beauty of ATE lies not just in its speed but also in its ability to gather extensive data during tests—data that can provide insights into long-term reliability trends across batches of electronic parts. With automation taking over repetitive tasks, engineers have more time to focus on analyzing results and improving design strategies based on empirical evidence collected during these tests. In essence, leveraging automated test equipment enhances both productivity and quality assurance within any electronics manufacturing environment.
Best Practices for Testing Circuit Board Components

When it comes to testing circuit board components, having a solid strategy is essential. A well-structured approach not only improves accuracy but also enhances the overall efficiency of electronic component testing. By following best practices, you can ensure that your electronic parts meet the required standards and function as intended.
Developing a Testing Plan
Creating a comprehensive testing plan is the cornerstone of effective electronic component testing. This plan should outline specific objectives, methodologies, and timelines for testing each type of electronic component on your circuit board. By identifying potential issues early in the process, you can choose appropriate testing methods for electronic components that will save time and resources down the line.
A good testing plan also includes criteria for success and failure, which helps streamline decision-making during the evaluation process. Furthermore, it’s important to involve all relevant stakeholders in developing this plan to ensure everyone is on the same page regarding expectations and responsibilities. Ultimately, a thoughtful approach to planning can significantly improve your outcomes when dealing with complex circuit board assemblies.
Documenting Results for Future Reference
Documentation is an often-overlooked aspect of electronic component testing that can have lasting benefits. Keeping detailed records of test results allows you to track performance over time and identify trends or recurring issues with specific electronic parts or components. This historical data not only aids in troubleshooting but also provides valuable insights when designing future products or iterations.
Moreover, thorough documentation serves as an excellent reference point during audits or inspections—whether internal or external—ensuring compliance with industry standards and regulations. By maintaining a systematic approach to recording results, you empower your team to make informed decisions based on past experiences rather than relying solely on memory or anecdotal evidence. In essence, good documentation practices are key to elevating your quality assurance efforts.
Following Safety Protocols During Testing
Safety should always be at the forefront when conducting tests on circuit board components; after all, mishaps can lead not just to damaged equipment but also pose risks to personnel involved in electronic component testing activities. Establishing clear safety protocols ensures that everyone understands how to handle equipment properly while minimizing hazards associated with electrical work.
This includes using appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), ensuring proper grounding of circuits before conducting tests, and being aware of potential hazards related to specific electronic components being tested. Regular training sessions can help reinforce these safety measures among team members while fostering a culture where safety is prioritized over expediency during testing procedures. Remember: no successful test result is worth compromising safety!
Leveraging Third-Party Inspection Services
In the world of electronic component testing, partnering with third-party inspection services can be a game-changer. These companies bring specialized expertise and resources that can elevate the quality of your electronic parts, ensuring that every resistor, capacitor, and integrated circuit meets rigorous standards. By leveraging these services, manufacturers can focus on their core competencies while leaving the nitty-gritty details of testing circuit board components to the pros.
Benefits of Working with China Inspection Pro
China Inspection Pro offers a plethora of benefits for businesses involved in electronic component testing. One major advantage is their extensive experience in evaluating a wide range of electronic components, which means they know what to look for when assessing quality and performance. Moreover, their advanced testing methods for electronic components are designed to identify potential issues early on, saving companies time and money in the long run.
Additionally, using China Inspection Pro helps streamline communication between manufacturers and suppliers. Their team understands the nuances of international trade and can help bridge any gaps that may arise due to language barriers or cultural differences. This ensures that all parties are on the same page regarding expectations for quality control and compliance with industry standards.
How Professional Services Enhance Quality Control
They provide an objective perspective on your products by conducting thorough inspections using state-of-the-art equipment—think oscilloscopes and LCR meters—that might not be readily available in-house. This unbiased approach allows for a more accurate assessment of your electronic components' reliability and functionality.
Furthermore, these services often employ standardized testing methods for electronic components that comply with international regulations. This means you can rest easy knowing that your products meet both local and global market requirements without having to navigate complex compliance landscapes alone. The result? A higher level of confidence in your product's performance—something every manufacturer aims for.
Case Studies of Successful Inspections
To illustrate the impact third-party inspection services can have on businesses engaged in testing circuit board components, consider several compelling case studies from China Inspection Pro’s portfolio. In one instance, a manufacturer faced significant delays due to defective capacitors causing production halts; after engaging China Inspection Pro's services, they were able to identify faulty batches before they reached assembly lines, drastically reducing downtime.
Another case involved an integrated circuit company whose products were consistently failing compliance checks during audits. By utilizing professional inspection services focusing on rigorous functional testing methods for electronic components, they revamped their quality assurance processes leading to an impressive 40% reduction in non-compliance incidents over six months.
These examples underscore how leveraging third-party expertise not only enhances product reliability but also fosters trust among stakeholders—from suppliers to end-users—ultimately paving the way toward long-term success.
Conclusion
In the world of electronics, effective electronic component testing is not just a luxury; it’s a necessity. Understanding the intricacies of electronic components and their functions allows engineers and technicians to ensure that every part operates as intended, contributing to the overall performance of electronic devices. By employing various testing methods for electronic components, we can identify issues early, saving time and resources while enhancing product reliability.
Key Takeaways on Effective Testing
Effective testing circuit board components involves a blend of strategy and technology. Firstly, developing a comprehensive testing plan tailored to specific applications ensures that all aspects of the electronic parts are evaluated thoroughly. Secondly, utilizing a variety of testing methods for electronic components—ranging from functional tests to automated test equipment—can significantly improve accuracy and efficiency in identifying faults.
The Future of Electronic Component Testing
The future of electronic component testing looks bright with advancements in technology paving the way for more sophisticated methods. Innovations such as artificial intelligence and machine learning are set to revolutionize how we approach testing circuit board components by enabling predictive analytics that can foresee failures before they occur. As we move forward, embracing these technologies will be crucial in maintaining high standards in quality control across the electronics industry.
Resources for Further Learning
For those eager to delve deeper into the realm of electronic component testing, there are numerous resources available that cater to both beginners and seasoned professionals alike. Online courses, webinars, and specialized books cover everything from basic principles to advanced techniques in testing circuit board components effectively. Additionally, engaging with industry forums or attending workshops can provide valuable insights into emerging trends and best practices.
