Introduction

In the fast-paced world of manufacturing, understanding quality control is crucial for ensuring that products meet the desired standards before they reach consumers. Finished product quality control serves as a gatekeeper, ensuring that only items meeting rigorous specifications are delivered to the market. By implementing effective quality management principles, manufacturers can not only enhance their reputation but also foster customer loyalty and satisfaction.
Understanding Quality Control in Manufacturing
Quality control in manufacturing is a systematic process aimed at maintaining and improving product quality throughout the production cycle. It involves various techniques and methodologies designed to control the quality of materials, components, and finished products. By focusing on quality inspection and adherence to established standards, manufacturers can effectively control the quality of their output while minimizing defects and waste.
Importance of Finished Product Quality Control
The significance of finished product quality control cannot be overstated; it directly impacts customer satisfaction and brand integrity. When manufacturers prioritize robust quality assurance processes, they reduce the risk of returns or recalls due to faulty products, which can be costly both financially and reputationally. Additionally, successful finished product quality control fosters continuous improvement within organizations by identifying areas for enhancement in production practices.
Overview of Quality Management Principles
At its core, effective quality management relies on a set of principles that guide organizations toward achieving excellence in their processes and outputs. These principles emphasize a customer-focused approach while promoting leadership engagement, employee involvement, and data-driven decision-making. By adopting these foundational concepts, companies can establish a culture that values continuous improvement in both production methods and finished product quality control.
The Basics of Quality Control
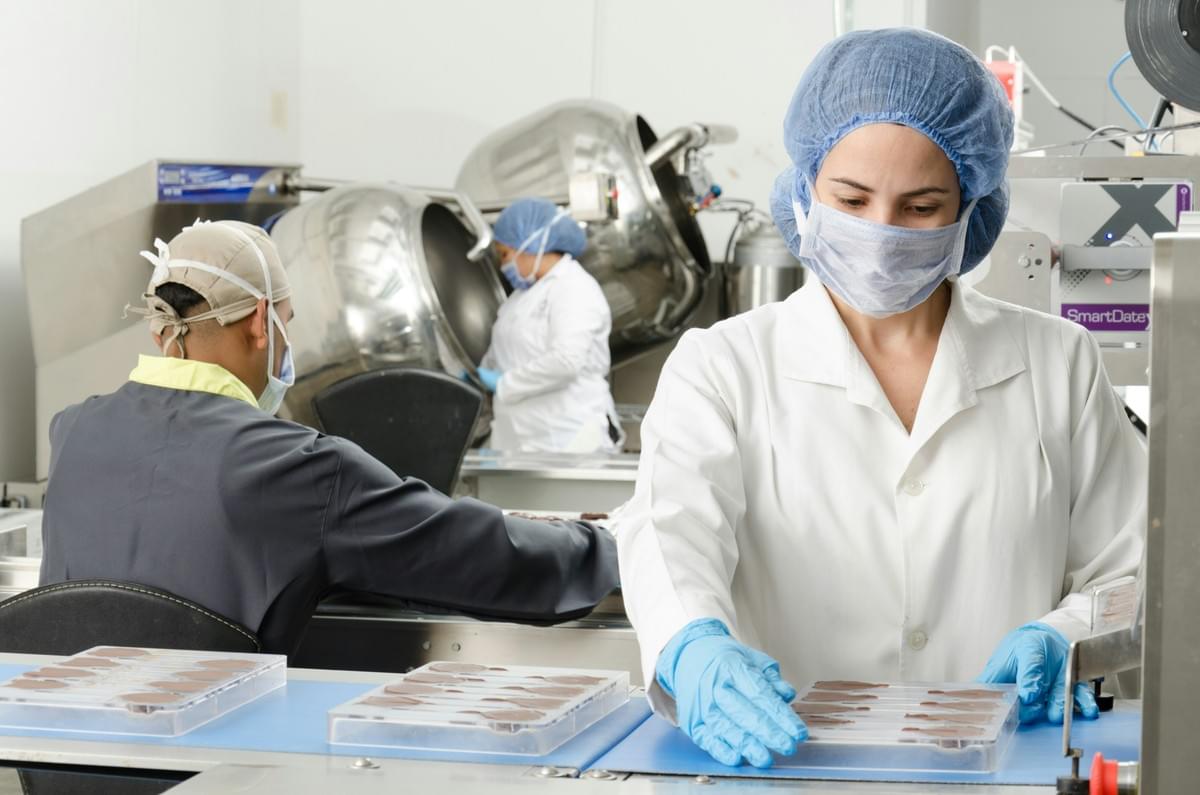

Quality control is the backbone of any successful manufacturing process, ensuring that finished products meet established standards and specifications. By implementing effective quality inspection techniques, manufacturers can control the quality of their output, thereby enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty. In this section, we will explore key concepts in quality control, the importance of quality management systems, and the integral role that quality control plays in manufacturing.
Key Concepts in Quality Control
At its core, finished product quality control revolves around several key concepts that ensure products are consistent and reliable. These include defining clear specifications, implementing systematic inspection processes, and utilizing statistical methods to analyze data. By understanding these concepts, organizations can better control the quality of their products while minimizing defects and enhancing overall performance.
One fundamental concept is the distinction between quality assurance and quality control. While quality assurance focuses on preventing defects through planned activities within a system (think proactive measures), quality control emphasizes identifying defects through inspections (the reactive side). Both approaches are essential for achieving high standards in finished product quality control; they complement each other perfectly to create a robust framework for success.
Additionally, understanding variations—both common cause variations (natural fluctuations) and special cause variations (unexpected anomalies)—is vital for effective quality management. By identifying sources of variation early on, manufacturers can implement corrective actions to maintain consistent product output while controlling costs. Overall, mastering these key concepts lays a strong foundation for any organization striving to excel in finished product quality control.
Importance of Quality Management Systems
A robust Quality Management System (QMS) is crucial for organizations aiming to enhance their finished product quality control efforts. A QMS provides a structured approach to managing processes that affect product consistency—ensuring compliance with industry standards while fostering continuous improvement initiatives. Without an effective QMS in place, organizations may struggle with inefficiencies that ultimately compromise their ability to deliver high-quality products.
Implementing a comprehensive QMS allows companies to document procedures related to production processes and establish clear guidelines for employees involved in quality inspection tasks. This level of organization not only streamlines operations but also instills confidence among stakeholders by demonstrating a commitment to maintaining high-quality standards throughout production cycles. Moreover, having well-defined roles—such as training dedicated quality assurance specialists—ensures accountability within teams tasked with controlling the overall process.
The importance of integrating technology into your QMS cannot be overstated either; automation tools can significantly enhance data collection methods used during inspections while providing valuable insights into performance trends over time. This synergy between human expertise and technological advancements enables organizations to cultivate an environment where continuous improvement becomes second nature—a win-win situation when it comes down to controlling product quality effectively!
Role of Quality Control in Manufacturing
In manufacturing environments where precision matters most, the role of quality control cannot be overlooked—it serves as both guardian and guide throughout every stage of production! By implementing rigorous inspection protocols at critical points along the assembly line or during final assessments before shipping out orders ensures that only top-notch products make it into customers' hands—a hallmark feature associated with successful brands today.
Quality control functions as an ongoing feedback loop; by analyzing data collected from various stages within production processes—including input materials used or machine settings altered—manufacturers gain insights necessary for refining operations continuously over time! These insights empower teams responsible for maintaining high standards while allowing them opportunities for growth through targeted training sessions aimed specifically at improving skillsets related directly back towards finished product quality controls.
Furthermore, establishing open lines of communication between departments fosters collaboration among those involved—from engineers designing new models down through floor workers executing daily tasks—to ensure everyone remains aligned toward shared goals surrounding exceptional outcomes! Ultimately this collaborative spirit fuels innovation across all facets associated with delivering superior goods reflecting commitment toward excellence—a true testament showcasing why prioritizing effective controls around product qualities remains paramount within modern-day manufacturing practices!
Quality Inspection Techniques
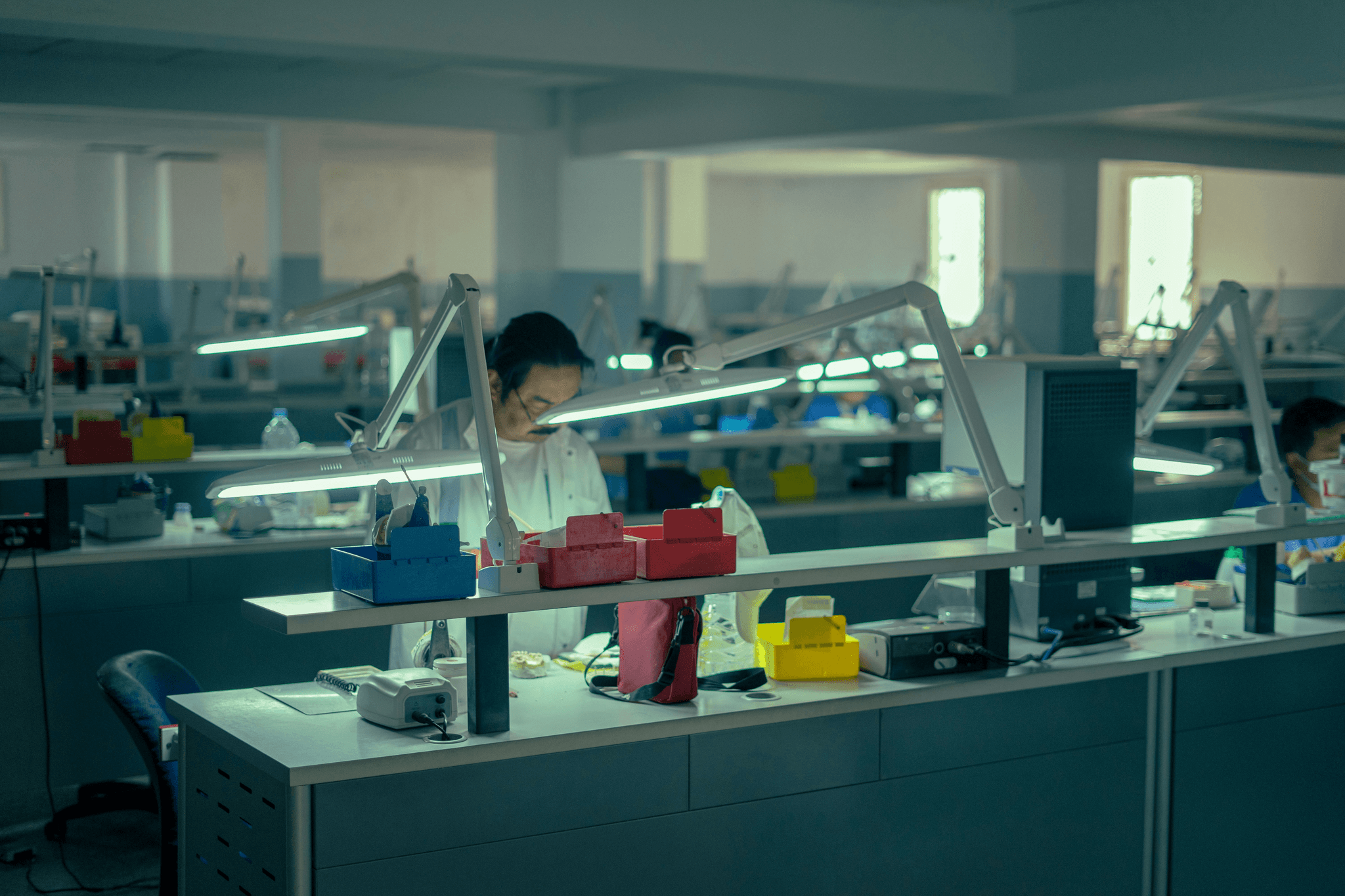

Quality inspection techniques are the backbone of finished product quality control, ensuring that products meet established standards before they reach consumers. These techniques encompass various methods, each designed to control the quality at different stages of manufacturing. By implementing effective quality inspection processes, organizations can significantly enhance their overall quality management and reduce defects.
Visual Inspection Methods
Visual inspection methods remain one of the simplest yet most effective ways to control the quality of finished products. Trained quality assurance specialists often conduct these inspections, using their keen eyes to identify visible defects such as scratches, dents, or color inconsistencies. This method is particularly useful in industries where aesthetics play a crucial role in consumer satisfaction.
However, while visual inspections are valuable, they should not be the sole approach for quality control; combining them with other techniques enhances overall effectiveness. For instance, a visual check can quickly flag obvious issues before more sophisticated measurement and testing procedures take place. Ultimately, integrating visual inspection into a broader quality management strategy helps ensure that all aspects of finished product quality control are addressed.
Measurement and Testing Procedures
Measurement and testing procedures form the scientific backbone of any robust quality control system. These methods involve quantifying specific attributes such as dimensions, weight, and performance characteristics to ensure compliance with predefined standards. By employing precise instruments like calipers or gauges during production processes, manufacturers can effectively monitor and control the quality of their output.
Moreover, regular testing helps identify potential issues early on—before they escalate into costly defects in finished products. Quality assurance specialists play a crucial role here by analyzing data from these tests to determine trends or anomalies that could indicate underlying problems in production processes. Thus, measurement and testing not only support immediate finished product quality control but also contribute to long-term improvements in manufacturing practices.
Statistical Quality Control Tools
Statistical Quality Control (SQC) tools offer an analytical approach to maintaining high standards in manufacturing processes. By utilizing statistical methods such as process capability analysis or control charts, companies can systematically monitor variations within their production lines and make informed decisions about how best to control the quality of their products over time. This data-driven approach is essential for identifying areas needing improvement while ensuring consistency in finished product quality.
Employing SQC tools allows manufacturers to establish benchmarks against which performance can be measured continuously—a vital component for any successful quality management system. Moreover, these tools empower teams by providing insights that inform strategic adjustments aimed at enhancing overall productivity without compromising on product integrity or safety standards. In essence, leveraging statistical tools is an indispensable practice for organizations committed to achieving excellence in finished product quality control.
Implementing Quality Control Processes
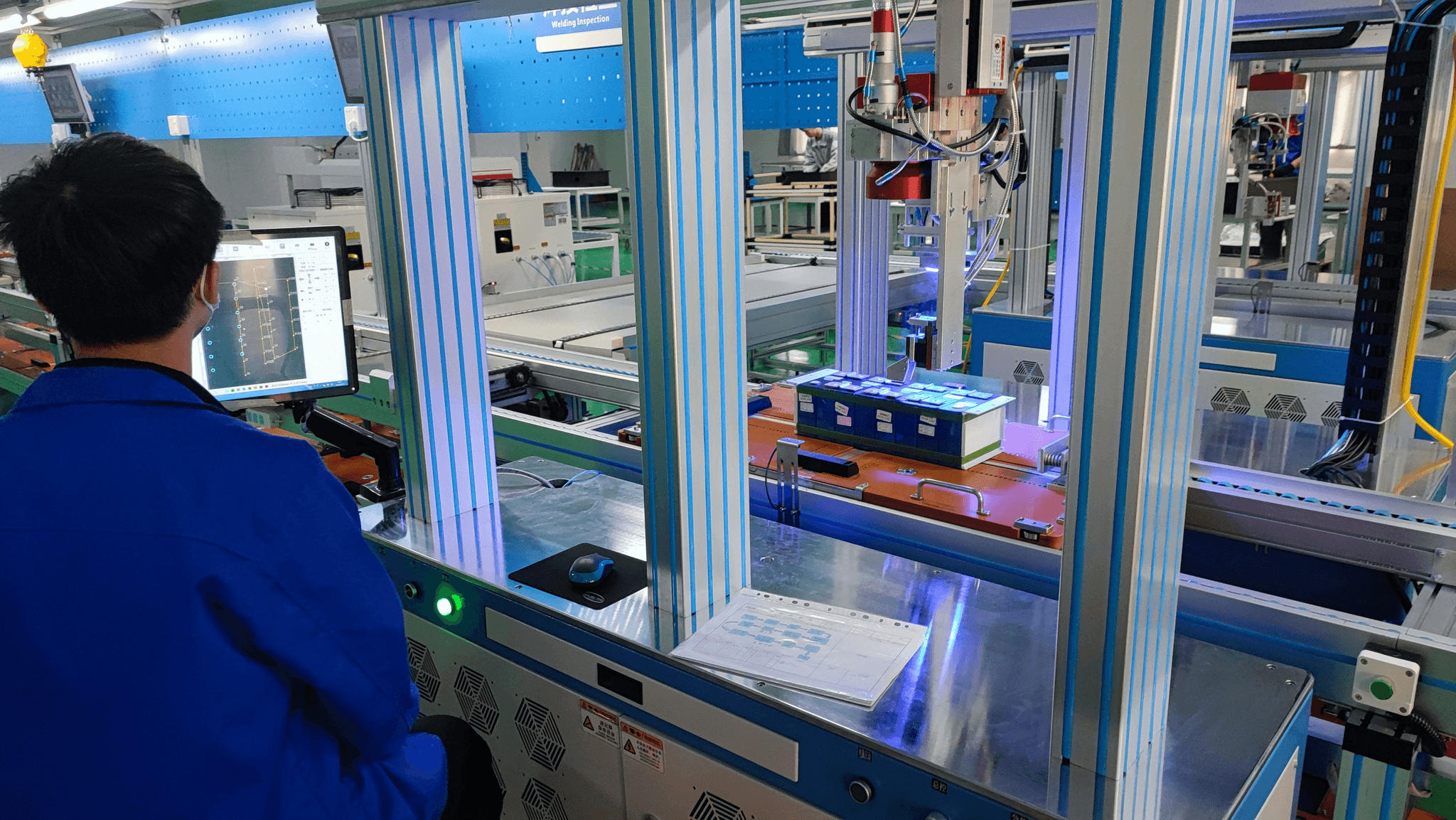
Implementing quality control processes is essential for ensuring that finished products meet the required standards of quality. This involves a systematic approach to control and quality, integrating various techniques and strategies that enhance the overall manufacturing process. By focusing on effective implementation, businesses can significantly improve their quality management systems and deliver exceptional products.
Steps to Control and Quality Implementation
The first step in controlling the quality is to establish clear objectives and standards for finished product quality control. This means defining what constitutes acceptable quality levels for each product, which will guide all subsequent actions. Once these benchmarks are set, organizations should develop a comprehensive plan outlining how to monitor performance against these standards regularly.
Next, it’s crucial to implement consistent measurement techniques that allow for real-time monitoring of production processes. Regular assessments help identify deviations from established standards early on, enabling timely corrective actions to be taken before issues escalate into larger problems. Ultimately, this proactive approach not only controls the quality but also fosters a culture of continuous improvement within the organization.
Lastly, documenting all procedures related to control and quality is vital for maintaining transparency and accountability throughout the manufacturing process. Detailed records help track progress over time, making it easier to pinpoint areas needing improvement or adjustment in practices. With thorough documentation at hand, teams can ensure compliance with industry regulations while also enhancing their overall efficiency.
Developing a Quality Inspection Plan
A robust quality inspection plan serves as the backbone of any effective finished product quality control strategy. This plan should outline specific inspection criteria tailored to each product type while incorporating methods such as visual inspection and measurement testing procedures. By clearly defining expectations upfront, manufacturers can streamline their processes and minimize variability in product outcomes.
In developing this plan, it's essential to involve cross-functional teams that include input from production staff, engineering experts, and even customers when applicable. Such collaboration ensures that all perspectives are considered when establishing metrics for success in controlling the quality of products produced. Furthermore, regular reviews of this inspection plan will allow organizations to adapt it based on evolving industry standards or technological advancements.
Moreover, integrating technology into your inspection plan can significantly enhance its effectiveness by automating certain aspects of the process through advanced tools like AI-driven analytics or specialized software programs designed specifically for quality management purposes. These innovations not only improve accuracy but also save valuable time during inspections—ultimately contributing positively toward finished product quality control efforts across all levels of production.
Training Quality Assurance Specialists
Training qualified professionals as dedicated quality assurance specialists is crucial in maintaining high standards throughout every phase of production processes aimed at controlling the quality effectively. These specialists need an extensive understanding of both theoretical concepts related to manufacturing practices alongside practical skills necessary for performing inspections accurately—ensuring they can uphold rigorous expectations set forth by established guidelines.
To achieve this goal effectively requires ongoing education initiatives that keep these specialists up-to-date with current trends within their respective industries while also reinforcing core principles surrounding best practices related specifically towards finished product quality control measures being implemented daily across various sectors involved in manufacturing operations today!
Furthermore engaging employees through workshops or hands-on training sessions helps reinforce key concepts learned during formal education programs while fostering teamwork among those responsible for ensuring adherence towards established protocols laid out previously discussed steps involved when implementing successful plans aimed at controlling overall output consistency achieved over time!
In conclusion: investing time resources into cultivating knowledgeable skilled workforce who understand importance behind maintaining strict adherence towards protocols laid out earlier leads directly towards achieving desired results seen consistently across board when it comes down delivering exceptional products meeting customer expectations consistently over long haul!
Utilizing Technology in Quality Control
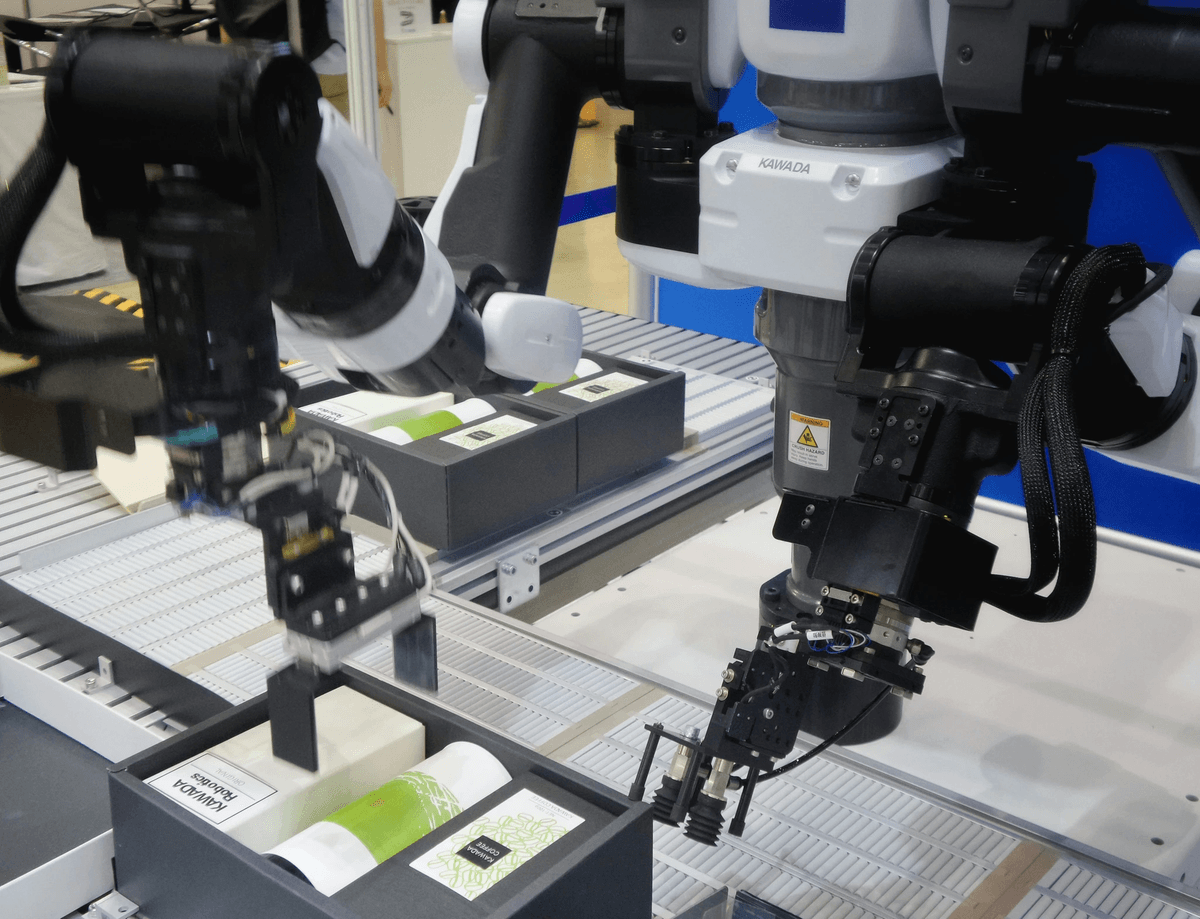
In today's fast-paced manufacturing landscape, leveraging technology is pivotal for effective quality control. Automation and sophisticated quality management systems streamline processes, reduce human error, and ensure that the finished product quality control measures are consistently met. By integrating these technologies, manufacturers can significantly enhance their ability to control the quality of their products.
Automation and Quality Management Systems
Automation has revolutionized how companies approach quality management. With automated systems in place, businesses can monitor production processes in real-time, ensuring that any deviations from established standards are promptly addressed. This proactive approach not only helps control the quality but also minimizes waste and rework associated with defective products.
Quality management systems (QMS) play a crucial role in maintaining high standards throughout the manufacturing process. These systems help organizations implement structured procedures for quality inspection and ensure compliance with industry regulations. By employing a robust QMS, manufacturers can systematically control and improve their processes, leading to enhanced finished product quality control.
Role of Artificial Intelligence in Quality Control
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is transforming the landscape of quality assurance by providing advanced data analysis capabilities that were previously unattainable. AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of production data to identify patterns or anomalies that may indicate potential issues with product quality. This allows businesses to take corrective action before defects occur, thereby streamlining efforts to control the quality of finished products.
Moreover, AI-driven tools can assist quality assurance specialists by automating routine tasks such as inspections and reporting. As these technologies evolve, they enable specialists to focus on more complex problem-solving tasks rather than mundane data entry or monitoring activities. In essence, AI not only enhances efficiency but also empowers teams dedicated to maintaining high-quality standards.
Case Study: How Siemens Uses Technology
Siemens serves as an exemplary model of how technology can be effectively utilized in finished product quality control within manufacturing environments. The company employs cutting-edge automation solutions alongside advanced analytics tools to monitor production lines continuously for any signs of defects or inefficiencies. Their integration of AI into their QMS has allowed Siemens to maintain exceptional levels of consistency while controlling the quality across various production stages.
By implementing these technologies, Siemens has successfully reduced inspection times while increasing accuracy—allowing its team of quality assurance specialists to focus on strategic improvements rather than routine checks alone. The results speak for themselves: higher customer satisfaction rates due to improved product reliability and reduced costs associated with rework and scrap materials have become hallmarks of Siemens' operational success.
Best Practices for Quality Assurance

In the realm of manufacturing, ensuring finished product quality control is not just a goal; it’s a necessity. Effective quality assurance practices form the backbone of any successful production process, allowing companies to maintain high standards and minimize defects. By implementing robust protocols, organizations can control the quality of their products while fostering a culture of continuous improvement.
Establishing Effective Quality Control Protocols
Establishing effective quality control protocols is crucial for maintaining consistency in finished product quality control. These protocols should outline specific procedures for every stage of production, from raw material inspection to final product testing. By clearly defining expectations and processes, manufacturers can better control and quality, minimizing variations that lead to defects.
Moreover, integrating regular training sessions for quality assurance specialists ensures that everyone involved understands their role in the process. This fosters accountability and encourages proactive approaches to identifying potential issues before they escalate. When everyone is on board with established protocols, the entire team becomes invested in maintaining high-quality standards throughout production.
Additionally, leveraging technology can enhance these protocols by streamlining communication and documentation processes. Automated systems can provide real-time data on quality metrics, allowing teams to quickly address any deviations from established standards. This proactive approach not only improves finished product quality control but also boosts overall efficiency within manufacturing operations.
Continuous Improvement Strategies
Continuous improvement strategies are essential for refining quality management practices over time. By regularly reviewing performance metrics and seeking feedback from employees at all levels, organizations can identify areas for enhancement within their existing frameworks. These strategies encourage a culture where every team member feels empowered to contribute ideas that could help control the quality of products further.
One effective method is adopting tools such as Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) cycles or Six Sigma methodologies to systematically evaluate processes and implement changes based on data-driven insights. Such approaches allow businesses to focus on eliminating waste while enhancing overall efficiency in their operations—both critical components of effective finished product quality control.
Moreover, fostering an environment where mistakes are viewed as learning opportunities rather than failures encourages innovation and collaboration among teams dedicated to improving product outcomes continuously. This mindset shift helps create an agile workforce capable of adapting quickly when faced with challenges related to maintaining high-quality standards.
Collaborating with China Inspection Pro
Collaborating with specialized entities like China Inspection Pro can significantly enhance your organization’s approach toward finished product quality control initiatives. Their expertise offers valuable insights into local regulations and industry best practices that may be overlooked otherwise—ensuring compliance while optimizing your overall manufacturing process through effective inspections and audits.
By engaging with such partners who focus solely on controlling the quality aspect through rigorous assessments during various stages—from sourcing materials right up until delivery—you gain an extra layer of assurance regarding your products' integrity before they reach consumers' hands or shelves alike! This collaboration allows manufacturers not only peace-of-mind but also confidence when it comes down assessing whether they’ve met established benchmarks consistently across all production lines.
Ultimately, building strong partnerships within this space empowers organizations by providing access to resources tailored specifically towards achieving excellence in both operational efficiency as well as customer satisfaction—two key elements necessary for long-term success amidst ever-changing market demands!
Conclusion
In the ever-evolving landscape of manufacturing, the future of quality control is not merely about maintaining standards; it’s about pushing boundaries. With advancements in technology and methodologies, finished product quality control is set to become more efficient and precise. Companies that embrace these changes will not only enhance their reputation but also ensure customer satisfaction through consistent quality.
The Future of Quality Control in Manufacturing
As we look ahead, the integration of artificial intelligence and automation into quality management systems will redefine how we control the quality of products. These innovations enable real-time monitoring and data analysis, allowing manufacturers to detect issues before they escalate. By leveraging cutting-edge technology, businesses can implement proactive measures to ensure that every aspect of finished product quality control meets or exceeds expectations.
Benefits of Robust Quality Management
A robust quality management system offers numerous benefits that extend beyond mere compliance with standards; it fosters a culture of excellence within organizations. When companies prioritize effective quality inspection and assurance practices, they experience reduced waste, lower costs, and enhanced productivity. Moreover, a strong focus on control and quality leads to improved customer trust and loyalty—key ingredients for long-term success in any industry.
Ensuring Consistency in Finished Product Quality Control
Consistency is the cornerstone of successful finished product quality control; without it, even the best products can fall short in meeting consumer expectations. To achieve this consistency, training qualified quality assurance specialists becomes imperative—they are the gatekeepers who ensure adherence to established protocols. By continuously refining processes and embracing a mindset geared towards improvement, organizations can maintain high standards that resonate throughout their operations.
