Introduction
In the world of production, ensuring that products meet high standards is paramount. This is where quality assurance (QA) and quality control (QC) come into play, serving as the backbone of effective quality checking processes. While they may sound similar, understanding their distinct roles is crucial for any organization aiming to deliver top-notch products.
Understanding Quality Assurance and Quality Control
Quality assurance focuses on the processes that ensure quality standards are met throughout production. It’s about building a framework for consistent quality checking before issues arise, emphasizing proactive measures rather than reactive fixes. On the other hand, quality control zeroes in on identifying defects in finished products through rigorous testing and inspection methods.
The Importance of Quality in Production
Quality plays a vital role in production as it directly impacts customer satisfaction and brand reputation. When companies prioritize effective quality checking, they not only reduce waste but also enhance efficiency and profitability. Ultimately, maintaining high-quality standards fosters trust among consumers and keeps businesses competitive in a crowded marketplace.
Key Differences Between QA and QC
While both QA and QC aim to improve product quality, their approaches differ significantly. QA is process-oriented, focusing on preventing defects through systematic planning and execution; QC is product-oriented, concentrating on detecting defects after production has occurred. By understanding these key differences, organizations can better implement strategies that integrate both QA and QC into their operations effectively.
Defining Quality Assurance
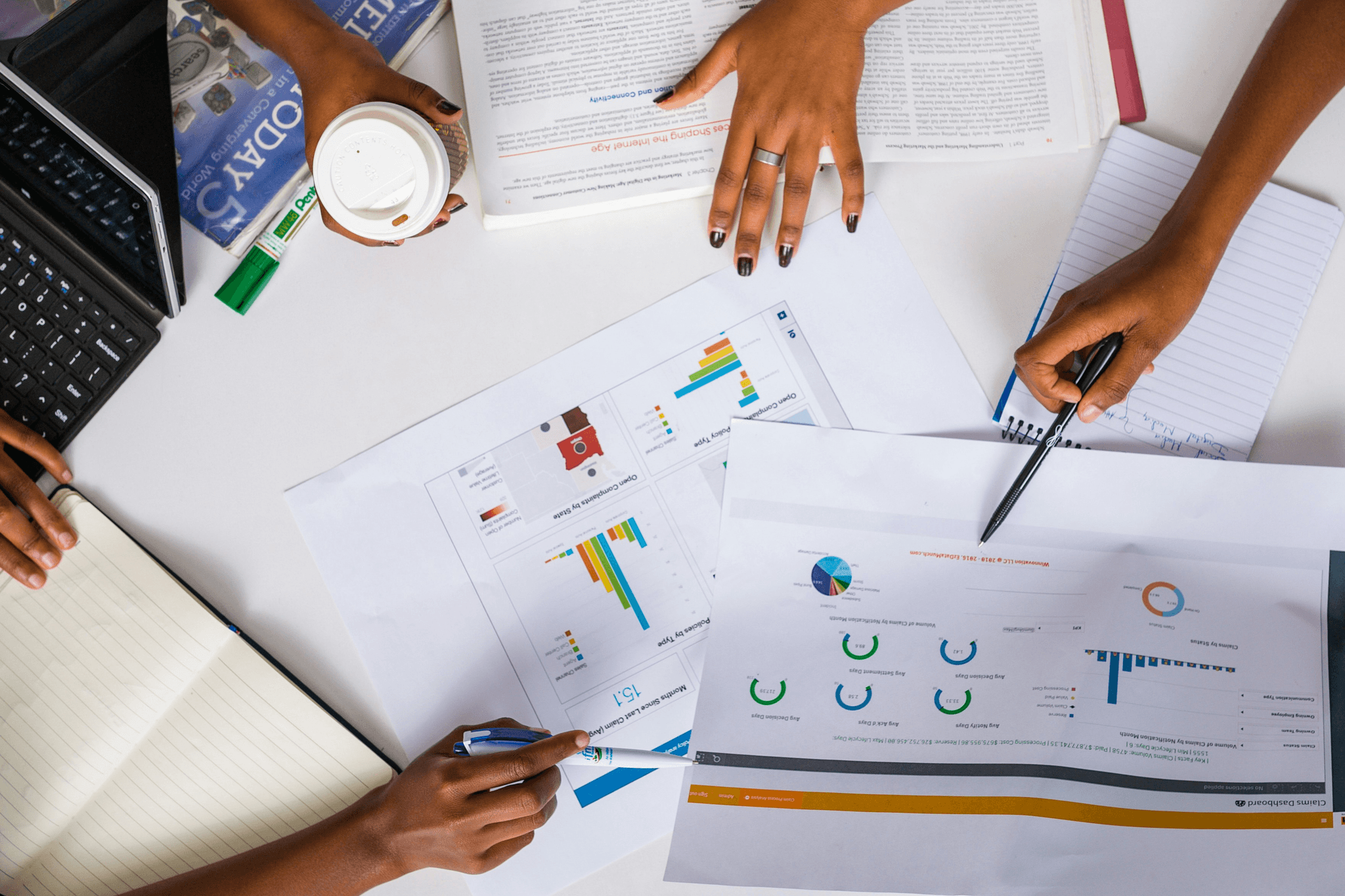

Quality Assurance (QA) is the backbone of maintaining high standards in production and service delivery. It encompasses all planned and systematic activities implemented within a quality system to ensure that quality requirements for a product or service will be fulfilled. By focusing on prevention rather than detection, QA aims to enhance customer satisfaction through effective quality checking processes.
What is Quality Assurance?
At its core, Quality Assurance is about establishing confidence that quality requirements will be met consistently. Unlike Quality Control, which focuses on identifying defects after they occur, QA emphasizes the importance of process-oriented methods to prevent issues from arising in the first place. This proactive approach involves defining standards and implementing systematic procedures to ensure that every aspect of production aligns with those standards.
The Role of Processes in QA
Processes play a crucial role in Quality Assurance by providing a structured framework for achieving consistent results. Effective quality checking methodologies involve planning, executing, and monitoring processes meticulously to identify potential areas for improvement before problems arise. By continuously refining these processes based on feedback and performance metrics, organizations can significantly enhance their overall product or service quality.
Famous Examples of QA in Action
Several renowned companies have successfully implemented robust Quality Assurance practices that serve as benchmarks in their industries. For instance, Toyota's Production System is celebrated for its focus on continuous improvement and waste reduction through effective quality checking strategies at every stage of manufacturing. Similarly, software giants like Microsoft employ rigorous QA protocols to ensure their products meet high-performance standards before release, showcasing how effective QA can lead to superior outcomes across various sectors.
Understanding Quality Control

Quality Control (QC) is a vital component of any production process, ensuring that products meet established standards before they reach the consumer. It encompasses various activities aimed at identifying defects and ensuring that the final output is consistent with quality expectations. In essence, QC acts as a safety net, catching issues before they escalate into larger problems.
What is Quality Control?
At its core, quality control refers to the systematic processes used to maintain and improve product quality in manufacturing and service delivery. This involves measuring and testing products against predefined criteria to ensure they meet specific standards of performance and reliability. The goal of QC is not just to identify defects but also to prevent them from occurring in the first place through rigorous quality checking practices.
The Role of Testing in QC
Testing plays a crucial role in quality control by providing tangible evidence of product performance under various conditions. Through different testing methodologies—such as inspections, sampling, and statistical analysis—companies can pinpoint areas for improvement and ensure adherence to quality standards. Effective testing not only identifies flaws but also fosters continuous improvement by informing future production processes based on findings from these quality checking efforts.
Notable Companies Excelling in QC
Several companies have set benchmarks in quality control through their unwavering commitment to excellence. For instance, Toyota has famously implemented its “Total Quality Management” approach, which integrates rigorous QC practices into every aspect of its operations, resulting in high customer satisfaction rates. Similarly, Apple’s meticulous attention to detail during product testing exemplifies how effective quality checking can lead to innovative products that resonate with consumers worldwide.
Quality Checking: Tools and Techniques

Quality checking is an essential part of any production process, ensuring that products meet the required standards before reaching consumers. To effectively implement quality checking, organizations utilize various tools and methodologies tailored to their specific needs. This section dives into some popular tools for quality checking, the methodologies used in QA and QC, and real-world applications that highlight their importance.
Popular Tools for Quality Checking
When it comes to quality checking, several tools have made their way into the toolkit of quality assurance professionals. Statistical Process Control (SPC) charts are among the most widely used tools, allowing teams to monitor processes and identify variations that could lead to defects. Additionally, software like Six Sigma helps streamline quality checking by providing a structured approach to problem-solving through data-driven decision-making.
Another valuable tool in the realm of quality checking is Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA), which systematically evaluates potential failure points within a process or product design. By identifying these risks early on, organizations can implement preventive measures before they escalate into costly issues. Moreover, automated inspection systems have revolutionized how companies approach quality checking; these systems utilize advanced technologies such as machine vision to detect defects at high speeds with remarkable accuracy.
Finally, checklists are a simple yet effective tool in ensuring all aspects of a product or process are reviewed during quality checking. They help standardize procedures and ensure no critical steps are overlooked during inspections. These popular tools collectively enhance the effectiveness of quality checking efforts across various industries.
Methodologies Used in QA and QC
The methodologies employed in both Quality Assurance (QA) and Quality Control (QC) play a pivotal role in successful quality checking practices. In QA, methodologies such as Total Quality Management (TQM) focus on continuous improvement by integrating all members of an organization into the effort towards enhanced customer satisfaction through better processes. This proactive approach emphasizes planning and prevention rather than solely relying on detection after problems arise.
On the QC side, methodologies like ISO 9001 provide a framework for establishing effective processes for consistent product delivery while adhering to international standards. Utilizing these frameworks allows companies to create robust systems for monitoring their products throughout production cycles—ensuring that every item meets predefined criteria during quality checking stages.
Lean Manufacturing is another methodology that has gained traction for its focus on reducing waste while improving efficiency within production environments—ultimately enhancing overall product quality as well. By employing these diverse methodologies tailored specifically toward either QA or QC functions, organizations can significantly improve their overall effectiveness in achieving high-quality outcomes.
Real-World Applications of Quality Checking
Quality checking finds its application across numerous industries where maintaining high standards is crucial for success—and often survival! In manufacturing settings such as automotive assembly lines or electronics production facilities, rigorous testing protocols ensure that every component meets safety regulations before being assembled into final products sold to consumers worldwide.
In healthcare settings too—where patient safety is paramount—quality checking plays an indispensable role in regulating medical devices through stringent testing procedures prior to use by medical professionals or patients alike; this ensures reliability when it matters most! The food industry also relies heavily on rigorous inspections during processing stages; companies implement Hazard Analysis Critical Control Points (HACCP) protocols designed specifically around food safety concerns via systematic monitoring techniques throughout production lines.
These real-world applications demonstrate how vital effective quality checking practices are across various sectors—not just from regulatory perspectives but also from customer satisfaction viewpoints! By embedding robust systems within organizational frameworks focused on continual improvement efforts surrounding both QA & QC aspects alike—companies can foster trustworthiness among clients while maximizing operational efficiencies!
The Relationship Between QA and QC
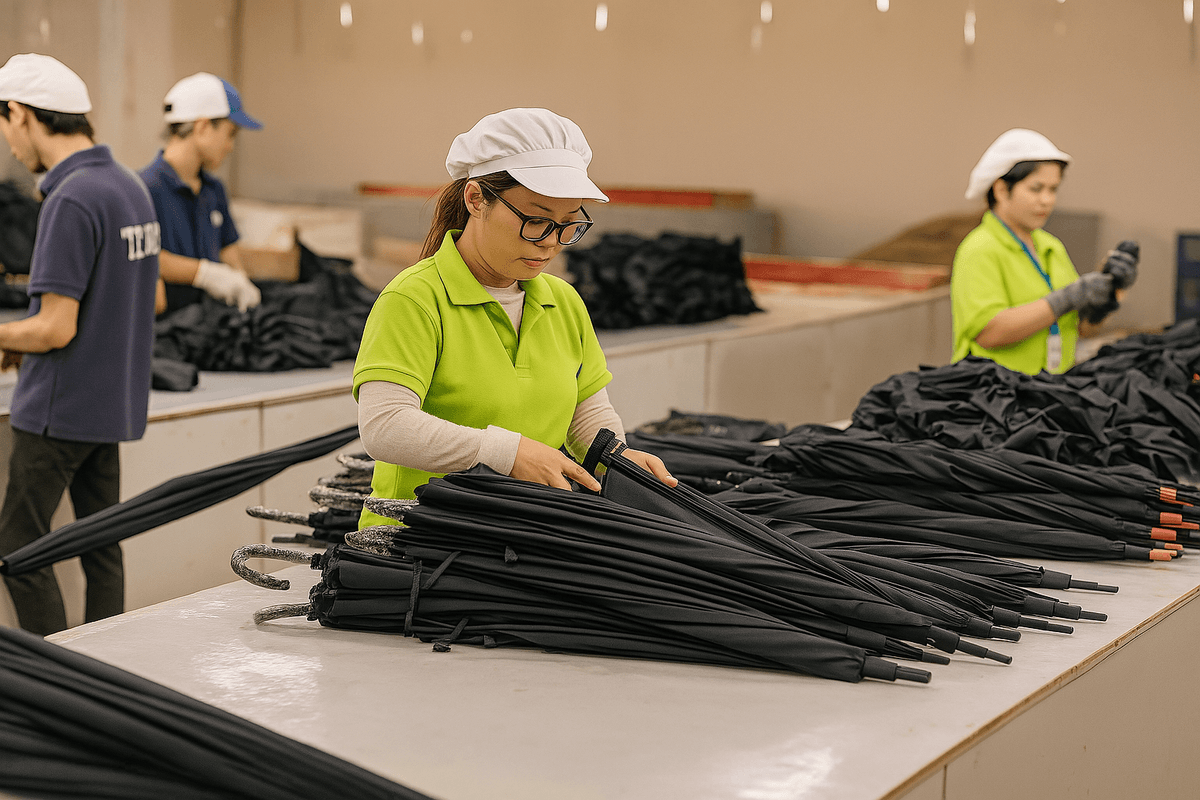

In the world of production and service delivery, Quality Assurance (QA) and Quality Control (QC) are two sides of the same coin. They complement each other to ensure that products not only meet established standards but also satisfy customer expectations. Understanding how these two processes work together can significantly enhance overall quality checking efforts.
How QA and QC Work Together
Quality Assurance lays the groundwork for Quality Control by establishing systematic processes aimed at preventing defects before they occur. While QA focuses on process design and implementation, QC zeroes in on identifying defects in finished products through rigorous testing. This collaboration ensures a seamless flow where effective quality checking during production leads to fewer issues down the line, creating a win-win scenario for manufacturers and consumers alike.
The synergy between QA and QC is evident in industries like automotive manufacturing, where stringent QA protocols dictate how components are built. These protocols guide the quality checking procedures used in QC to assess whether those components meet safety standards before reaching consumers. When executed effectively, this partnership results in higher customer satisfaction rates and lower return rates due to defective products.
The Impact of QA on QC Processes
The influence of Quality Assurance on Quality Control cannot be overstated; effective QA processes directly enhance the efficiency of QC measures. By implementing robust QA strategies, organizations can reduce variability in production, making it easier for QC teams to identify when something goes awry during quality checking phases. This proactive approach minimizes costly rework or recalls that can arise from poor-quality outputs.
Moreover, a strong foundation in QA allows for continuous improvement within QC practices by providing valuable insights into recurring issues or trends that may affect product quality over time. As teams analyze data collected from both QA and QC activities, they can refine their approaches to achieve even better results during quality checking stages. Ultimately, this interconnectedness fosters a culture of excellence throughout an organization.
Case Studies Showcasing Integration
One notable example of successful integration between QA and QC is Toyota's renowned production system, which emphasizes continuous improvement through meticulous quality checking at every stage of manufacturing. Their commitment to both processes has led them to develop innovative techniques such as jidoka, which empowers workers to stop production if they detect any anomalies during quality checking activities—ensuring that problems are addressed immediately rather than later down the line.
Another case study worth mentioning is Boeing's approach with its 787 Dreamliner project, where rigorous adherence to both QA and QC principles was necessary due to complex supply chains involving multiple global partners. By establishing clear guidelines for both processes early on—combined with real-time data monitoring—the company achieved significant milestones in maintaining high standards while minimizing delays caused by defects identified during quality checking phases.
These examples illustrate how integrating Quality Assurance with Quality Control not only enhances product reliability but also drives innovation within organizations striving for excellence in their offerings.
Real-World Examples: Success Stories
Quality assurance and quality control are not just abstract concepts; they have real-world implications that can make or break a business. Companies that prioritize quality checking often see significant returns on their investment, while those that neglect it can face dire consequences. Let’s delve into some notable examples of organizations excelling in these areas, along with valuable lessons learned from failures.
Companies Notable for Quality Practices
Several companies have made a name for themselves by implementing rigorous quality checking processes. Toyota, for instance, revolutionized the automotive industry with its Toyota Production System, which emphasizes continuous improvement and defect prevention rather than merely inspecting finished products. Similarly, Apple is renowned for its meticulous quality control protocols that ensure every device meets high standards before reaching consumers’ hands.
These organizations understand that effective quality checking not only enhances customer satisfaction but also fosters brand loyalty. By investing in quality assurance and control measures, they can consistently deliver products that exceed expectations. Their success stories serve as a blueprint for others aiming to elevate their own standards of excellence.
Lessons Learned from Quality Failures
On the flip side, there are cautionary tales of companies that suffered due to inadequate quality practices. Take Boeing’s 737 MAX crisis as an example; lapses in both QA and QC led to tragic accidents and significant financial losses. The fallout highlighted the importance of thorough quality checking at every stage of production—not just at the end.
Another example is Samsung's Galaxy Note 7 recall due to battery malfunctions, which resulted from insufficient testing and oversight during manufacturing. These incidents underscore how overlooking quality assurance can lead to catastrophic results, affecting not only profits but also public trust in a brand. Businesses must learn from these failures to avoid repeating mistakes and ensure robust systems are in place for effective quality checking.
How China Inspection Pro Sets Standards
China Inspection Pro has emerged as a leader in establishing high-quality standards across industries through rigorous inspection services and adherence to global best practices. They specialize in ensuring products meet stringent requirements before they hit the market—effectively combining both QA and QC principles into their operations. Their commitment to excellence demonstrates how proactive quality checking can drive success while minimizing risks associated with poor-quality outputs.
By offering tailored solutions based on specific client needs, China Inspection Pro exemplifies how organizations can enhance their reputation through diligent oversight and comprehensive testing methodologies. Their approach serves as an inspiration for businesses worldwide looking to refine their own processes around quality assurance and control practices effectively.
Conclusion
As we wrap up our exploration of quality assurance (QA) and quality control (QC), it’s clear that both play vital roles in ensuring products meet the highest standards. The future of quality assurance and control is set to be shaped by advancements in technology, including automation and artificial intelligence, which will enhance the efficiency of quality checking processes. Organizations that embrace these innovations will likely see significant improvements in their production lines, reducing errors and elevating customer satisfaction.
The Future of Quality Assurance and Control
The landscape of QA and QC is evolving rapidly, with digital tools becoming increasingly integral to effective quality checking. Predictive analytics and machine learning are paving the way for more proactive approaches to identifying potential issues before they arise. As companies adopt these technologies, we can expect a shift from reactive problem-solving to a more strategic focus on prevention, ultimately leading to higher-quality products.
Implementing Quality Checking in Your Processes
To effectively implement quality checking in your processes, start by defining clear standards for what constitutes acceptable quality. Training staff on these standards is crucial; everyone involved must understand their role in maintaining quality assurance throughout production. Regular audits and feedback loops are essential for continuous improvement, allowing organizations to adapt their practices based on real-world performance data.
Final Thoughts on QA vs QC
In conclusion, while QA focuses on preventing defects through systematic processes, QC emphasizes identifying defects through inspection and testing—both are essential for delivering high-quality products. Understanding the interplay between QA and QC can lead organizations to create robust frameworks that enhance overall product integrity. Embracing both philosophies will not only streamline operations but also foster a culture of excellence that resonates with customers.
